CT of Bladder Masses: Pearls and PitfallsCT of Bladder Masses: Pearls and Pitfalls |
Technique: Hematuria
 |
MPRs for Characterization
 |
PRIMARY MALIGNANCIES: Transitional Cell Carcinoma Range of morphologies of TCC that may be indentified on CT 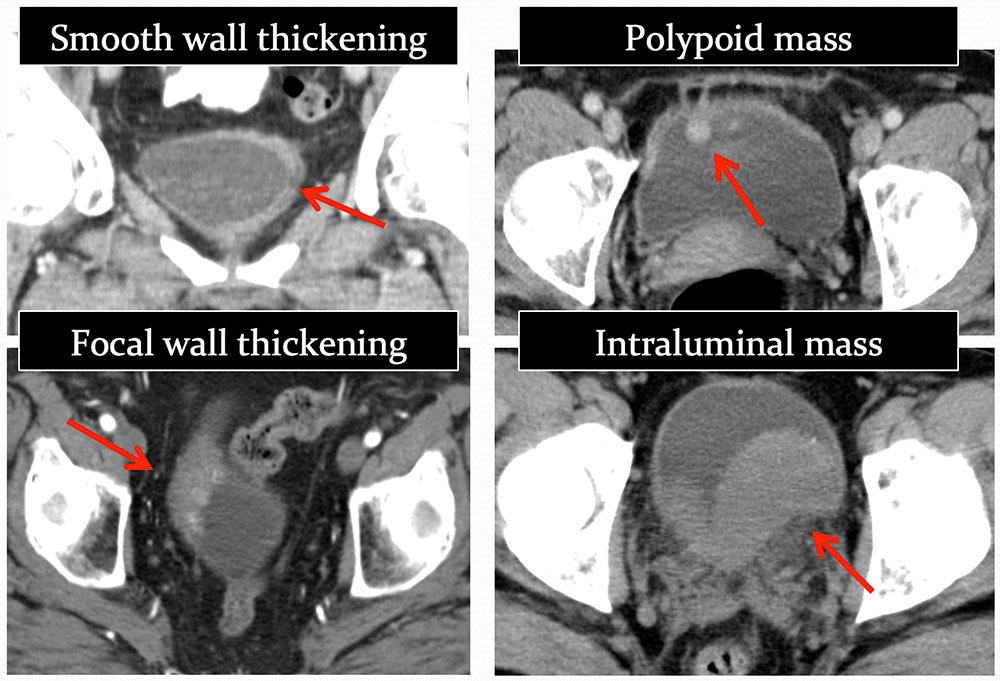 |
Transitional Cell Carcinoma 42 year old man with papillary transitional cell carcinoma- polypoid configuration. TCC features on CT: calcification is present in 0.7-6% of bladder TCC Vikram R, Sandler CM, Ng CS. Imaging and staging of transitional cell carcinoma: part 1, lower urinary tract. AJR 2009 Jun;192(6):1481-7. 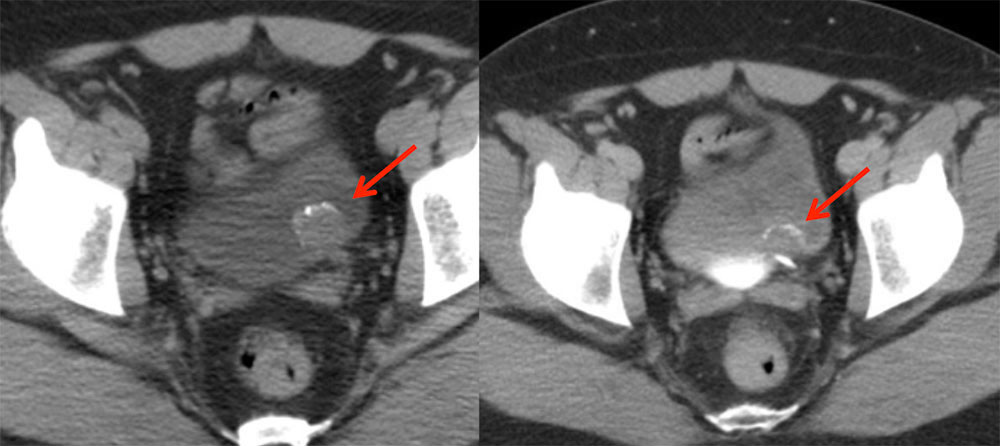 |
Multifocal TCC 69 year old man with papillary transitional cell carcinoma of the right renal pelvis and subtle right bladder wall TCC. TCC features on CT: Multifocal TCC at presentation occurs in 17% of patients. Cosentino M, Palou J, Gaya JM, et al. Upper urinary tract urothelial: location as a predictive factor for concomitant bladder carcinoma. World J Urol 2013;31:141–5. 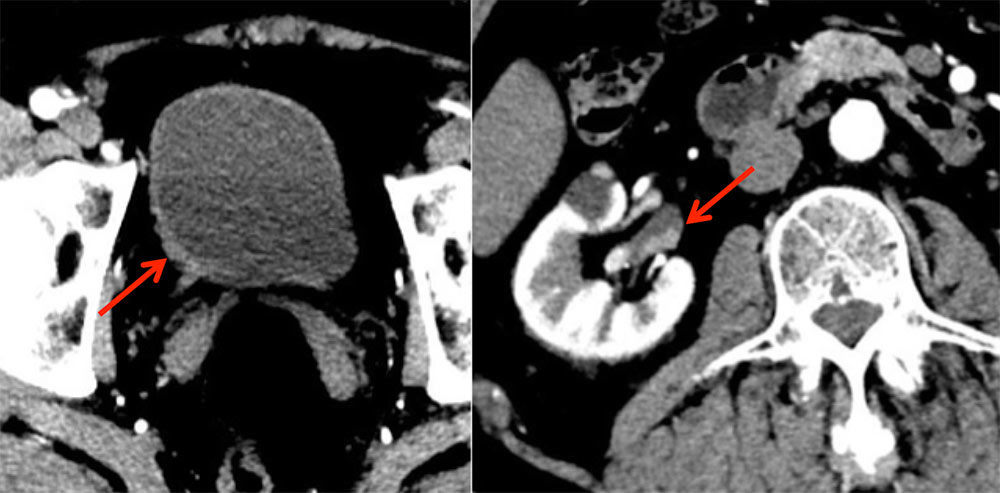 |
TCC: Incidental/Unsuspected
