Chest CT Appearances
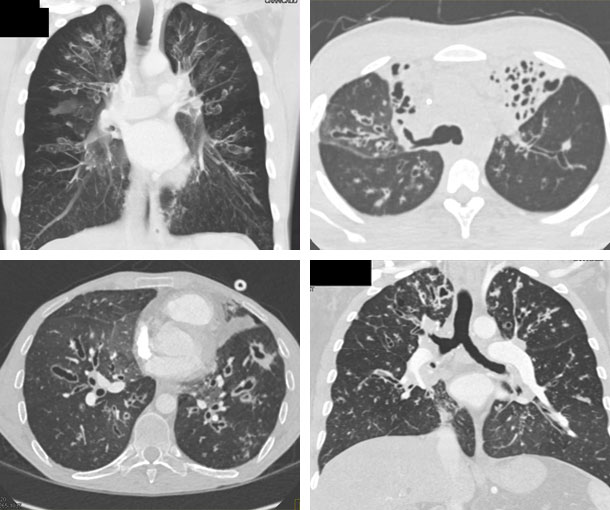
Cystic Fibrosis CT Findings
- Air trapping
- Mucous plugging
- Consolidation
- Usually found with bronchiectasis
- Bronchial diameter > adjacent pulmonary artery diameter
- Terminal bronchioles lack normal tapering
- Can be focal, diffuse, unilateral or bilateral
- Can be a sequelae of aspiration
- Dilated bronchi are extensive and may include both the upper and lower lung fields
Other Information About Cystic Fibrosis
Etiology:
- Genetic mutation
Epidemiology:
- Usually detected in infants and children
Presentation:
- Recurrent lung infection
- Neonatal jaundice
- Meconium ileus
- Poor weight gain
- Multi-organ involvement through lung is primary site of complications
Prognosis:
- Patients generally live until the 4th decade of life
