Liver CT Appearances
Cirrhosis CT Findings
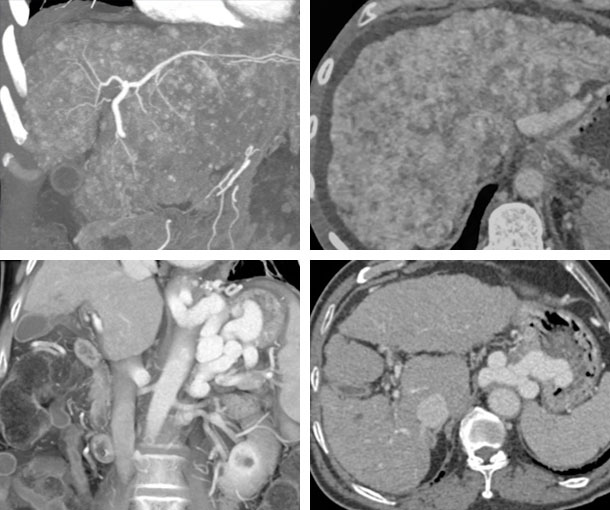
- Nodular liver with increase in size of left lobe with decrease size of the right lobe
- Increased distance between abdominal wall and liver surface
- Nodularity to the liver will vary with nodules often seen on non-contrast CT as high density nodules
- Hypervascular nodules on arterial phase are usually hepatoma
- Heterogenous liver texture
- Surface nodularity
- High density nodules in the liver on non-contrast images
- Caudate Hypertrophy
- Transverse caudate width : right lobe width
- > 0.65
- Segmental hypertrophy of segments II and III
- Segmental atrophy of segments VI, VII, and IV
- Enlarged gallbladder fossa
- Enlarged periportal space
- Peribiliary cysts
Other Information About Cirrhosis
Etiology:
- Alcohol use
- Hepatitis
- Fatty Liver Disease
Epidemiology:
- Usually presents after age 50
Presentation:
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Weakness
- RUQ pain
- Spider angiomas
- Palm redness
- Jaundice
- Itchy skin
Prognosis:
- Cirrhosis cannot be cured but can be managed
- Prognosis depends heavily on the diseaseís advancement and patientís health; some patients may succumb in a few months and others may live more than a decade
Related Pearls: Cirrhosis
Related Lectures:
MDCT Evaluation of Parenchymal Liver Disease Part 1
