Pancreas CT Appearances
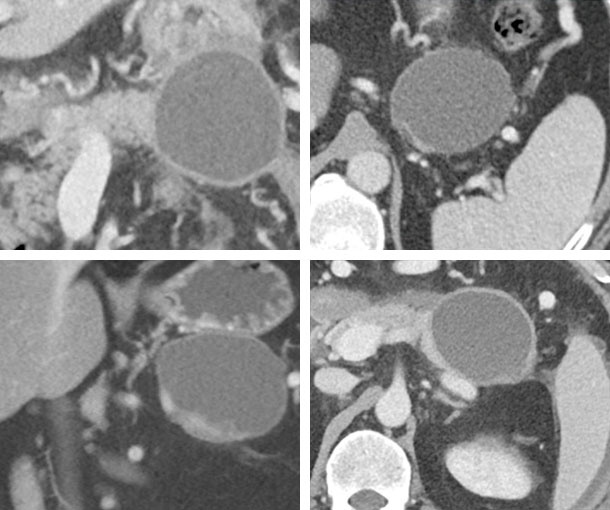
Pancreatic Pseudocyst CT Findings
- Encapsulated collection of fluid with well-defined wall
- > 4 weeks after onset
- Well-circumscribed fluid collection with defined wall
- Homogeneous fluid density without non-liquid component
Other Information About Pancreatic Pseudocysts
Etiology:
- Most commonly caused by pancreatitis
Epidemiology:
- More common in males
- Anyone with pancreatitis is susceptible to developing pancreatic pseudocysts
Presentation:
- Commonly asymptomatic
- Abdominal pain
- Abdominal distension
- Fever
- Nausea and/or vomiting
Prognosis:
- Many pseudocysts spontaneously resolve
- Pseudocysts will need to be monitored since they can lead to severe complications
Related Lectures:
MDCT of Acute Pancreatitis Part 1
Cystic Pancreatic Lesions: What You Need to Know - Part 1
Cystic Pancreatic Lesions: Detection, Diagnosis and Management - Part 1
