Liver CT Appearances
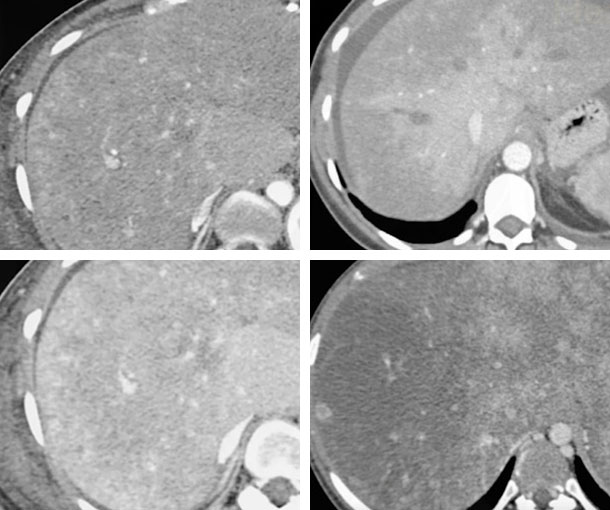
Budd-Chiari Syndrome CT Findings
- Patchy enhancement especially in arterial phase with increased enhancement of central portion of the liver
- Enlarged caudate lobe
- Compressed IVC
- Absence of hepatic veins
- Ascites
- Regenerating nodules
- Acute phase
- Early enhancement of caudate love and central portion of liver around IVC, with decreased enhancement of the rest of the liver
- Delayed enhancement of peripheral portions of liver and central portion of low density (called “flip-flop appearance”)
- Narrow hypodense hepatic vein and IVC with dense walls
- Chronic
- Failure to visualize IVC or hepatic veins
- Intrahepatic collateral veins
- Heterogenous liver enhancement
- Large avidly enhancing regenerative nodules
- Marked caudate hypertrophy with peripheral atrophy
Other Information About Budd-Chiari Syndrome
Etiology:
- Myeloproliferative disorders
- Oral contraceptive use
- Pregnancy
- Hepatic or renal masses
Epidemiology:
- Usually presents between ages 20-40
Presentation:
- RUQ pain
- Jaundice
- Ascites
- Hypertension
- Hepatomegaly
- Splenomegaly
Prognosis:
- Life can be extended with portosystemic shunting or liver transplant
- Untreated Budd-Chiari Syndrome has a poor prognosis
Related Pearls: Budd-Chiari
Related Lectures:
MDCT Evaluation of Parenchymal Liver Disease Part 2
Evaluation of the IVC: Spectrum of Disease - Part 2
