The Role of Cinematic Rendering in the Analysis of Complex Vascular and Mediastinal Pathology: How We Do It
The Role of Cinematic Rendering in the Analysis of Complex Vascular and Mediastinal Pathology: How We Do It Elliot K. Fishman, MD The Russell H. Morgan Department of Radiology and Radiological Science, The Johns Hopkins Hospital |
The Role of Cinematic Rendering in the Analysis of Complex Vascular and Mediastinal Pathology: How We Do It Cinematic rendering (CR) involves volumetric data alteration by application of complex mathematical modeling (Monte-Carlo simulations) based on the simulations performed on the lighting patterns of the real-life objects and the interactions of light with real life objects. This encodes information about expected lighting patterns of 3D anatomy with improved depth perception and realistic appeal to the images. 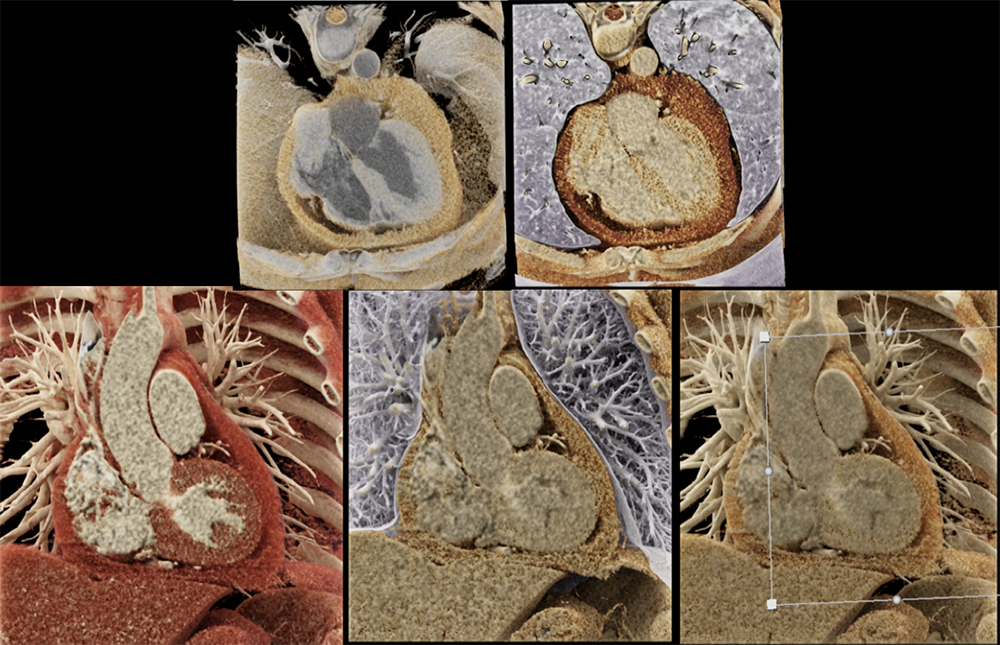 |
