MDCT and 3DCT Diagnosis of Lymphoepithelial Cysts of the Pancreas
MDCT and 3DCT Diagnosis of Lymphoepithelial Cysts of the Pancreas |
Introduction
|
Clinical Findings
|
CYTOLOGY (EUS-FNA)
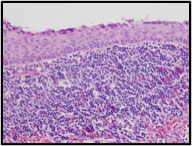 |
Pathogenesis Etiology is currently unknown. Hypotheses for histogenesis of lymphoepithelial cysts include:
|
Differential Diagnosis
|
Findings on CT
|
Findings on CT
|
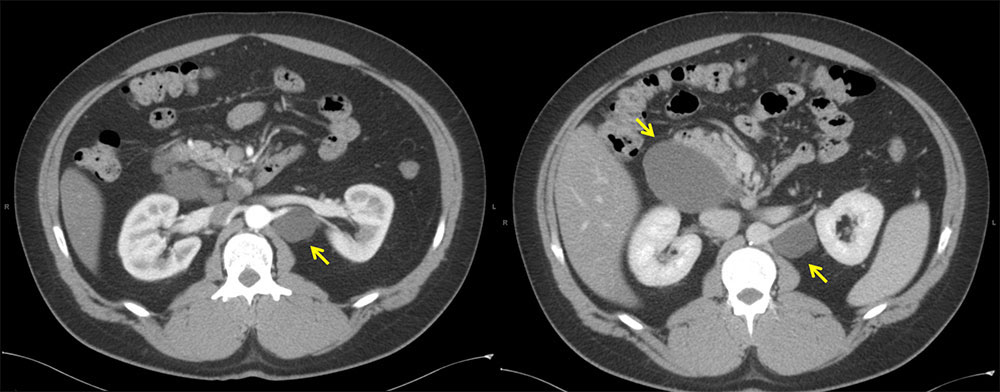 Case 1: 37-year-old M with history of testicular seminoma/embryonal testicular cancer who presented with an incidentally found peripancreatic cystic lesion. FNA of lesion demonstrated anucleated squamous cells and rare macrophages consistent with lymphoepithelial cyst. Left: Axial contrast-enhanced arterial phase CT demonstrates a cystic mass of water-density adjacent to left kidney. Right: Axial contrast-enhanced venous phase CT demonstrates multiple cystic masses of water-density adjacent to pancreas and left kidney. |
