Imaging Pearls ❯ Chest ❯ Pediatric Pathology
|
-- OR -- |
|
Congenital Lung Anomalies in Adults
Marcos Mestas Nuñez, et al.
RadioGraphics 2024; 44(9):e240017- “CPAMs, previously known as congenital cystic adenomatoid malformations, are a heterogeneous group of cystic and noncystic congenital pulmonary lesions. While CPAM is the most commonly diagnosed CLA in the pediatric population, it is increasingly being recognized in adults. CPAM results from early airway maldevelopment at various stages and is characterized by the overgrowth of primary bronchioles that communicate with an abnormal bronchial tree lacking cartilage.”
Congenital Lung Anomalies in Adults
Marcos Mestas Nuñez, et al.
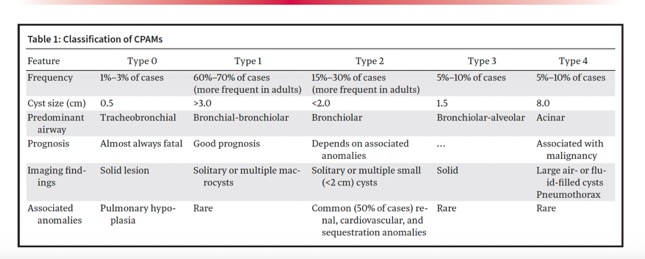
RadioGraphics 2024; 44(9):e240017 - “At imaging, CPAM appears as a unilocular or multilocular thin-walled cystic lesion with or without air-fluid levels, more commonly in the lower lobes. Cyst size can help differentiate CPAM type 1 from type 2, favoring type 1 when the cyst is larger than 2.5 cm and type 2 when it is smaller than 2.0 cm. However, on pathologic resection specimens, more than one CPAM subtype coexisting in the same lesion can be seen.”
Congenital Lung Anomalies in Adults
Marcos Mestas Nuñez, et al.
RadioGraphics 2024; 44(9):e240017 - “CPAMs typically have a pulmonary arterial blood supply; however, in some cases, systemic arteries may supply the malformation, indicating a coexisting intralobar sequestration . These malformations are termed hybrid lesions (see “Hybrid Lesions” section). Type 2 CPAM may be associated with other congenital malformations, including renal agenesis, cardiovascular anomalies (truncus arteriosus, tetralogy of Fallot), diaphragmatic hernia, and esophageal and jejunal atresia. Findings of thickened cyst walls, surrounding ground-glass opacities, or consolidation may indicate superimposedinfection or hemorrhage .”
Congenital Lung Anomalies in Adults
Marcos Mestas Nuñez, et al.
RadioGraphics 2024; 44(9):e240017
- Congenital Lung Anomalies
• Normal vascularity
• Congenital lobar hyperinflation
• Congenital pulmonary airway malformation
• Bronchogenic cyst
• Bronchial atresia
• Parenchymal agenesis, hypoplasia
• Abnormal vascularity
• Scimitar syndrome
• Sequestration - Congenital Lobar Hyperinflation
• Formerly, lobar emphysema-misnomer
• Etiology-partial bronchial obstruction
• deficient bronchial cartilage
• intraluminal web, stenosis, malacia
• Onset: > 90% cases < 6 months
• Neonates : dyspnea, cyanosis, cough
• Older pts: wheezing or incidental - Congenital Pulmonary Airway Malformation
• Formerly, Congenital Cystic Airway Malformation (CCAM)
• 25% of congenital lung lesions
• Not true “cyst”, rather dilated bronchioles
• Normal arterial supply & venous drainage
• Communicates with bronchial tree - CPAM : Clinical
• Most symptomatic as neonates
• cyanosis, grunting, tachypnea
• 10% found in older children & adults
• Often presents as recurrent pneumonia - CPAM: Imaging
• Type 0 (1-3%) perinatal death (not imaged)
• Type 1 (60-70%) (ADULT lesion)
• one or more dominant cysts: 3-10 cm in size
• surrounding smaller cysts
• Type 2 (15-20%) cysts, 1-3 cm
• Type 3 (5-10%) microcysts (< 5mm) on cut sections (not imaged, high mortality)
• Type 4 (15%) cysts up to 10 cm - CPAM: Associated Lesions
• Malignant processes have been described in
• association with CPAM types and 4
• Type 1: bronchoalveolar carcinoma (BAC)
• Type 4: pleuropulmonary blastoma
• Benign process associated with types 2 and 3
• Type 2: bronchial atresia & sequestration’
• Type 3: pulmonary hypoplasia - Pleuropulmonary Blastoma
• Children < 3 years ( 1 or 2 cases in adults)
• Malignancy of lung/pleura
• sarcomatous and embryonal cells
• 3 types-1 (cystic), 2 (cystic/solid), 3 (solid)
• Increasing malignancy 1 to 3
• Survival 80-85% type 1; 40-50% type 3
- Cystic Adenomatoid Malformation:Facts
- AKA CAM
- Intralobar mass of disorganized pulmonary parenchyma that communicates with bronchial tree
- 25% of congenital lung disorders
- On CT and CXR can look like lung abscess or necrotizing pneumonia
- Equal frequency in all lobes - Differential Dx Includes
- Congenital
- lobar emphysema
- Diaphragmatic hernia
- Neurogenic cyst
- Sequestration
- Mediastinal teratoma
- Lung abscess