The Role of Cinematic Rendering in the Analysis of Complex Vascular and Mediastinal Pathology: How We Do It Conventional volume rendering (VR) in comparison is a regular 3D representation of the isotropic voxel-based volume. Cinematic Rendering is a comparative imaging post-processing technique with numerous imaging applications especially problem solving in complex cases given the depth perception, illumination patterns and delineation of anatomical relations. These features lead to numerous applications in complex vascular and post-surgical imaging and the imaging for surgical planning and mediastinal pathology. 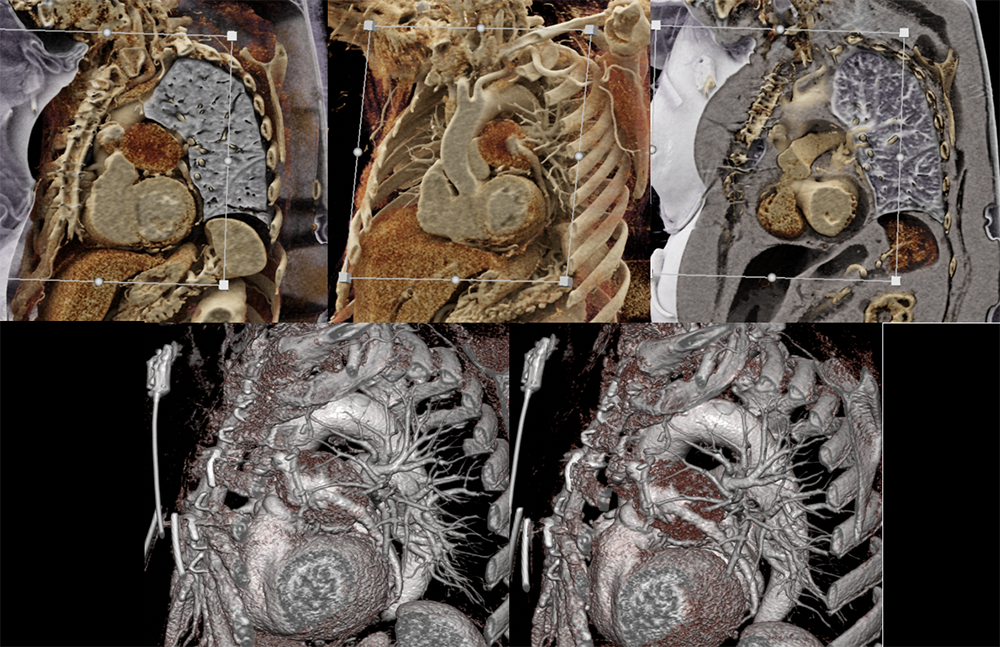 |
The Role of Cinematic Rendering in the Analysis of Complex Vascular and Mediastinal Pathology: How We Do It Image acquisition
 |
How we do it! a) CT protocol optimization – mostly Standard angiographic acquisition
 |
How we do it! b) Post processing techniques
 |
