Foot Anatomy Quiz
1. Which of the following is true with respect to the fracture depicted here:
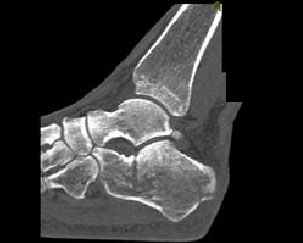
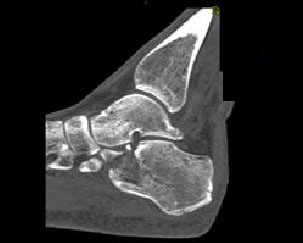
B. This fracture is extraarticular
C. Extraarticular fractures have a better prognosis
D. Associated fractures in other locations are rare
E. A and C
Correct! Incorrect. The correct answer is E.
2. Which of the following is true with respect to tarsal and metatarsal fractures following hyperflexion injury?
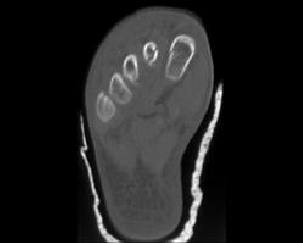
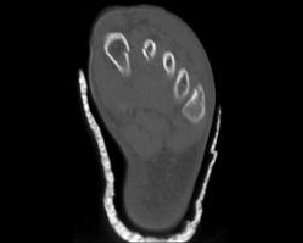
B. More metatarsal fratcures are detected with CT compared to radiographs
C. Joint malalignment may be detected on CT but not evident on a radiograph
D. CT can reveal more fractures than MR in this setting
E. All of the above
Correct! Incorrect. The correct answer is E.
3. What is the most common site of tarsal fracture?
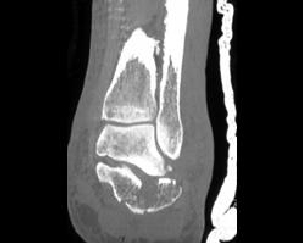
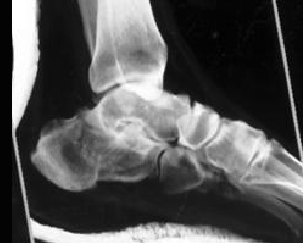
B. Talus
C. First Cuboid
D. Cuneiform
E. Navicular
Correct! Incorrect. The correct answer is A.
4. Which of the following is true with respect to the entity displayed here:
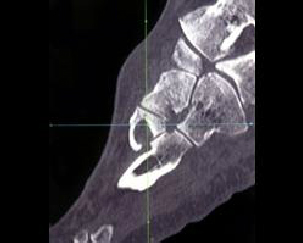
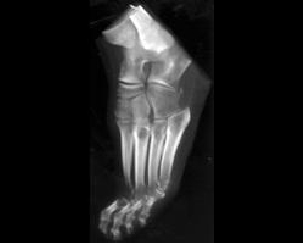
B. No other MTP joints are ever involved
C. Erosions typically occur on the medial and dorsal surface of the head of the first metatarsal
D. All of the above
E. A and C
Correct! Incorrect. The correct answer is E.
5. The most common site of the entity displayed here is:
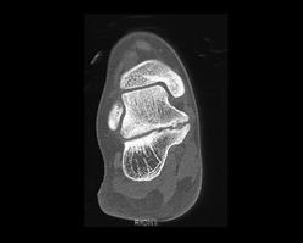
B. Talonavicular
C. Calcaneonavicular
D. Calcaneocuboid
E. A and C
Correct! Incorrect. The correct answer is E.
6. Which of the following is true?
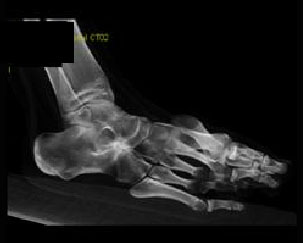
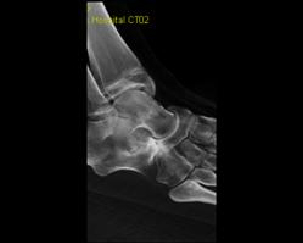
B. Plain film radiograph diagnosis of talocalcaneal caoalition is more challenging than calcaneonavicular coalitions
C. CT or MR can determine id the coalition is fibrous, cartilaginous or bony
D. Patients often present with pain in the 2nd decade
E. All of the above
Correct! Incorrect. The correct answer is E.
7. With respect to the enitity displayed in this image, which of the following is true:
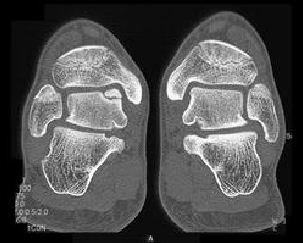
B. The most common cause is trauma.
C. These lesions can occur medially or laterally on the talar dome.
D. The medical lesions occur in the posterosuperior half of the dome of the talus; however, the lateral lesions are situated anterosuperiorly.
E. All of the above.
Correct! Incorrect. The correct answer is E.
8. Which of the following is a false with respect to the fracture depicted on this case:
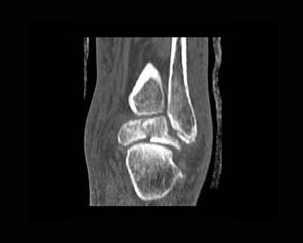
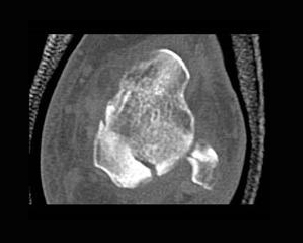
B. Higher staged fractures have increased risk of ischemia due to blood supply disruption
C. Mechanism of fracture is abrupt force from below with dorsiflexion of the foot
D. CT is useful for follow up to determine joint alignment, to exclude any residual intrarticular bone fragments and to detect complicaitons of nonunion and osteoarthritis
E. All of the above
Correct! Incorrect. The correct answer is E.
9. Which of the following is true with respect to the pathology depicted here:
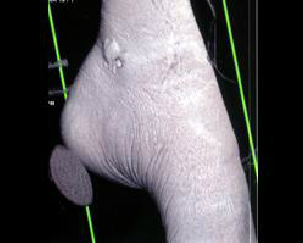
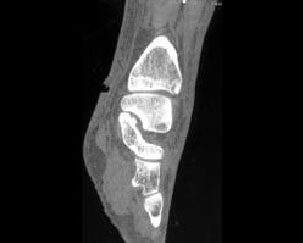
B. Common locations include skin below the metatarsal heads, distal toes, under calcaneus and over malleoli
C. Although pedal infection typically arises from the region of an ulcer in diabetics, ischemic ulcers do not always develop infections
D. Nearly 90% of the bone infection arises adjacent to infected foot ulcers
E. All of the above
Correct! Incorrect. The correct answer is E.
10. Which findings distinguish this from the talar beak of a tarsal coalition?
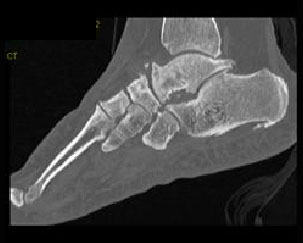
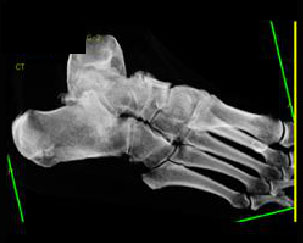
B. Location anterior to the talonavicular joint
C. Associated findings of OA
D. A and C
Correct! Incorrect. The correct answer is D.
