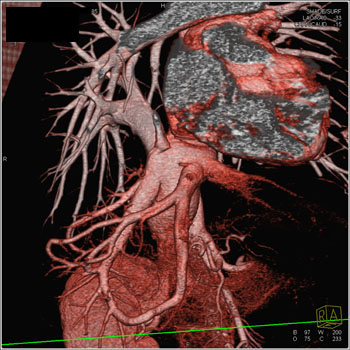
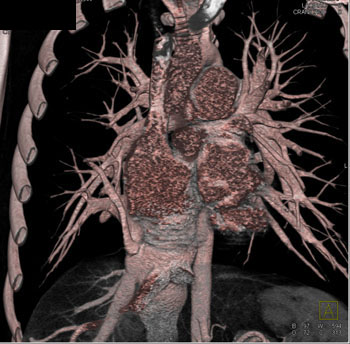
Diagnosis: Total Anomalous PVR (TAPVR) Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (APVR)
All pulmonary veins communicate to the right atrium either directly or indirectly via the SVC or IVC. TAPVR: 3 Types All pulmonary veins communicate to the right atrium either directly or indirectly via the SVC or IVC. - Pulmonary veins may connect anomalously in three ways;
- in a supracardiac manner to the vena cava
- To the heart; usually to right atrium or coronary sinus
- To a vein beneath the diaphragm
Partial Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (PAPVR) All pulmonary veins communicate to the right atrium either directly or indirectly via the SVC or IVC. - One or more pulmonary veins communicate directly to the right atrium or vena cava
- Connection of right pulmonary vein(s) to IVC often in association with hypoplastic right lung and anomalous systemic arterial supply is called scimitar syndrome
Congenital Causes of Right Heart Dilatation in Adults All pulmonary veins communicate to the right atrium either directly or indirectly via the SVC or IVC. - Pretricuspid left to right shunts
- Atrial septal defects
- Partially Anomalous PV connection
- Systemic AVM
- Coronary cameral fistula to the rt atrium
- Coronary aa fistula to the coronary sinus
- Berbode defect (LV to RA shunt)
|