Kidney CT Appearances
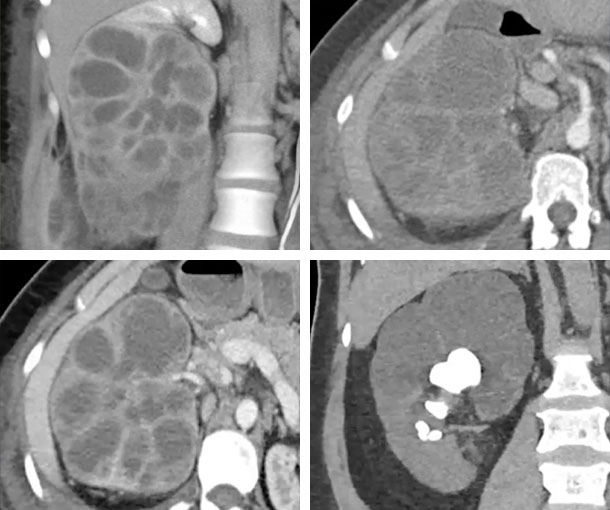
Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis (XGP) CT Findings
- Large staghorn calculus in most but not all cases with contracted pelvis
- Extensive inflammatory process
- Decreased renal function
- Enlarged kidneys
- Severe hydronephrosis, expansion of calices
- Can be associated with extrarenal disease (psoas involvement)
Other Information About XGP
Etiology:
- Chronic UTI or urinary obstruction
Epidemiology:
- More common in women
- Usually present during 5th and 6th decades of life
Presentation:
- Dull flank pain
- Fever
- Chills
- General malaise
Prognosis:
- Unilateral XGP can be treated
- Bilateral XGP is usually fatal
Related Lectures:
CT Evaluation of Hematuria: A Practical Approach Part 2
CT of the Acute Abdomen: GU Applications Part 2
CTA of the Renal Arteries: What You Need to Know - Part 1
CT Evaluation of Hematuria: A Practical Approach - Part 2
Abdominal Pain in the ED: GU Pathology - Part 1
Renal Infection Thru Infarction: What You Need to Know - Part 2