Vascular CT applications CR has numerous applications for the interpretation of vascular pathologies, especially among complex post-surgical vascular anatomy/complications, variant anatomy or subtle findings. 1. Aortic pathologies
 |
Coarctation of Aorta with Collaterals 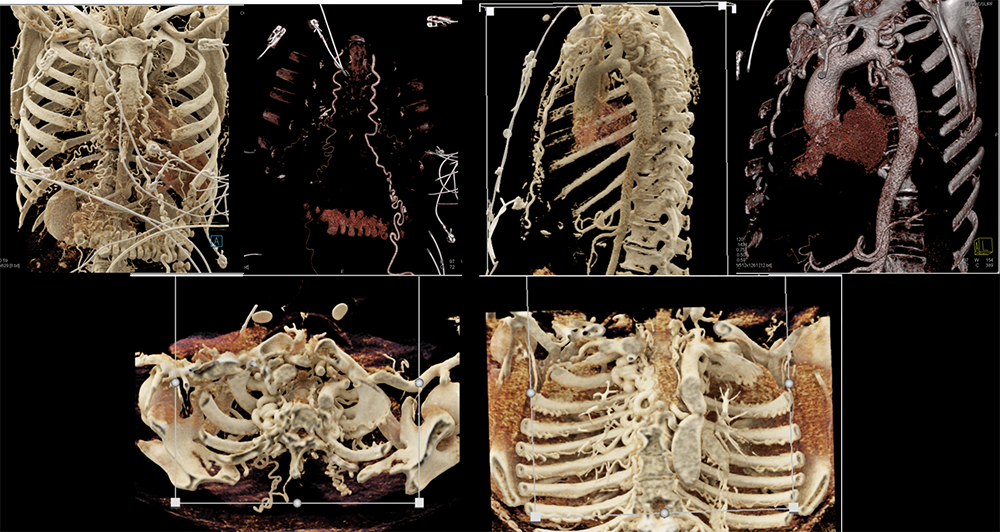 |
Cardiac CT Different windowing settings or presets and alterations of the trapezoid ROI can provide different imaging contrasts to help add or remove layers based on density which can be essential for assessment of the anatomy and anomalies of the heart. Blood pool based images can be obtained by changing presets for problem solving. New technique called Dark blood imaging has numerous applications for cardiac CT. A case of LVAD outflow obstruction is shown below 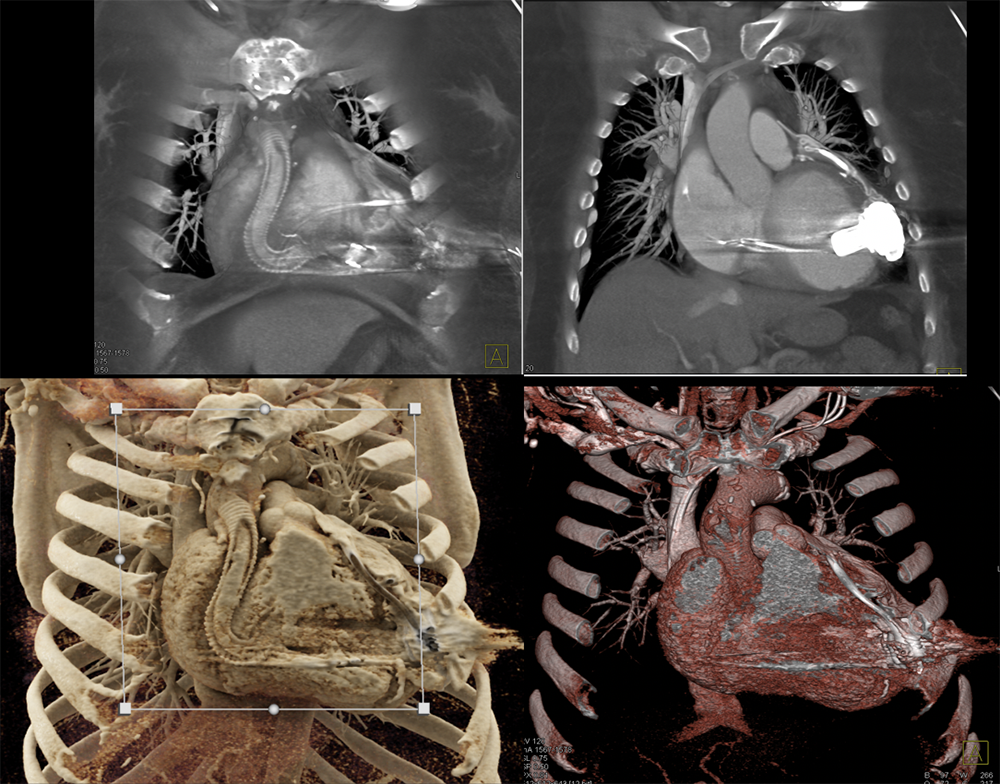 |
LVAD outflow obstruction 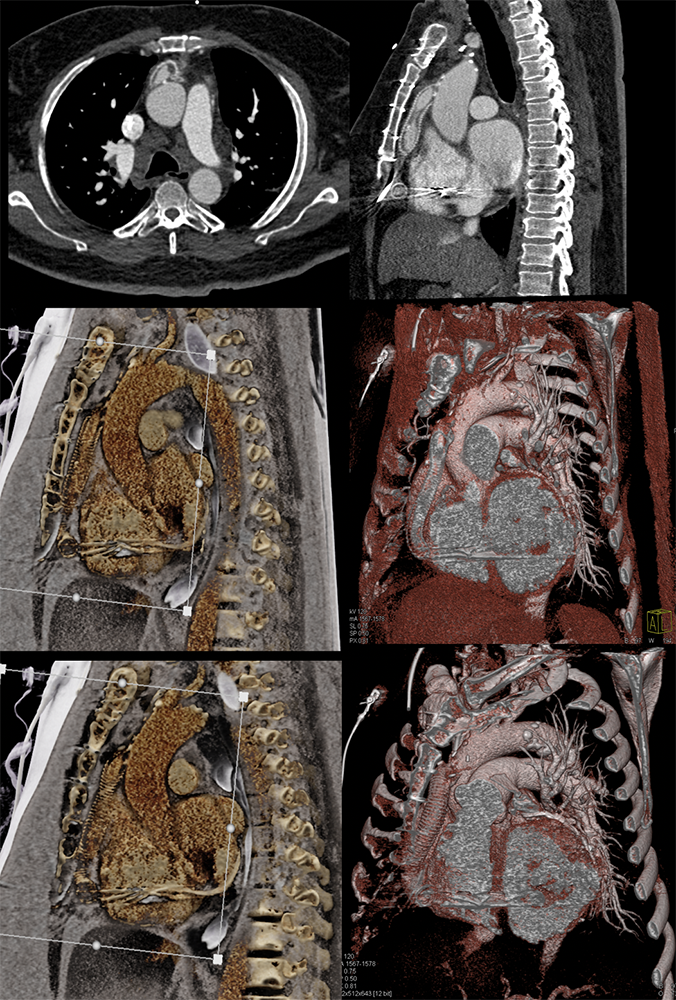 |
Cardiac CT Valve planning CT cardiac and post-procedural imaging.