Iezzi R, Cotroneo AR, Filippone A, et al. Extravascular incidental findings at multislice CT angiography of the abdominal aorta and lower extremity arteries: a retrospective review study. Abdom Imaging 2007; 32: 4894–4894 |
Incidental Bladder Tumor 43 y/o male with extensive history of smoking presents for CTA runoff study to evaluate vasculature of the pelvis and lower extremities for claudication. Arterial phase coronal (A) and sagittal (B) MPRs of the pelvis with incidental note made of superior bladder wall thickening/enhancement, highly suspicious for transitional cell carcinoma. 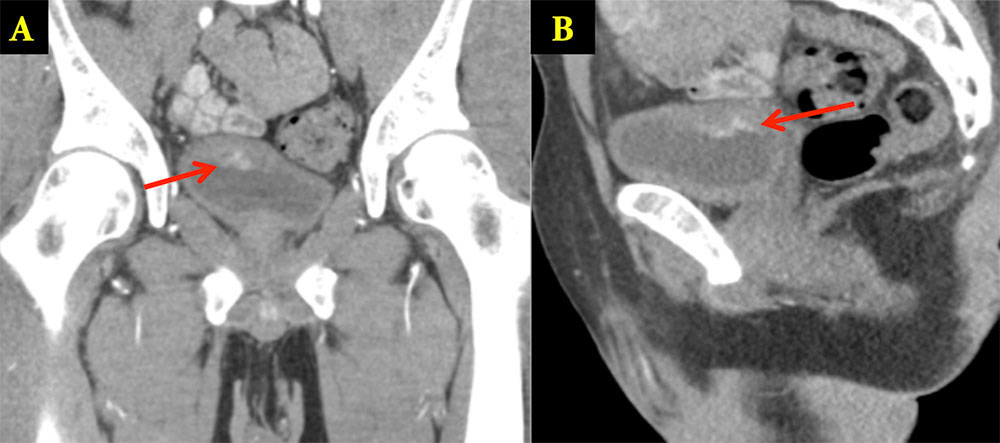 |
Primary cancer: Atypical Location
Golijanin D, Yossepowitch O, Beck SD, Sogani P, Dalbagni G. Carcinoma in a bladder diverticulum: presentation and treatment outcome. J Urol. 2003 Nov;170(5):1761-4 Wong-You-Cheong, J. J., P. J. Woodward, M. A. Manning, and I. A. Sesterhenn. "From the Archives of the AFIP: Neoplasms of the Urinary Bladder: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation." Radiographics (2006): 553-80. |