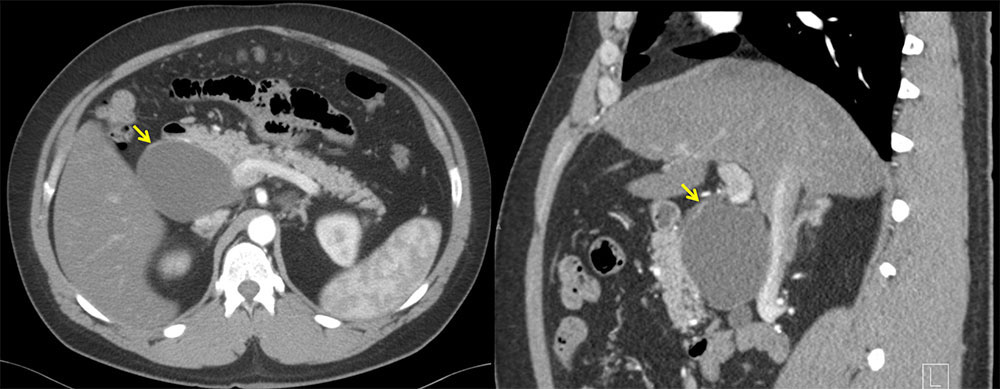 Left: Axial contrast-enhanced arterial phase CT demonstrate large mass (9.5 x 6.3 cm) of water-density adjacent to head of pancreas. The pancreas enhances normally with normal-sized pancreatic duct. Right: Sagittal multi-planar reconstruction contrast-enhanced arterial phase CT demonstrates large mass adjacent to head of pancreas. |
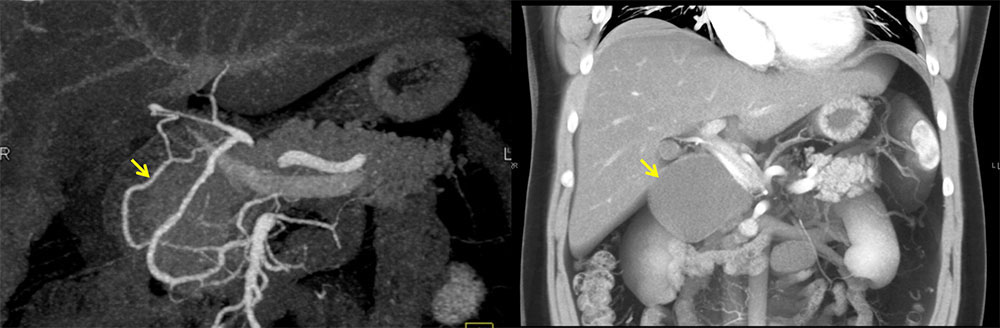 3DCT demonstrates large mass adjacent to pancreatic head. |
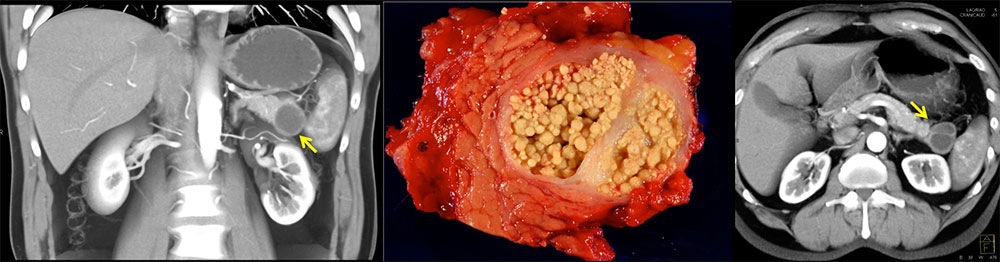 Case 2: 70-year-old M with incidentally found pancreatic lesion. FNA of lesion demonstrated proteinaceous keratinaceous debris and rare histiocytes. Patient underwent distal pancreatectomy with pathological confirmation of lymphoepithelial cyst. 3DCT coronal and axial views demonstrate cyst near pancreatic tail with single thick septation. |