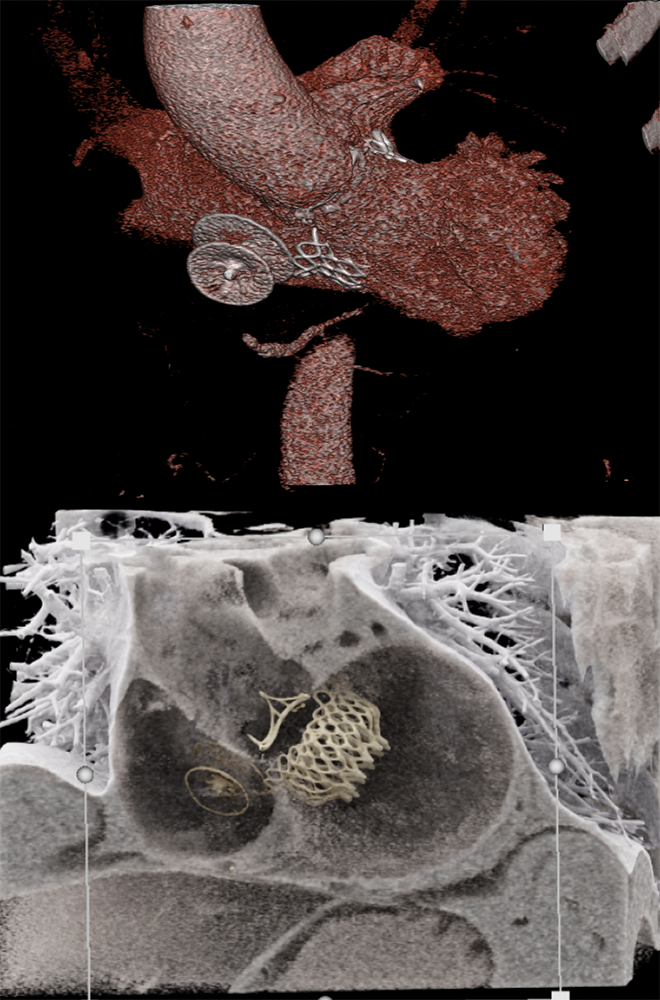 |
Post TMVR (trans-catheter mitral valve replacement) 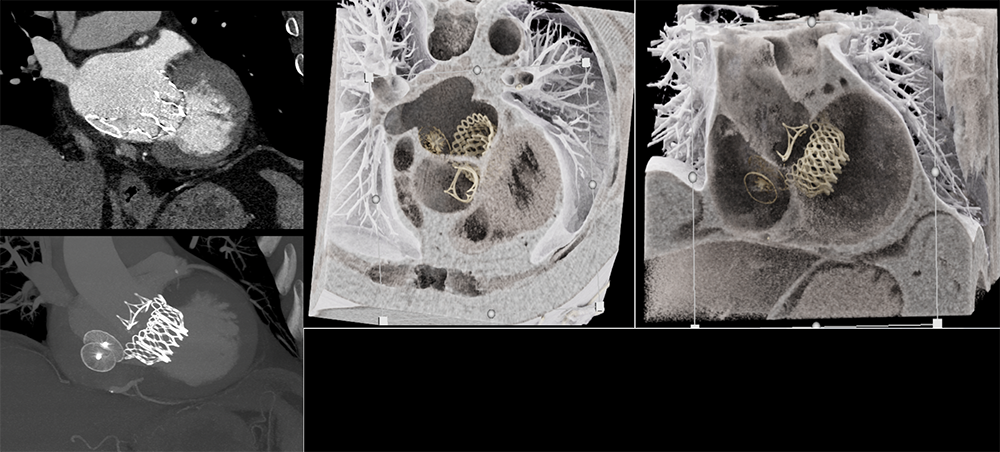 |
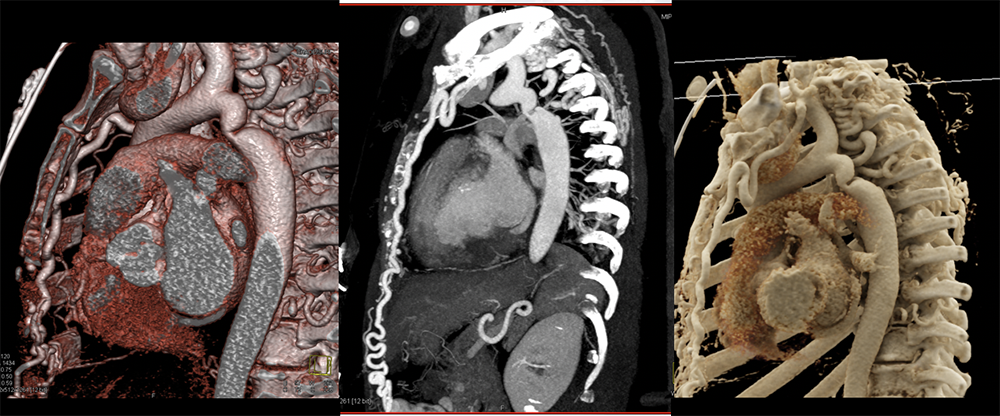
Pericarditis 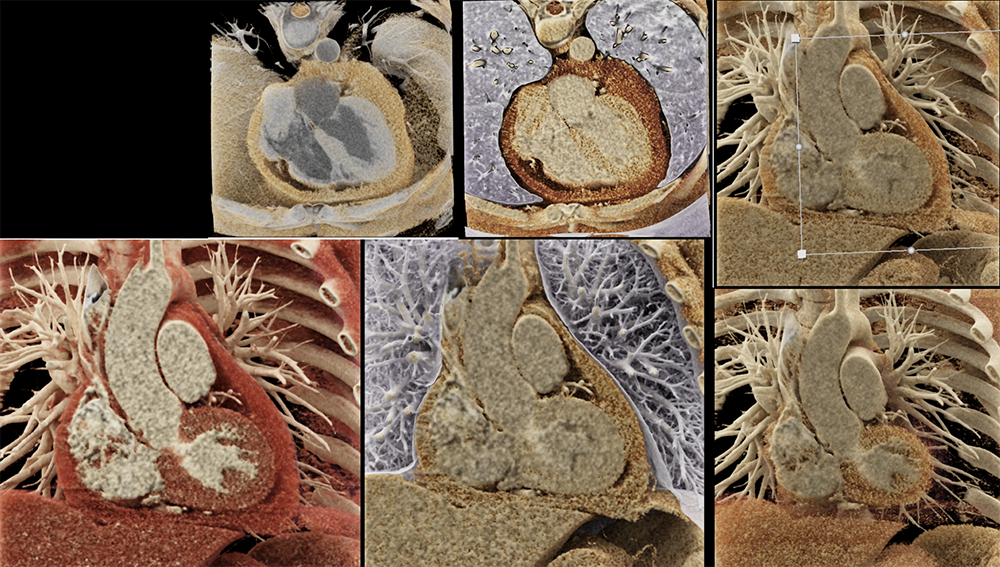 |
Benign pericardial cyst 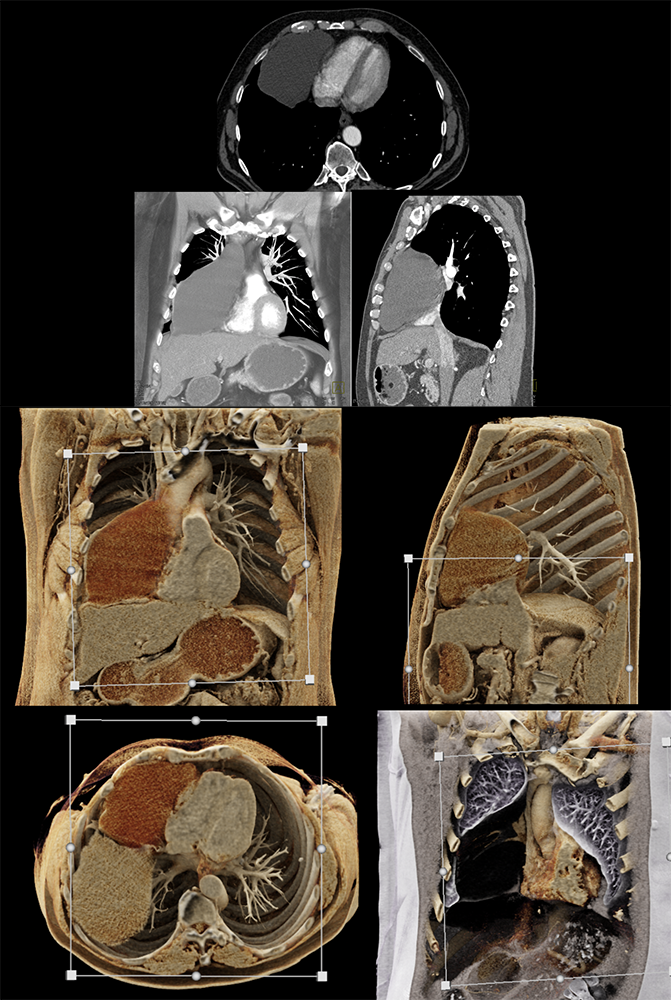 |
Case of Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasias (HHT) 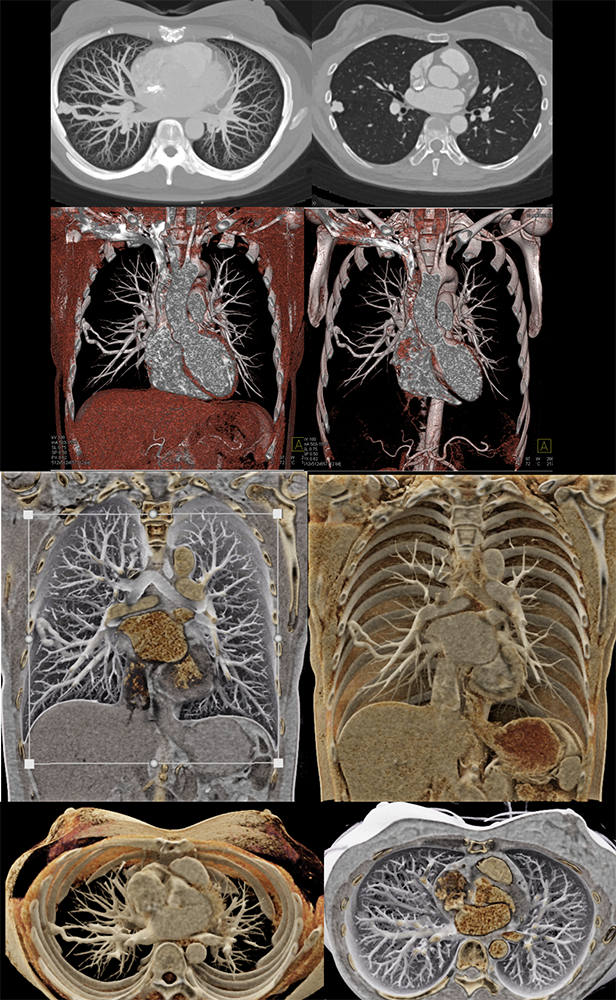 |