TCC in Bladder Diverticulum 79 year old male with history of bladder diverticula and recent onset hematuria Axial (A), sagittal (B) and coronal (C) images from oral and IV contrast enhanced CT show multiple large bladder diverticulae, one of which contains a soft tissue mass (arrow).
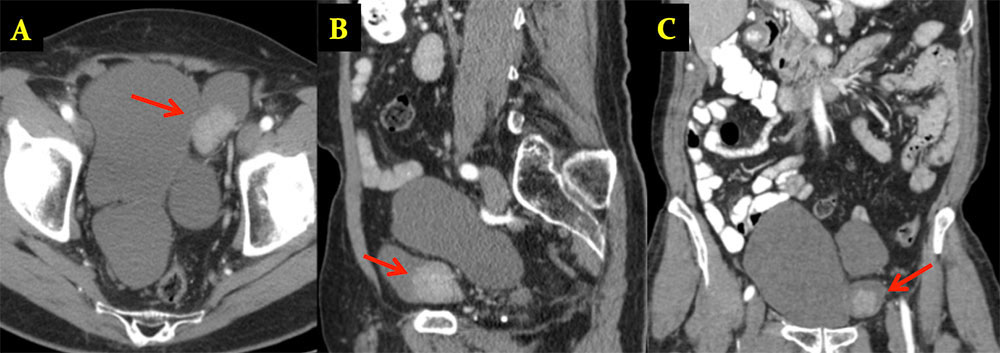 |
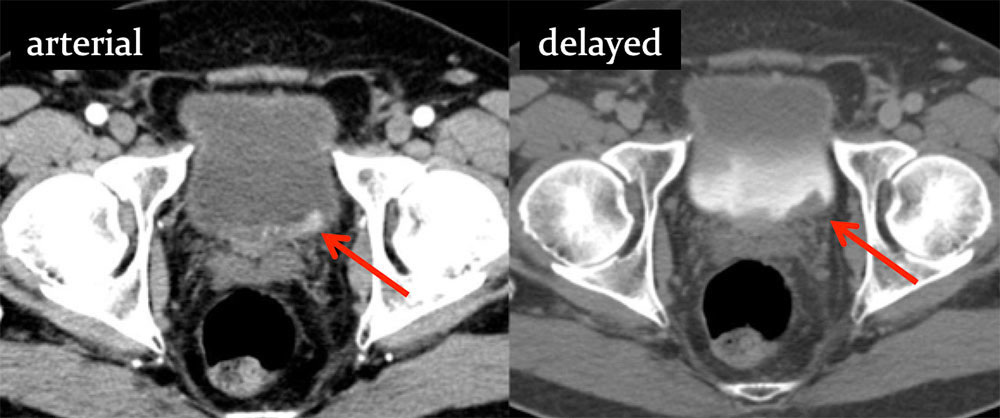
TCC in Bladder Diverticulum 57 year old male with recurrent bouts of right pelvic pain “concerning for prostatitis”. Images from outside CT. Precontrast (A), venous phase (B) and delayed phase (C) axial images from IV contrast enhanced CT show an enhancing mass posterior to the right bladder wall. Differential diagnostic considerations included a mass arising from the seminal vesicle, paraganglioma/neuroendocrine tumor, adenopathy or a diverticulum (although no communication with the bladder was observed. Repeat CT and MRI imaging were performed… 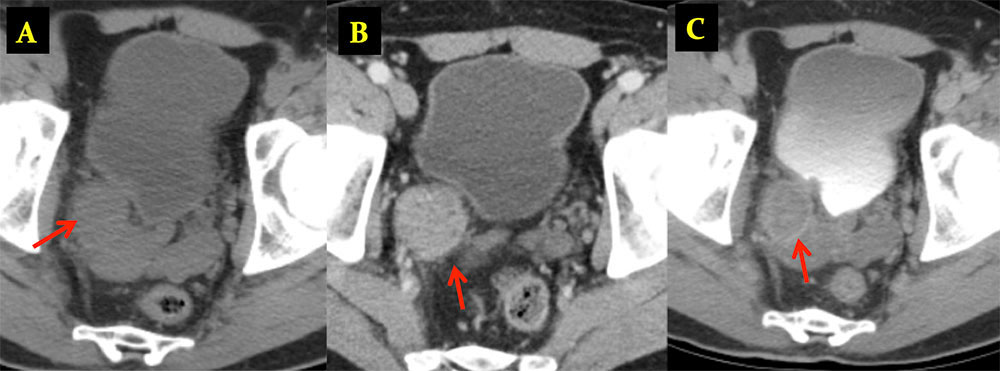 |
TCC in Bladder Diverticulum Delayed high resolution axial CT (A) reveals diverticulum with direct communication (arrows) with the bladder. Communication to bladder also confirmed on axial T2 weighted MRI (B). Pathology revealed invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder arising in a periureteral diverticulum. 