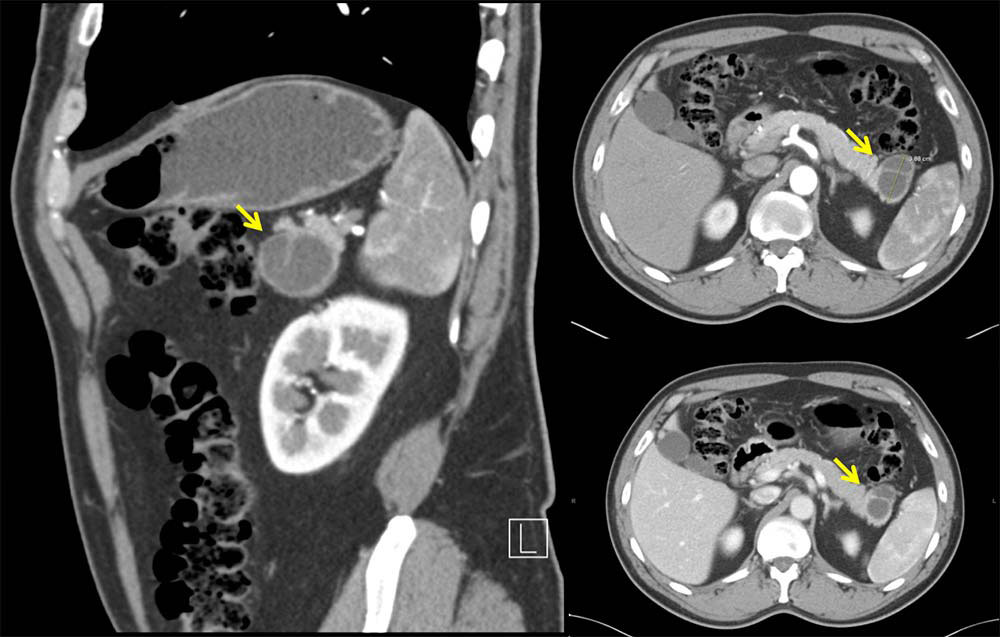 Top: Axial and sagittal contrast-enhanced arterial phase CT demonstrate 3.9 cm cyst with a thick septation in the tail of pancreas. Right: Axial venous phase CT demonstrates pancreatic cyst with a thick septation. |
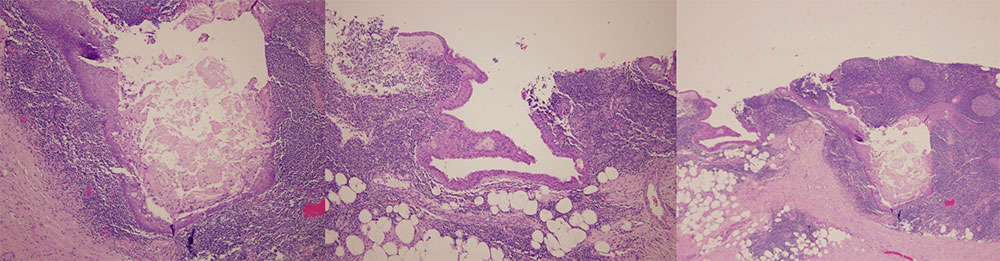 Pathology demonstrates a cyst lined by squamous epithelium, with lymphocytes and germinal centers in the cyst wall. Keratin debris is also seen. |
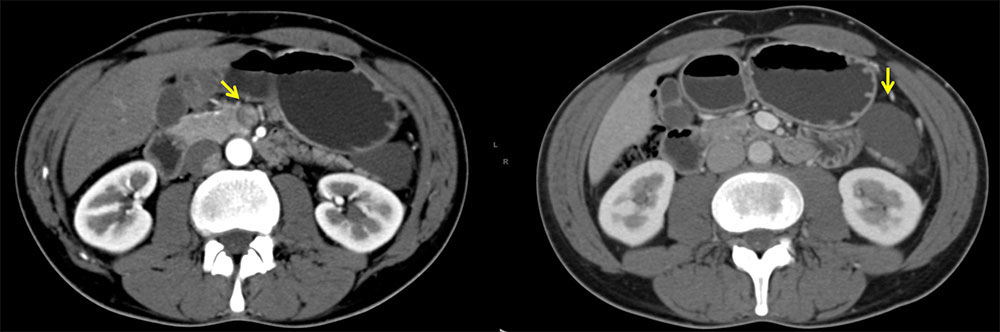 Case 3: 47 yo M with history of alcohol abuse presenting with weight loss and epigastric pain. CT scan demonstrated cyst in tail of pancreas. The lesion was resected and pathology confirmed diagnosis of lymphoepithelial cyst. Left: Axial contrast-enhanced arterial phase CT demonstrates cystic lesion near tail of pancreas. No evidence of acute pancreatitis. Right: Axial contrast-enhanced venous phase CT demonstrates well-defined cystic lesion of water density with no solid components. |