Relapsing polychondritis 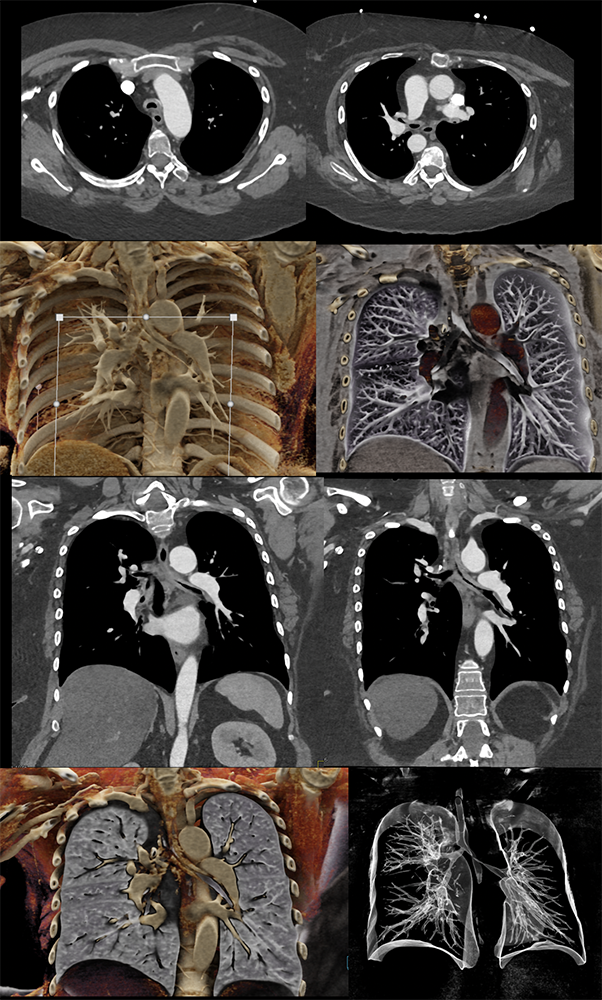 |
Thymoma 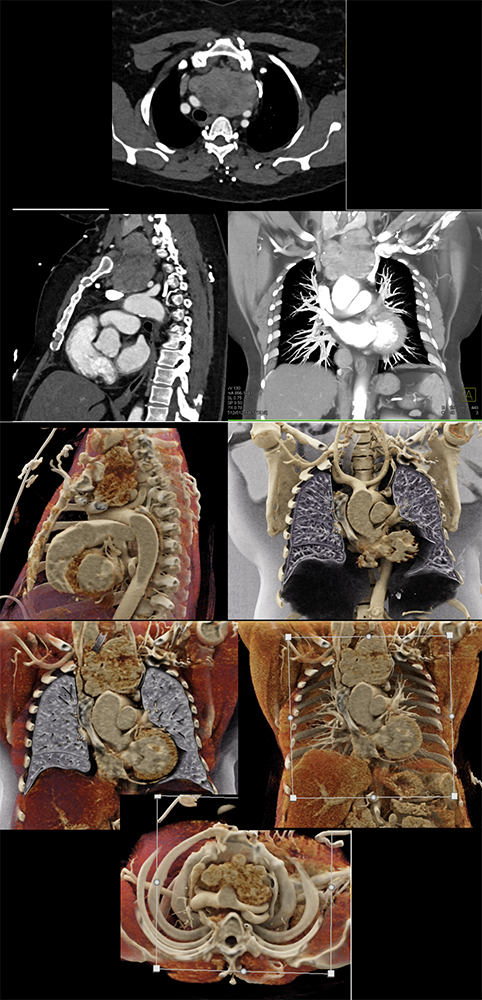 |
Cystic thymoma 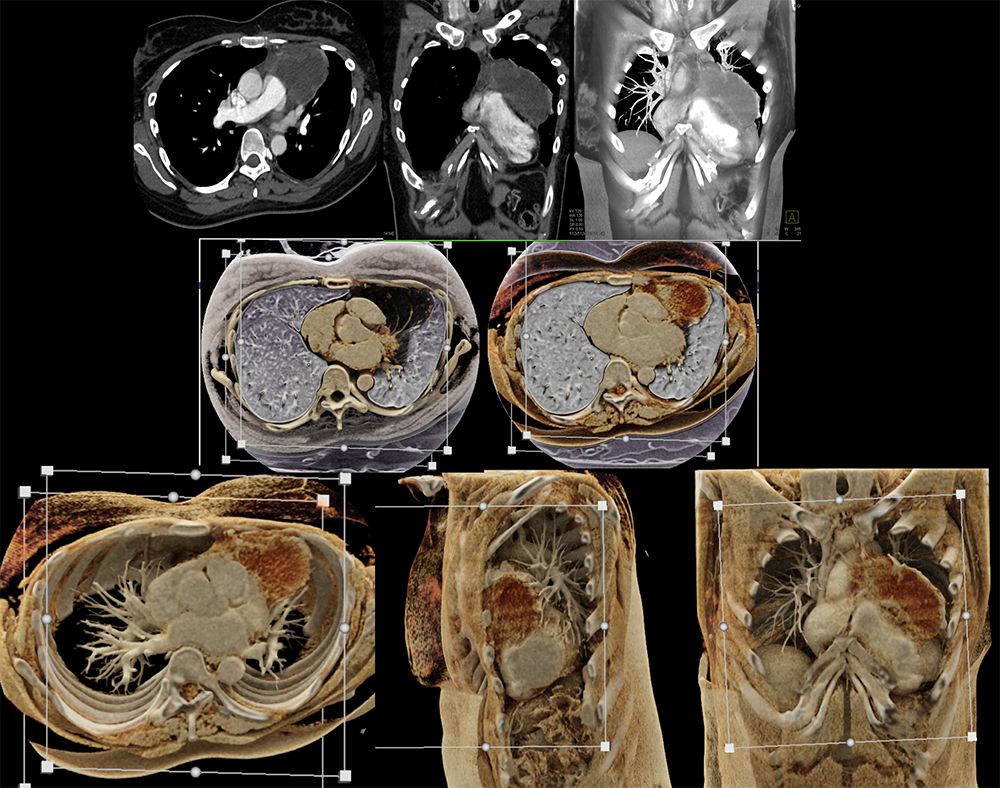 |
Advanced applications 1. Black blood Cinematic Rendering (BBCR) A recent advancement in cardiovascular application of the cinematic rendering where a reconstruction preset is used to create