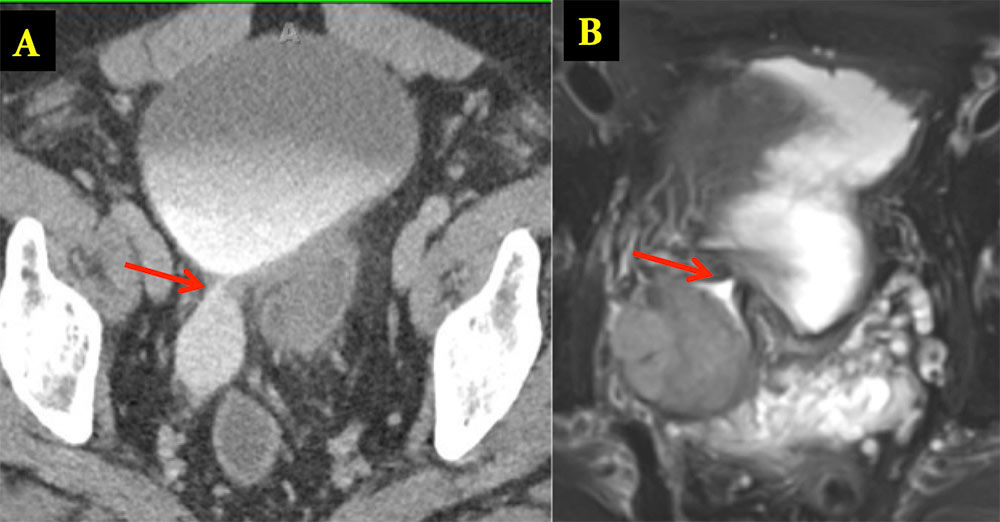 |
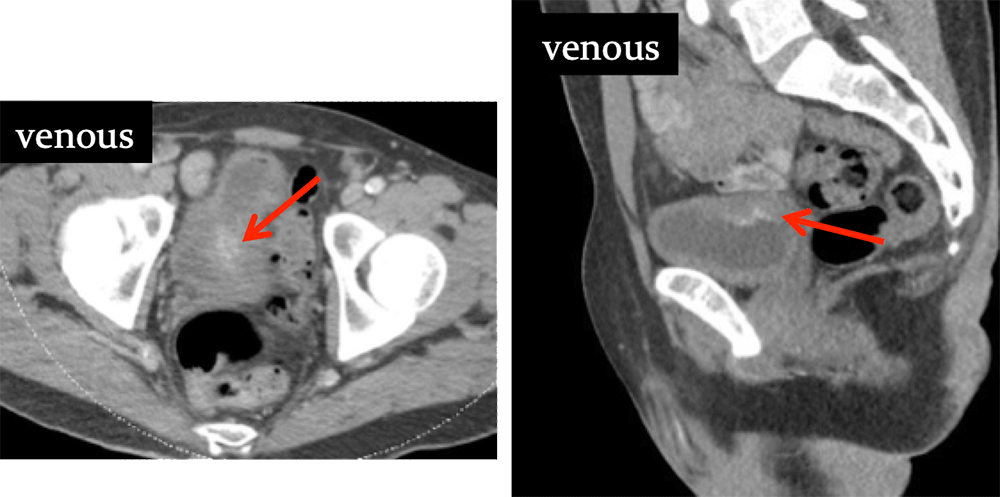
Urachal Carcinoma 60 year old man with history of pancreatitis and incidentally noted bladder lesion on CT Axial image (A) and sagittal MPR (B) from IV contrast enhanced CT shows small polypoid mass in the anterior bladder. Pathology revealed adenocarcinoma of the bladder dome
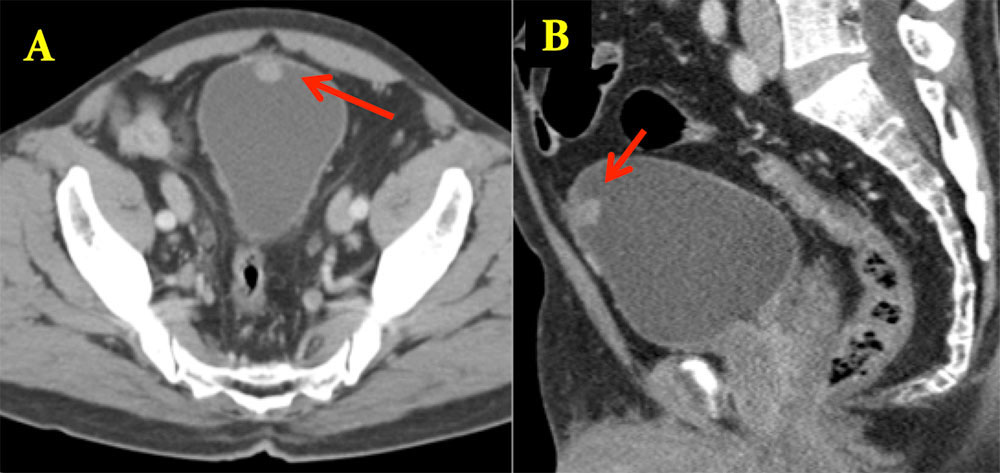 |
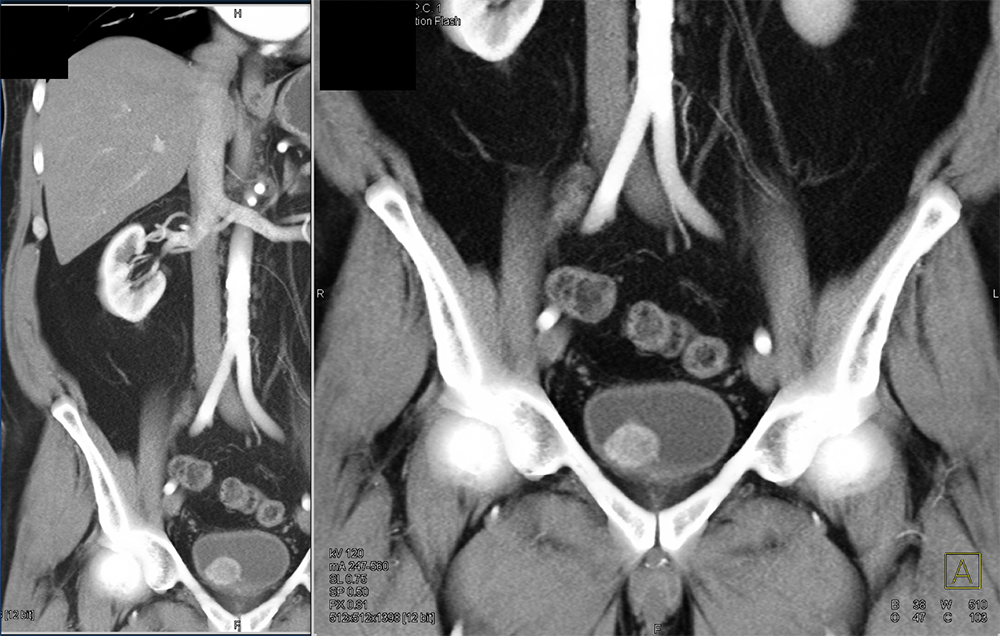
Pheochromocytoma in Organ of Zuckerkandl 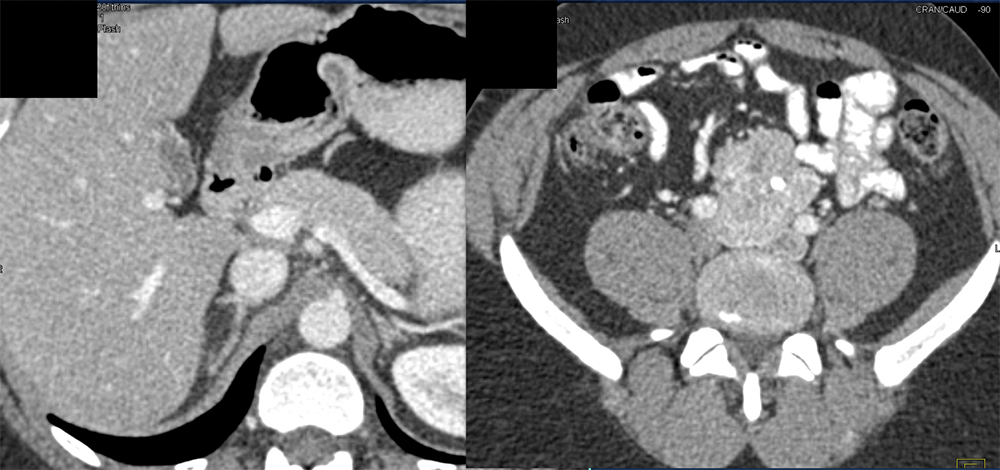 |
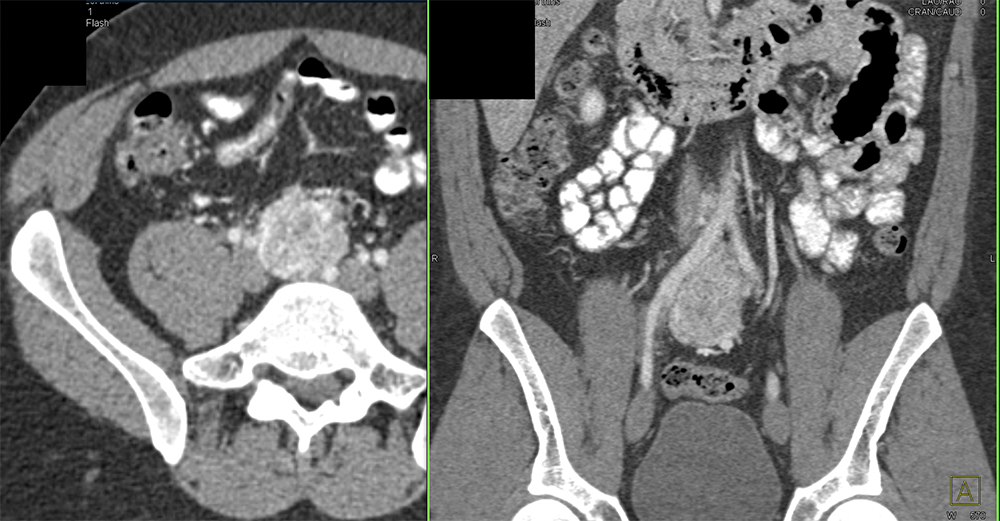 |
Bladder Pheochromocytoma 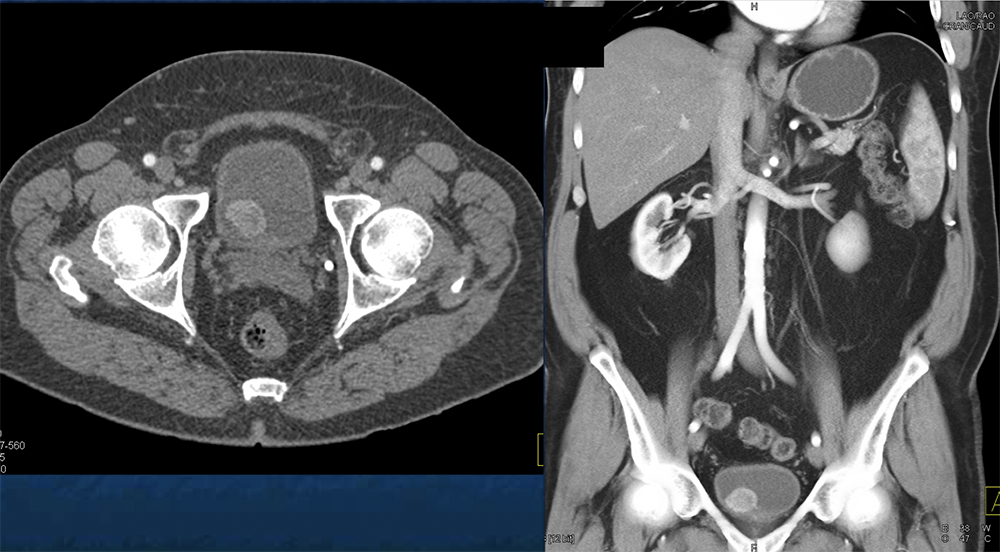 |
 |
Extraadrenal Paragangliomas: CT Findings
|
Bladder Paraganglioma 66 year old male with history of palpations, headaches and hypertension. Axial arterial (A), axial delayed (B) and coronal arterial phase (C) from IV contrast enhanced CT show a hypervascular polypoid intraluminal mass in the bladder (arrows).
