Kidney CT Appearances
Acute Pyelonephritis CT Findings
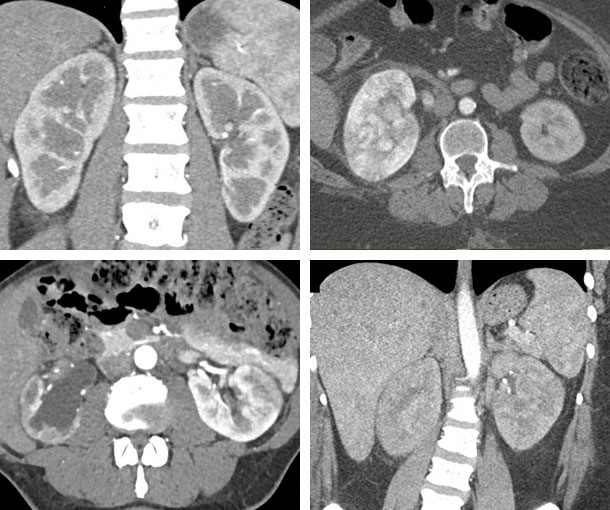
- IV contrast needed
- Poorly defined areas of hypoattenuation in the kidney
- Can be focal, unilateral or bilateral
- Extends from the papillary to the cortical surface
- May or may not have swelling of the kidney
- Reduced corticomedullary differentiation (classic)
- May be difficult occasionally to distinguish from a renal infarct
Other Information About Acute Pyelonephritis
Etiology:
- Caused by bacteria
Epidemiology:
- More common in females
Presentation:
- Fever
- Chills
- Flank pain
- Dysuria
- Frequent urination
- Nausea
- Vomiting
Prognosis:
- Can be managed with antibiotics
Related Lectures:
CT Evaluation of Hematuria: A Practical Approach Part 1
CT of the Acute Abdomen: GU Applications Part 1
CT Evaluation of Hematuria: A Practical Approach - Part 1
Abdominal Pain in the ED: GU Pathology - Part 1
Renal Infection Thru Infarction: What You Need to Know - Part 1