dark blood images which are invaluable for luminal assessment of the heart and vessels. Rowe SP, Chu LC, Recht HS, Lin CT, Fishman EK. Black-blood cinematic rendering: a new method for cardiac CT intraluminal visualization. Journal of cardiovascular computed tomography. 2020 May 1;14(3):272-4. 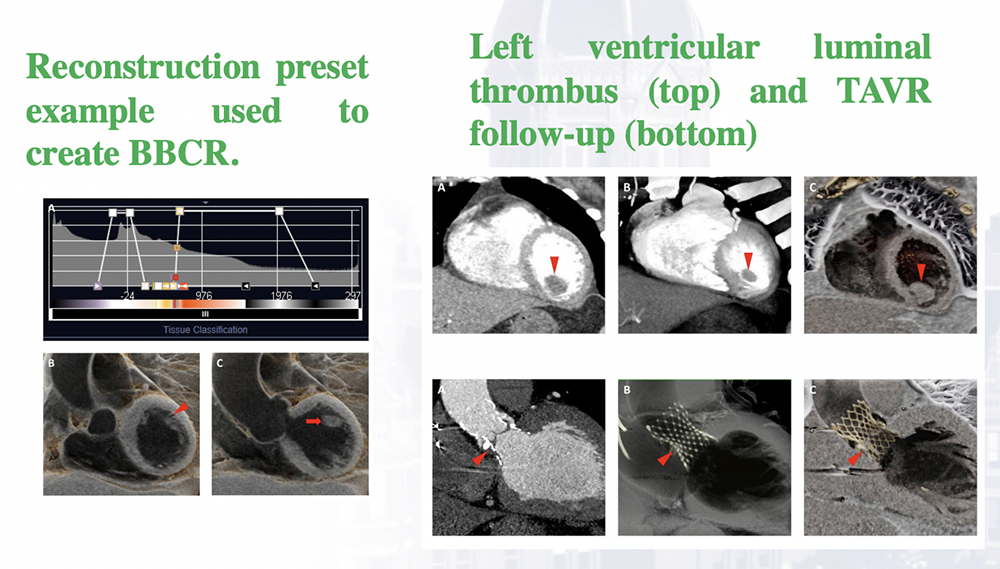 |