Lee JA, Duh QY. Sporadic paraganglioma. World J Surg. 2008;32(5):683-7. 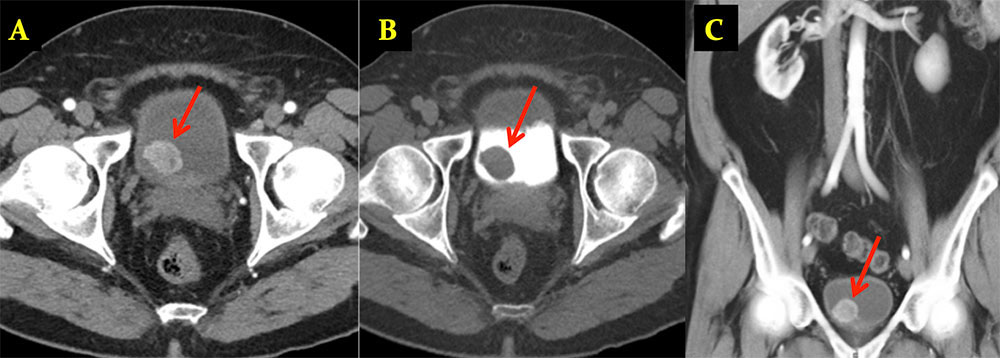 |
Bladder Paraganglioma 60 year old man with metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Axial (A) and sagittal (B) images from corticomedullary phase CT reveal a small enhancing mural nodule along the left bladder wall (arrows), presumed to be metastasis. Pathology revealed paraganglioma. 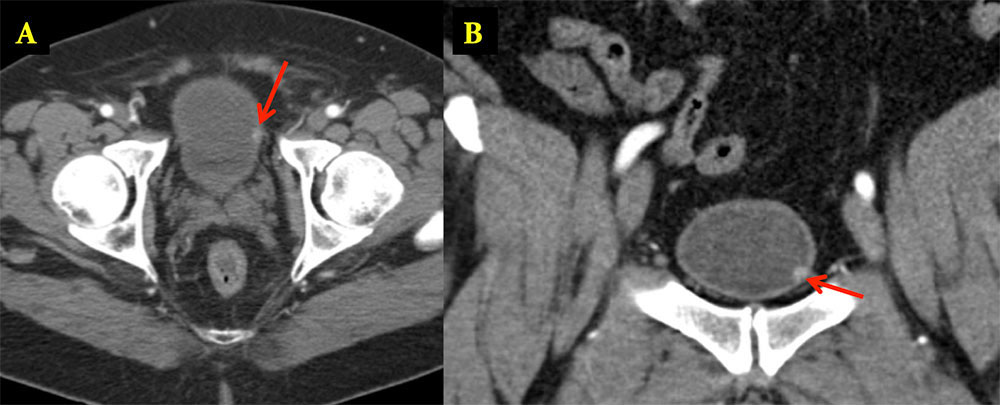 |
Bladder Paraganglioma 65 year old woman with history of hypertension that increased during urination, palpitations and diaphoresis. Axial arterial (A) and delayed phase (B) IV contrast enhanced CT shows a large mass inseparable from the anterior left wall of the bladder. Pathology revealed 4.5 cm paraganglioma involving the muscularis propria and serosal fat. 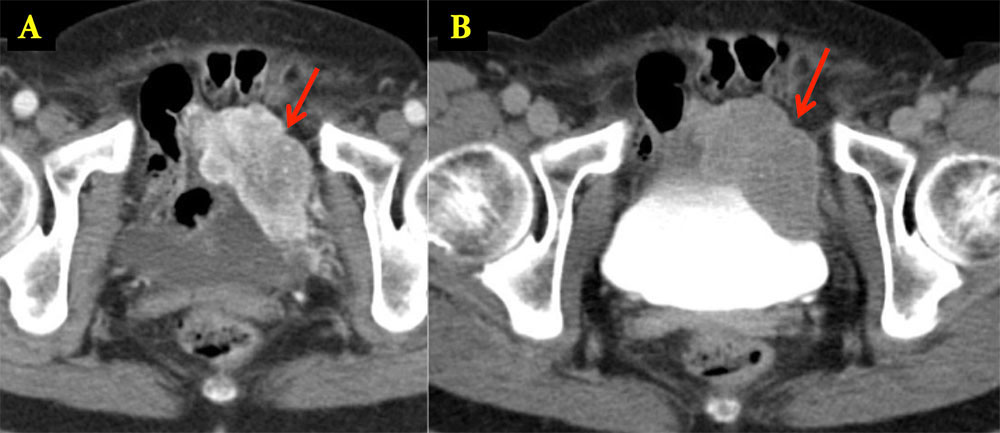 |
SECONDARY MALIGNANCIES: Metastatic Disease 65 year old man with metastatic prostate cancer. Coronal MPRs (A,B) and sagittal MPR (C) from IV contrast enhanced CT of the abdomen and pelvis show multiple masses in the bladder in a patient with prostate cancer, new from prior exam in 2 years earlier and in the setting of new spine and adrenal metastases (not shown). Appearance similar to transitional cell carcinoma, but multiplicity and this setting favor metastatic etiology. 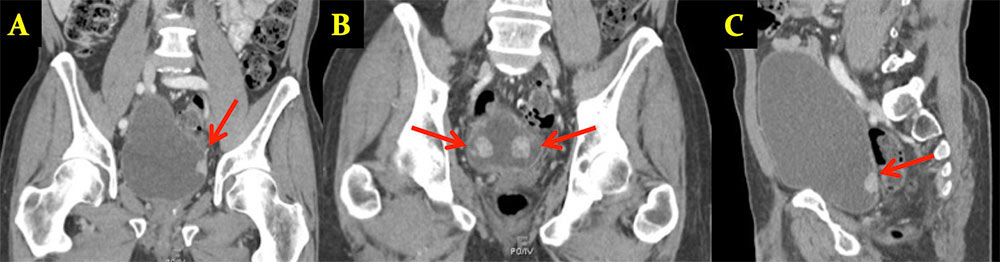 |
Metastatic Disease 58 year old female who initially presented with hematuria.