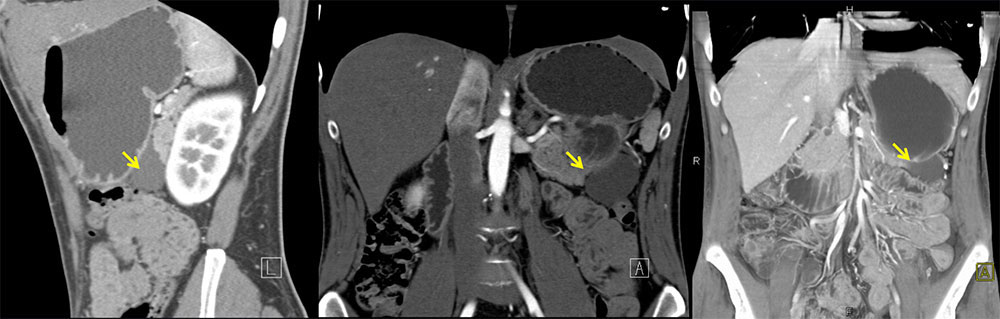 Left x2: Coronal and sagittal contrast-enhanced arterial phase CT demonstrate cystic lesion near tail of pancreas. Bottom: Coronal 3DCT demonstrates cystic lesion near tail of pancreas |
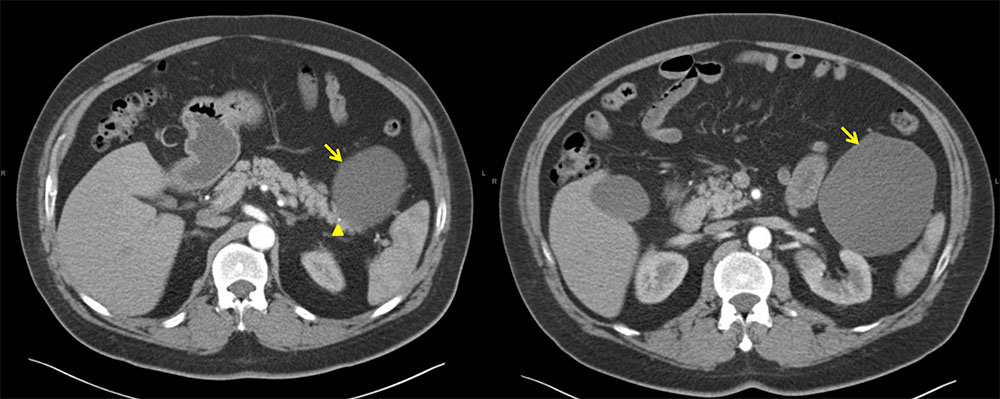 Case 4: 62 year old M with incidentally discovered pancreatic cyst. Pancreatic cyst fluid did not show evidence of malignant cells and was initially followed. Enlarging cyst prompted surgical resection. Pathology confirmed diagnosis of lymphoepithelial cyst Axial contrast-enhanced arterial phase CT demonstrates cystic mass near tail of pancreas and anterior to left kidney. Cross sectional diameter measured 10.1 cm. Tiny calcification adjacent to lesion was visualized (arrowhead). |
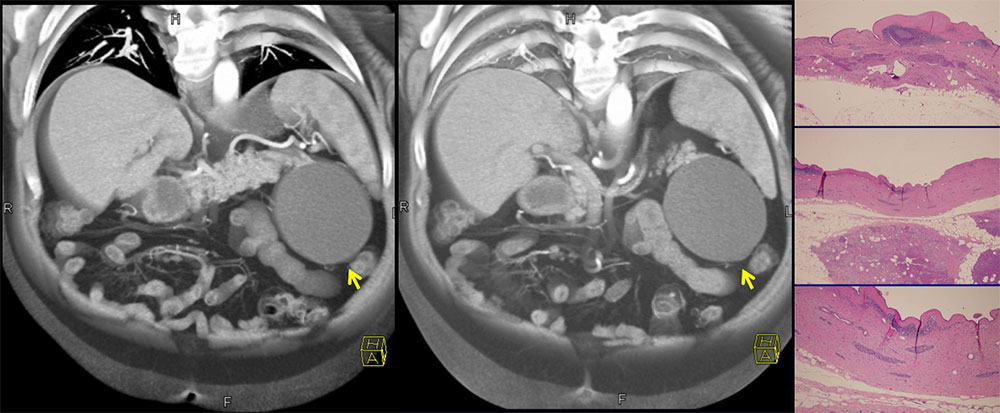 Pathology demonstrates a cyst lined by squamous epithelium, with lymphocytes and marked hyalinization in the cyst wall. Coronal 3D CT demonstrates a large pancreatic cyst near tail of pancreas. Cystic lesion is well-defined, water density, with no septations. |
