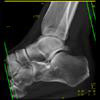
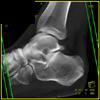
Foot Pathology: Calcaneal fractures
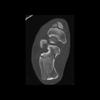
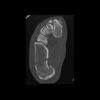
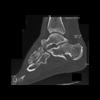
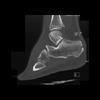
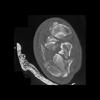
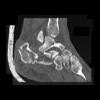
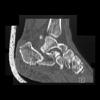
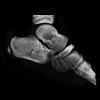
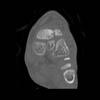
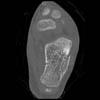
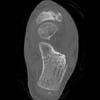
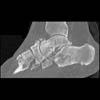
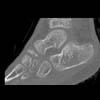
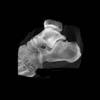
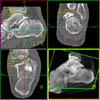
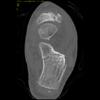
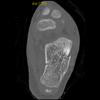
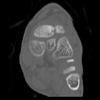
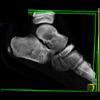
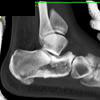
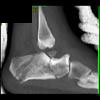
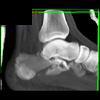
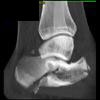
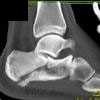
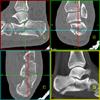
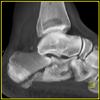
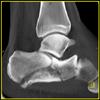
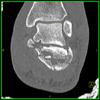
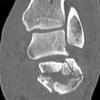
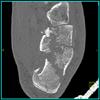
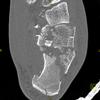
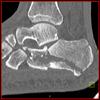
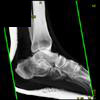
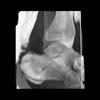
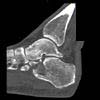
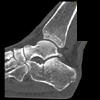
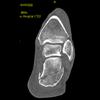
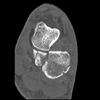
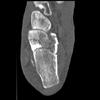
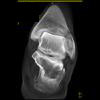
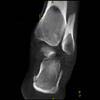
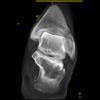
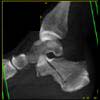
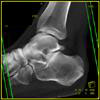
The calcaneus is the most commonly fractured tarsal bone. Calcaneal fractures are classified as intraarticular and extraarticular. The intraarticular fracturesaccount for 70-75% of calcaneal fractures and carry a worse prognosis. The inciting trauma is usually a fall or motor vehicle accident, and these fractures are bilateral in 10% of cases. Concomitant ipsilateral lower extremity fractures are present in 20-46% of cases, and spinal fractures in 10-30%. Extrarticular fractures (Figure: extraarticular fracture of calcaneus) account for 25-30% of calcaneal fractures, and are the sequela of a twisting injury. Anatomic regions affected include the anterior or medial process, the sustentaculum tali, the body or the tuberosity. Severe fractures are readily evident on conventional radiographs; however, CT is essential for elucidating the extent of injury. The intraarticulur fractures are often comminuted and may be displaced. CT is also used for follow up after fracture treatment. CT is very helpful for detecting fracture malunion or nonunion . In addition, the presence and extent of secondary osteoarthritis is readily detected by CT. Several features of intraarticular fractures which can be elucidated on CT have been shown to correlate with the outcome. A central depression fracture has a worse prognosis than a tongue-type fractures, but a better prognosis than a comminuted fracture. An unsatisfactory result is more likely in the setting of subtalar incongruity, decreased fibulocalcaneal space and osteoarthrosis of the talonavicular joint and the ankle.