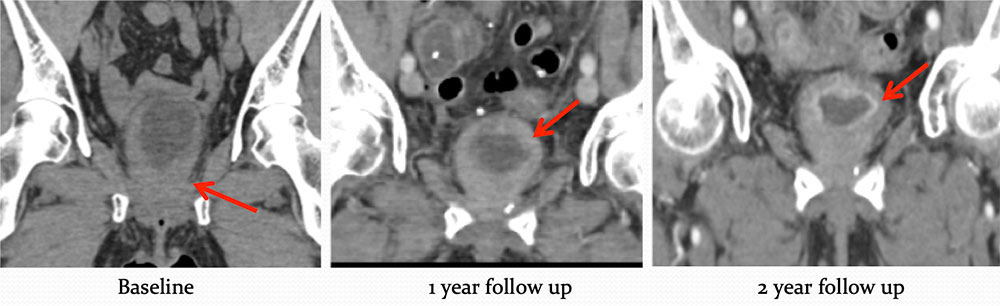 |
Bladder Lymphoma 60 year old man with abnormal labs. Axial contrast enhanced images of the pelvis show diffusely thickened and enhancing bladder (red arrows) along with inguinal and iliac adenopathy (yellow arrows), raising concern for bladder lymphoma. Pathology revealed widely disseminated, large B-cell follicular lymphoma.
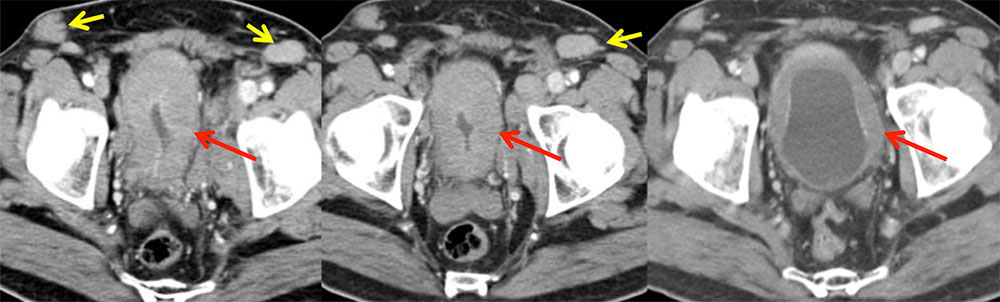 |
BENIGN MIMICS OF TUMOR: Bladder Hematoma Noncontrast coronal MPR images of a 66 year old woman with large infiltrative left renal cell carcinoma (RCC) invading left renal vein (V) and gross hematuria. Large hyperattenuating left bladder mass (arrow) was a hematoma, resolved at follow up (not shown). 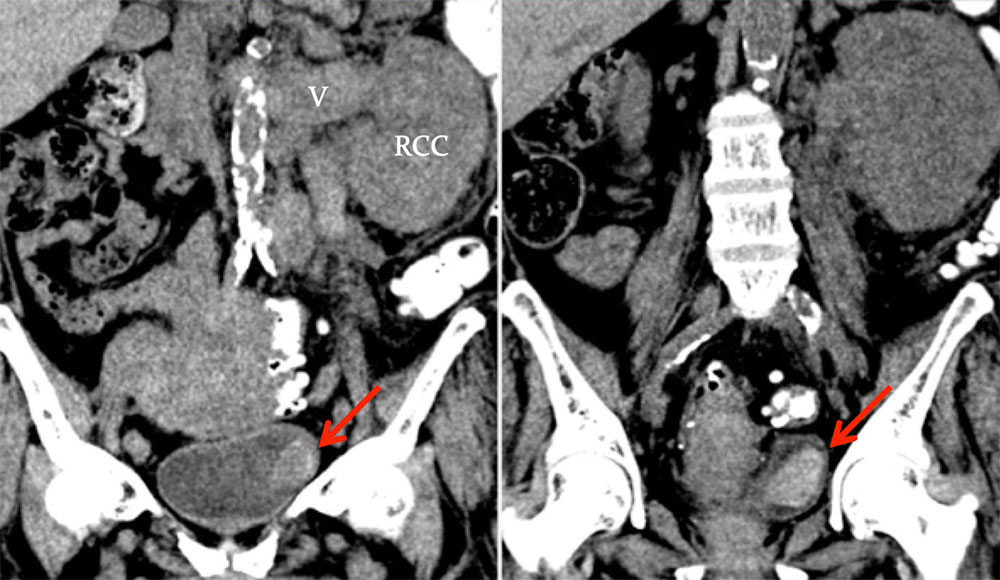 |
Malakoplakia 48 y/o female who was referred for an approximately 20-year history of symptoms of cystitis with dysuria, urinary frequency, and intermittent hematuria. Axial precontrast (A), axial arterial phase (B) and coronal arterial phase (C) images from IV contrast enhanced CT show a 3.6 x 1.4 cm enhancing nodular mass (arrows) along the posterolateral wall of the bladder. Pathology revealed malakoplakia. 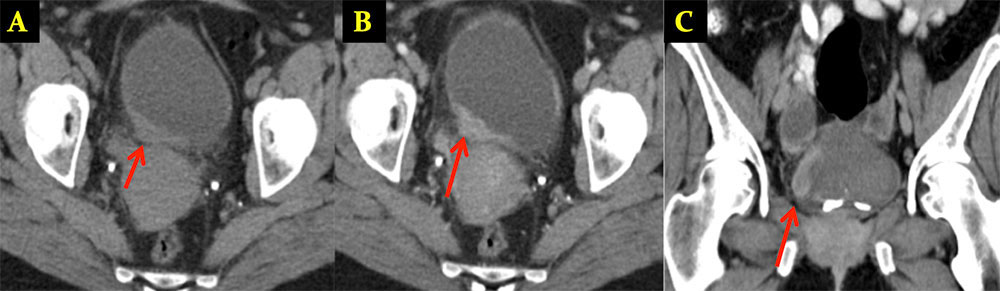 |
Malakoplakia
Sulman, A., & Goldman, H. (2002). Malacoplakia presenting as a large bladder mass. Urology, 60, 163-163. |