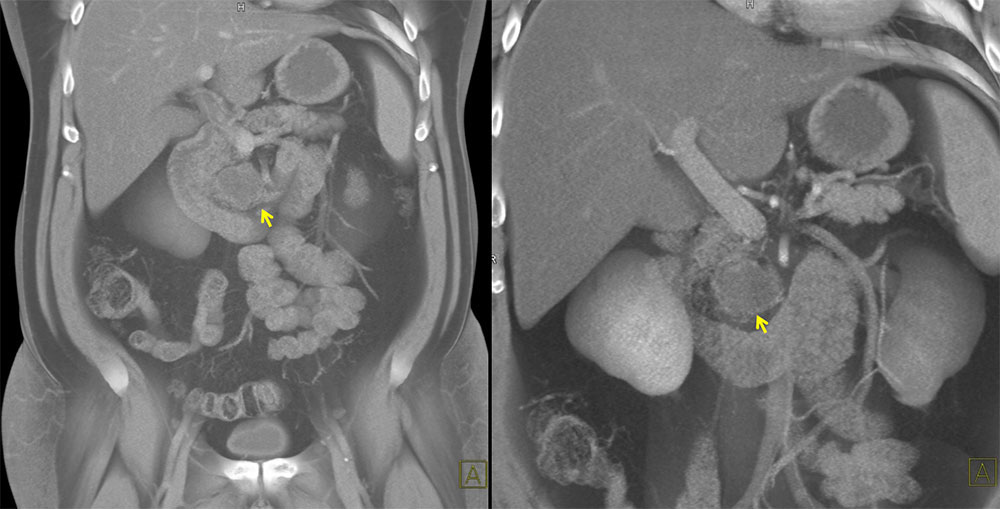 Case 5: 54 yo M with abdominal pain, incidentally found to have 3 cm pancreatic lesion. FNA demonstrated predominantly acute inflammation. He underwent resection of the lesion. Pathology confirmed epidermoid cyst with surrounding lymphoid reaction. Coronal 3D CT demonstrates pancreatic cyst. |
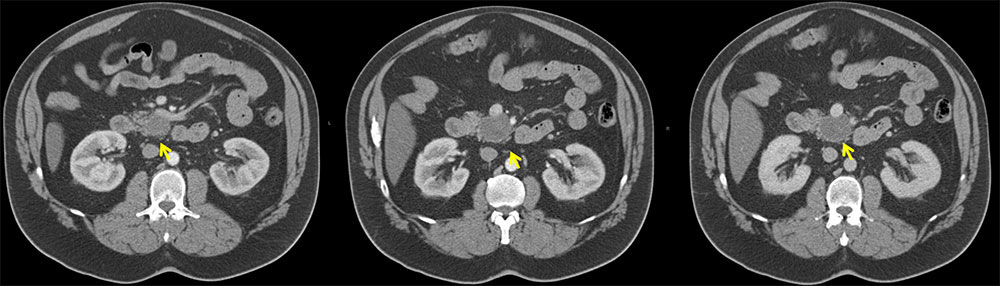 Left: Axial contrast enhanced arterial phase CT demonstrates pancreatic head cyst, abutting SMA. Middle: Axial arterial phase CT demonstrates pancreatic head cyst, abutting SMV. Right: Axial venous phase CT demonstrates pancreatic cyst |
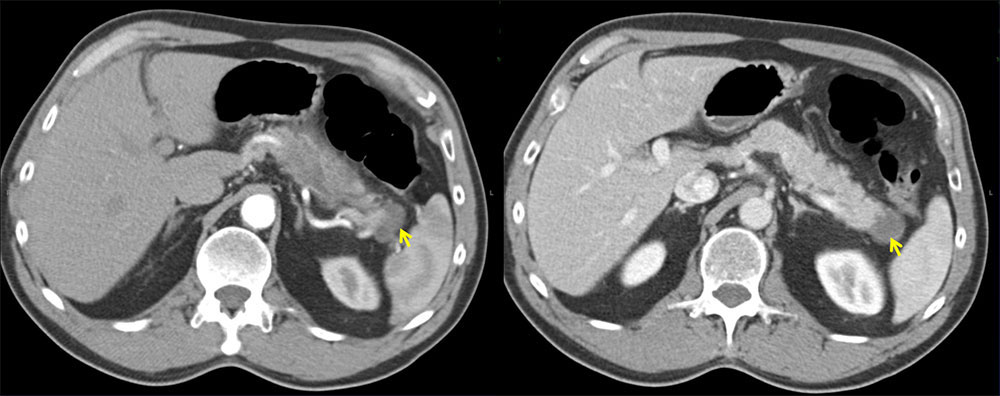 Case 6: 62-year-old M with an incidentally found pancreatic lesion near tail of pancreas. Patient underwent distal pancreatectomy with pathological confirmation of lymphoepithelial cyst. Left: Axial contrast-enhanced arterial phase CT demonstrates cystic lesion in tail of pancreas, near splenic vasculature. Right: Axial contrast-enhanced venous phase CT demonstrates 2.0 cm cystic lesion in tail of pancreas. |
