Kidney CT Appearances
Kidney Stone Disease CT Findings
- Over 99% of renal stones contain calcium
- Variable in size
- Visible on CT as bright “dots” usually over 100HU
- Can appear from the calyx to the bladder but symptoms occur when it reaches the ureter
- Accompanied by asymmetric kidney size and dilation of proximal ureter if long standing
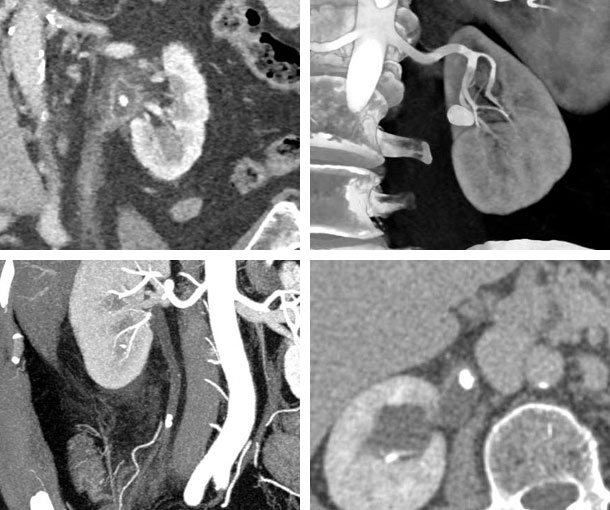
Other Information About Kidney Stone Disease
Etiology:
- Diet is mostly responsible for kidney stones
- Not enough water intake
- More common during summer months
Epidemiology:
- More common in males
- Most common during the 4th and 5th decades of life
Presentation:
- Abdominal pain
- Hematuria
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Fever
- Chills
Prognosis:
- Most kidney stones pass on their own
- Kidney stones are benign
Related Pearls: Renal Stone Disease
Related Lectures:
CT Evaluation of Hematuria: A Practical Approach Part 1
CT of the Acute Abdomen: GU Applications Part 1
CT Evaluation of Hematuria: A Practical Approach - Part 1
Abdominal Pain in the ED: GU Pathology - Part 1