Cystitis Cystica 37 y/o man with hematuria. Mass identified in posterior bladder at cystoscopy. Delayed axial image (A) and sagittal MPR (B) of the bladder reveal a soft tissue mass (arrows) along the posterior wall of the bladder. Pathology revealed cystitis cystica and glandularis
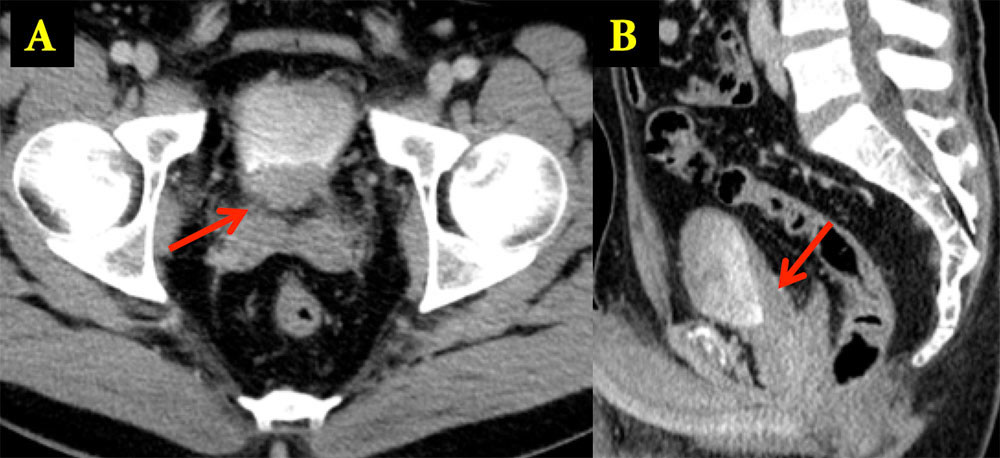 |
Mullerianosis 28 year old female with pelvic pain and hematuria. Initial urinalysis revealed “tissue fragments of endometrial type cells”. CT was performed for further analysis Axial precontrast (A), coronal and sagittal (B,C) delayed phase CT after IV contrast administration show a 3.7 x 2.5 cm anterolateral mass (arrows) of the bladder. Pathology returned as mullerianosis. 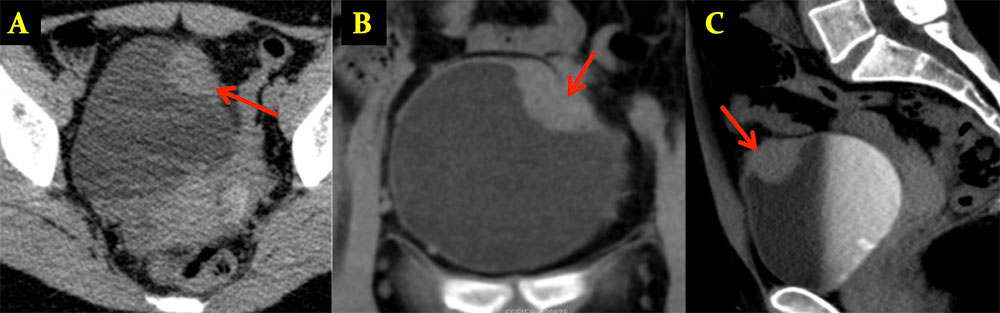 |
Mullerianosis
|
Urachal Cyst 62 year old woman with history of lung and endometrial cancer. Small enhancing lesion in anterior bladder increasing in size over serial examinations. At cystoscopy, this was noted to be submucosal. Coronal (A) and sagittal MPRs (B) from oral and IV contrast enhanced CT show small enhancing nodule in the anterior bladder. Pathology revealed urachal cyst.
Friedland GW, Devries PA, Matilde NM, Cohen R, Rifkin MD. Congenital anomalies of the urinary tract. In: Pollack HM, eds. Clinical Urography. Philadelphia, Pa: Saunders, 1990;559-787. 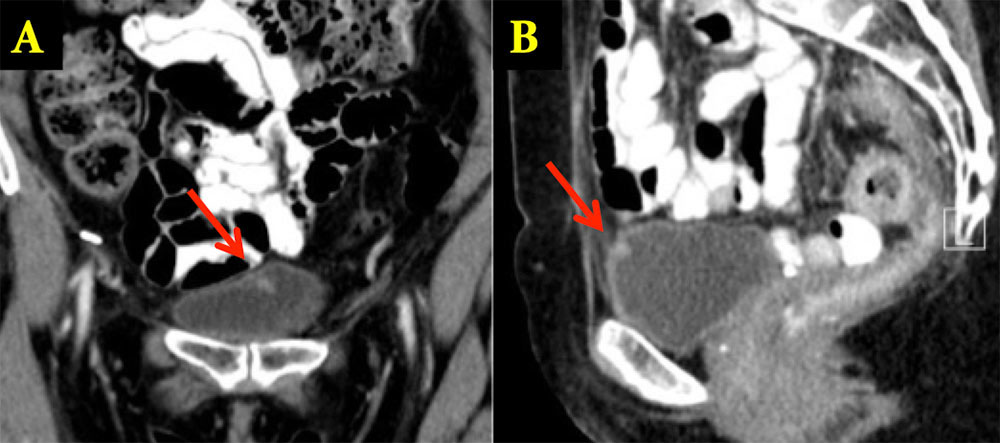 |