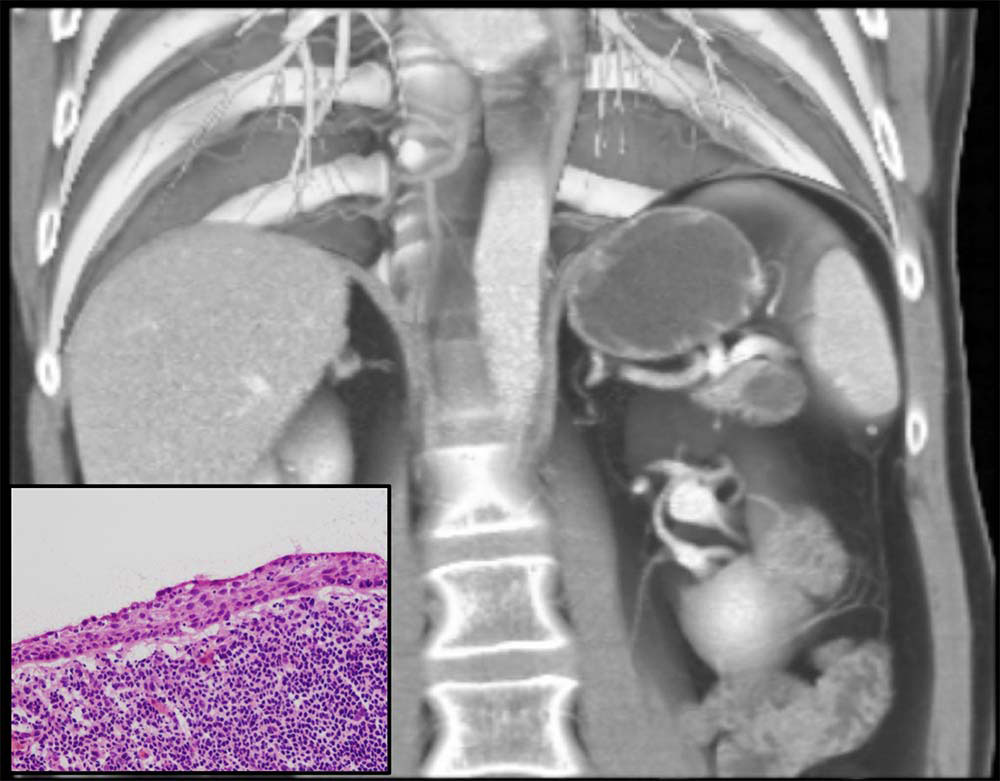 FNA of lesion demonstrated few epithelial cells with focal atypia in background of acellular debris, macrophages, and lymphocytes, consistent with cyst contents. 3D Coronal contrast-enhanced CT demonstrates cystic lesion in tail of pancreas in close proximity to splenic vasculature |
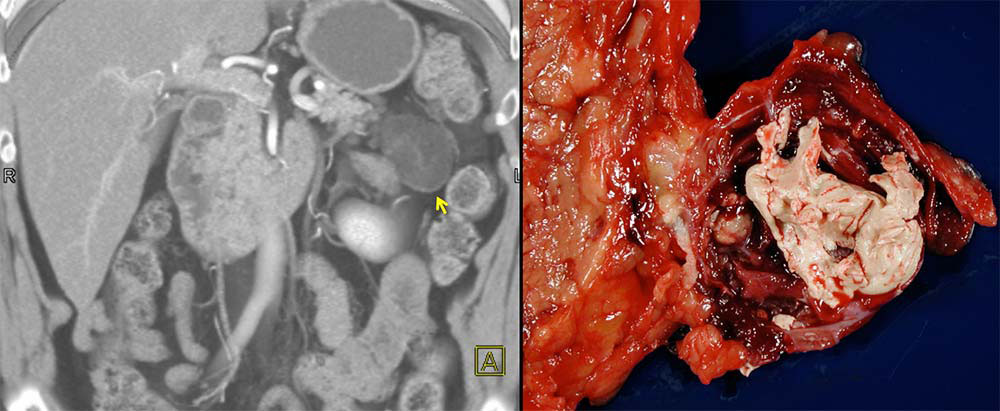 Case 7: 73 yo M with incidentally discovered pancreatic cyst. 3D CT demonstrates cystic mass with thin septations near tail of pancreas The lesion was resected (above: gross specimen) and found to be a lymphoepithelial cyst. |
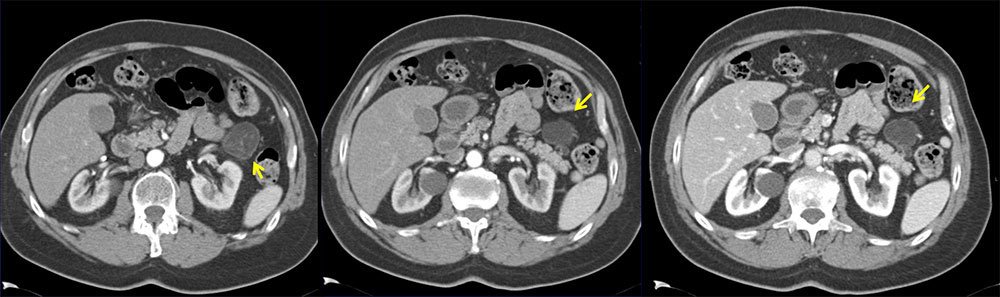 Left: Axial contrast-enhanced arterial phase CT demonstrates 4 cm cystic lesion near tail of pancreas. Thin septations are visible. Right: Axial contrast-enhanced venous phase CT demonstrates lesion |
