- 2
- ,
- 3
- 8
- 1
To Quiz Yourself: Select OFF by clicking the button to hide the diagnosis & additional resources under the case.
Quick Browser: Select ON by clicking the button to hide the additional resources for faster case review.
CASE NUMBER
231
Diagnosis
Petrous Apicitis, left
Note
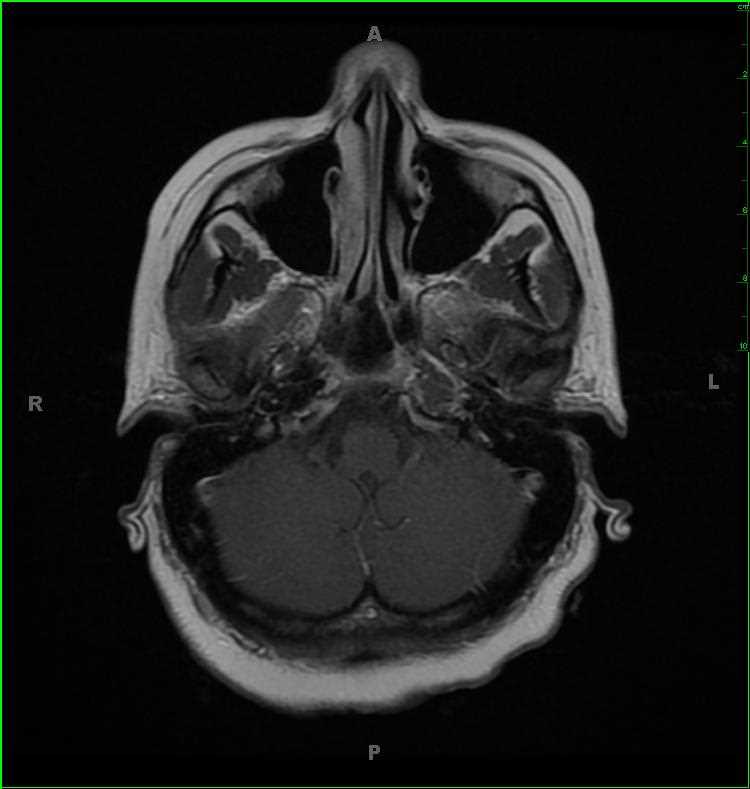
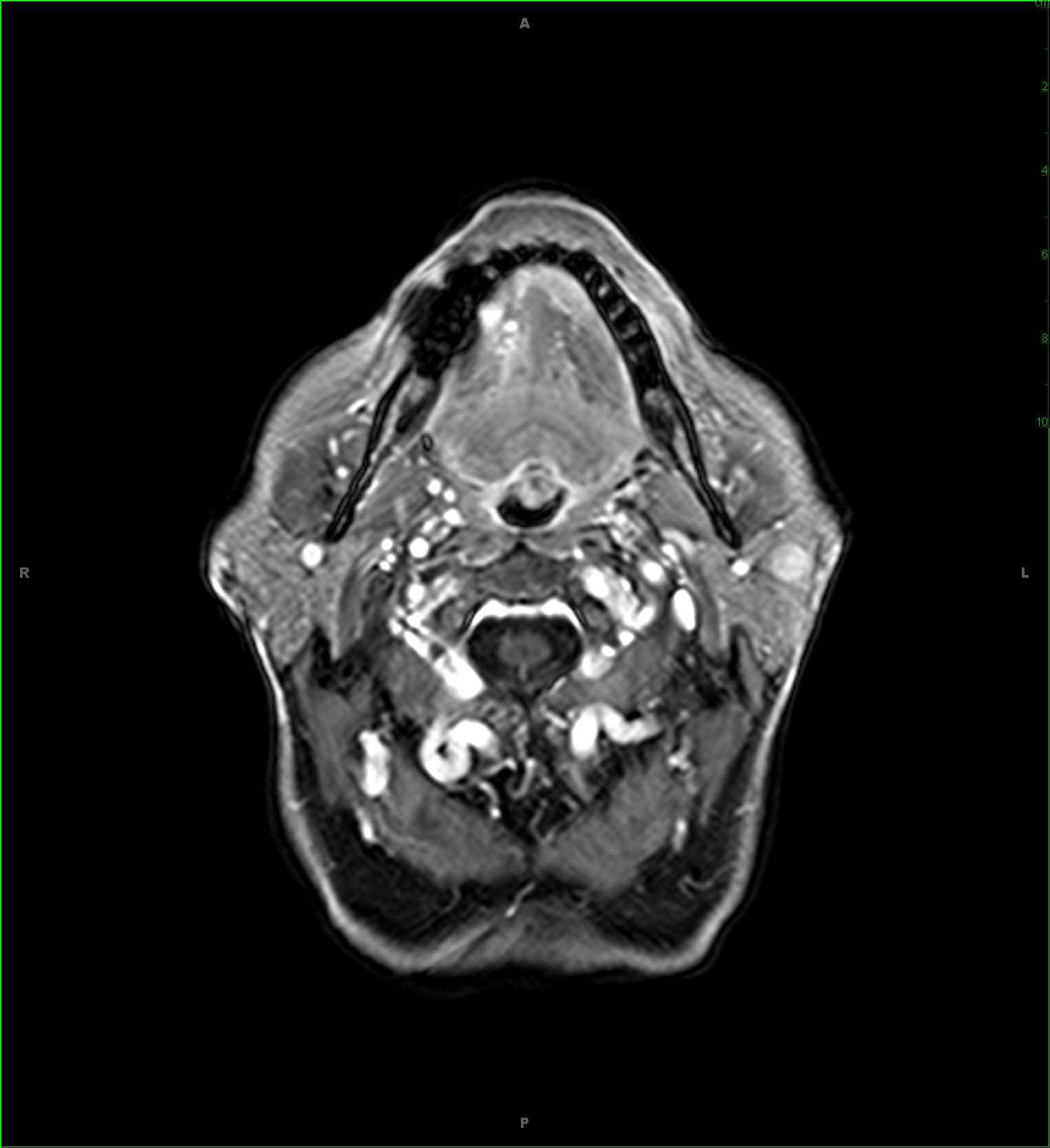
42-year-old female recently treated for mastoiditis on the left, now presenting for recurrent left ear pain and decreased hearing. Within the left petrous apex, there is a confluent region of T1-iso- to slightly hypointense signal, T2-hyperintense signal which does not suppress on STIR weighted images. There is also FLAIR-hyperintense signal, no diffusion restriction, and mild mucosal enhancement within the involved air cells at the left petrous apex. A small mastoid effusion and mucosal enhancement was identified near the left mastoid tip (not included on these images). The differential includes petrous effusion, petrous apicitis, epidermoid, focal fat, cholesteatoma and cholesterol granuloma. Given the overall imaging features, the findings are most compatible with a focal left petrous apicitis. Petrous apicitis is infection of the petrous temporal bone segment. The incidence has decreased with increased use of antibiotics in the setting of otomastoiditis. Common symptoms include deep facial pain secondary to inflammation of the trigeminal nerve in Meckelís cave. There may also be abducens nerve palsy due to involvement of Dorelloís canal. Additional complications include dural venous sinus thrombosis, subdural empyema/abscess, and frank meningitis.
THIS IS CASE
231
OF
396