CHANGES IN MORPHOLOGY: Colovesical Fistula 52 year old man with h/o longstanding diverticulitis and recurrent peridiverticular abscess Axial venous-phase CECT (A) shows a gas and fluid collection (yellow arrows) adjacent to the bladder, compatible with abscess. Coronal and sagittal (C,D) venous-phase CECT image shows the fistulous connection (red arrows) between the inflamed sigmoid colon and the abscess cavity, and adjacent bladder wall thickening. Patient subsequently underwent open rectosigmoid colectomy. 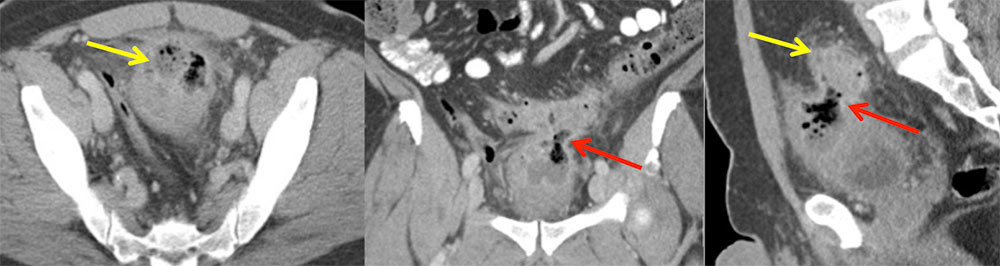 |
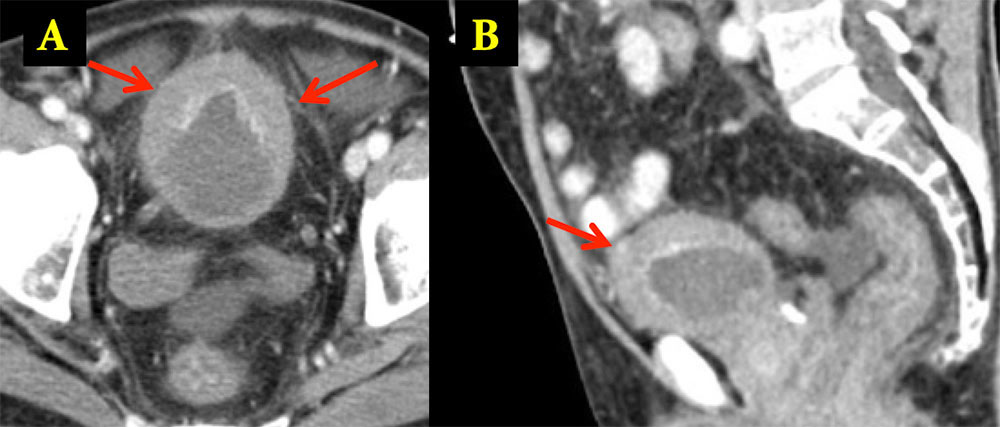
Herniating Bladder Axial IV contrast enhanced CT images show the right anterolateral bladder herniating into the right inguinal canal (arrows).
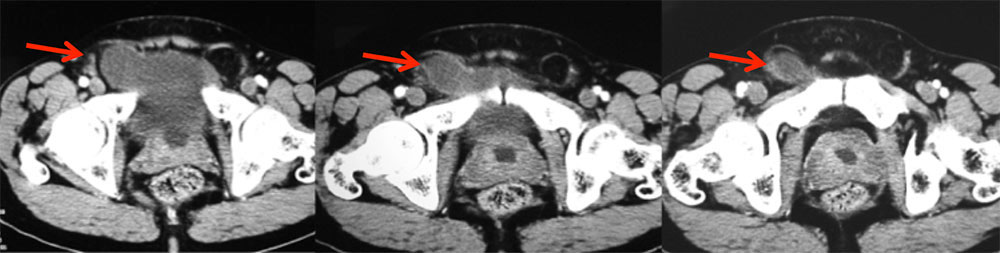 |
INFECTIOUS PROCESSES: BK Cystitis 57 y/o male with follicular lymphoma, AML, s/p bone marrow transplant, who developed dysuria, hematuria and fever due to BK cystitis Axial (A) and sagittal (B) images from oral and IV contrast enhanced CT shows asymmetric bladder wall thickening (arrows), mucosal enhancement, and minimal perivesicular stranding. Polyomavirus BK cystitis:
 |
Emphysematous Cystitis Axial (A) and coronal (B) images from IV contrast enhanced CT show intramural (arrows) and perivesicular gas.
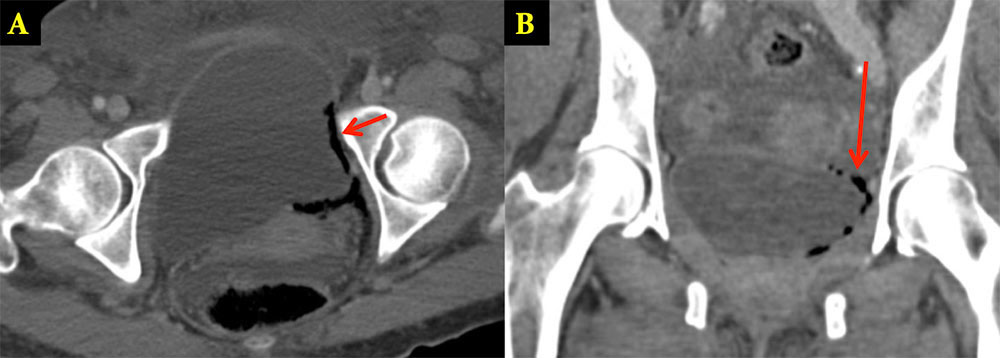 |
Schistosomiasis 48 year old man from Africa. Axial (A) and coronal (B) noncontrast CT images show dense coarse calcifications within the bladder wall in a “fetal head” pattern (red arrow). Right sided hydronephrosis (yellow arrow) shown in image C.
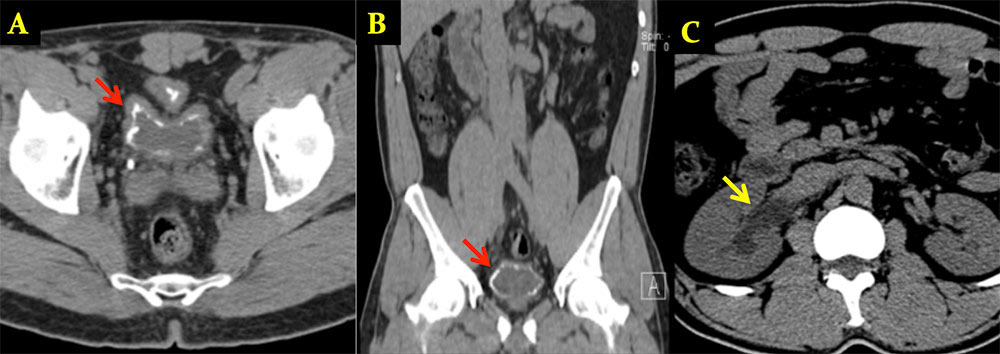 |
Summary
|