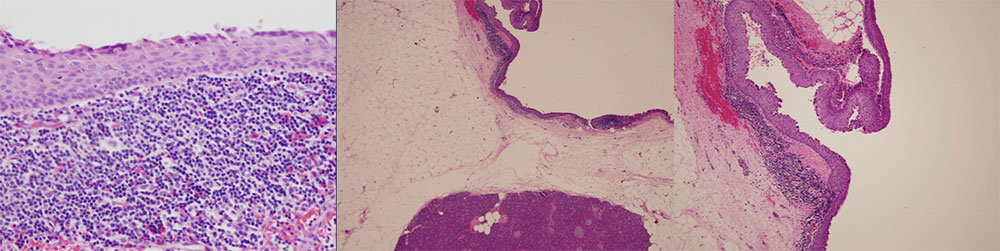 Pathology confirmed a cyst lined by squamous epithelium with lymphocytes and germinal centers in the cyst wall. Adjacent uninvolved pancreatic parenchyma shows no diagnostic findings. |
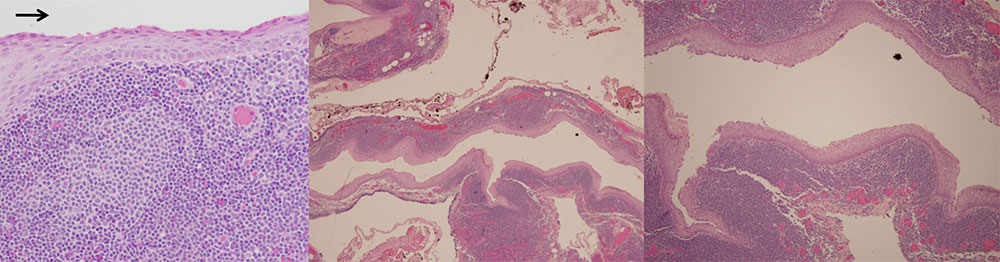 Case 8: 56 yo M with incidentally found pancreatic cyst. CT demonstrated 5.5 cm x 4.0 xm pancreatic cyst near tail of pancreas. He underwent distal pancreatectomy. Pathology demonstrates a cyst (luminal side indicated by arrow) lined by lymphoid tissue with overlying superficial squamous epithelium. |
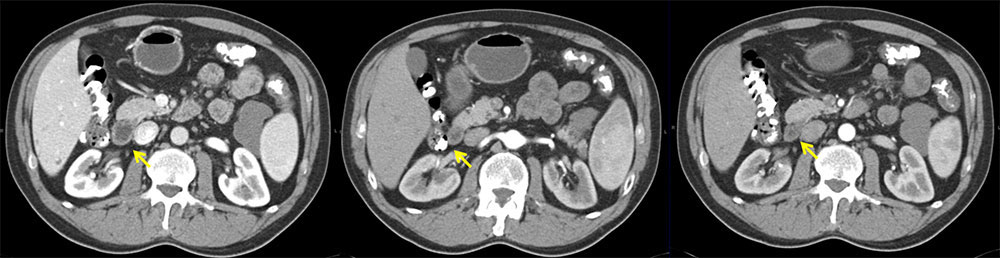 Right: Axial contrast-enhanced arterial phase CT demonstrates cystic lesion arising from tail of pancreas, abutting spleen and left kidney. Left: Axial contrast-enhanced venous phase CT demonstrates pancreatic cyst. |
Prognosis
|
Pearls
|
Conclusions
|
References
Karen M. Horton, MD Ralph H. Hruban, MD Barish H. Edil, MD Christopher L. Wolfgang, MD Richard D. Schulick, MD and Elliot K. Fishman, MD |