Advanced applications 2. Cinematic rendering in PET-CT dataset A recent advancement in the field. “CR of PET/CT data provides a photorealistic means of visualizing complex fusion imaging datasets. Such visualizations may aid anatomic understanding for surgical or procedural applications.” Applications in cardiac PET-CT are hoped to follow. Application of cinematic rendering in 18F-DCFPyL PSMA-targeted PET/CT demonstrating uptake in the prostate and left external iliac lymph nodes. Rowe SP, Pomper MG, Leal JP, Schneider R, Krüger S, Chu LC, Fishman EK. Photorealistic three-dimensional visualization of fusion datasets: cinematic rendering of PET/CT. Abdominal Radiology. 2022 Aug 2:1-5. 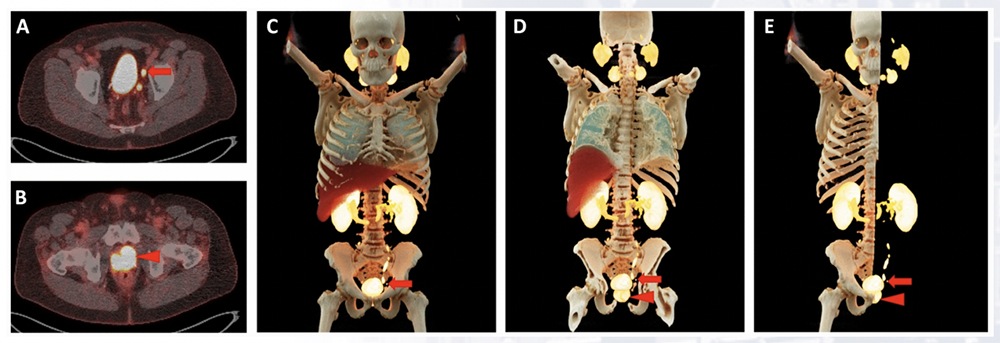 |
Applications of Cinematic Rendering (CR) to cardiovascular imaging Limitations and barriers
|
