Taming the Broncho: An Imaging Guide to Acute Bronchial Disorders
Taming the Broncho: An Imaging Guide to Acute Bronchial Disorders Elliot K. Fishman M.D. Johns Hopkins Hospital |
Teaching Points
|
Differential Dx: Endobronchial Lesions Benign
|
Aspiration Pneumonia 38 yo F with history of respiratory failure status post tracheostomy presenting with tachycardia and dyspnea. Large amount of debris is seen in the bronchus intermedius (arrows) with distal consolidations in the right middle and lower lobes.
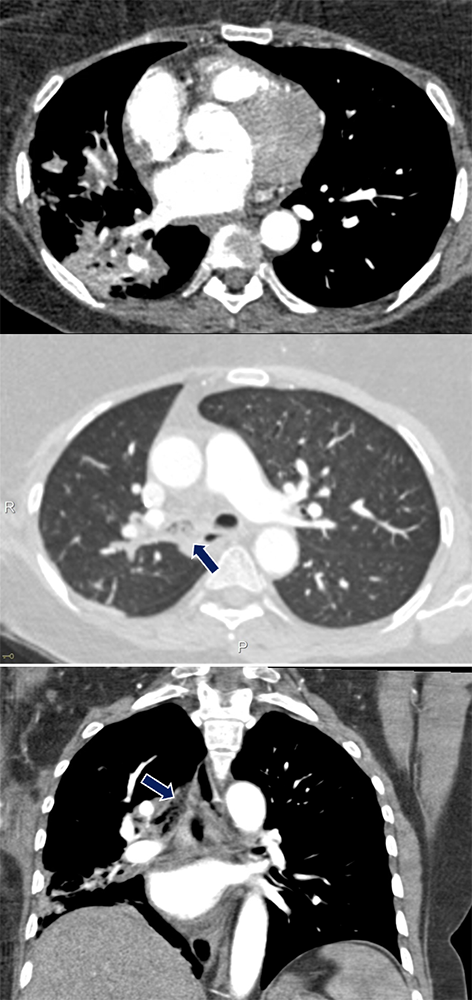 |
Foreign Body 58 yo F with recent history of pneumonia presenting with sudden onset of dyspnea. An ovoid endobronchial object is seen within the right lower lobe bronchus (arrows). Subsequent bronchoscopy was performed with extraction of an aspirated nut.
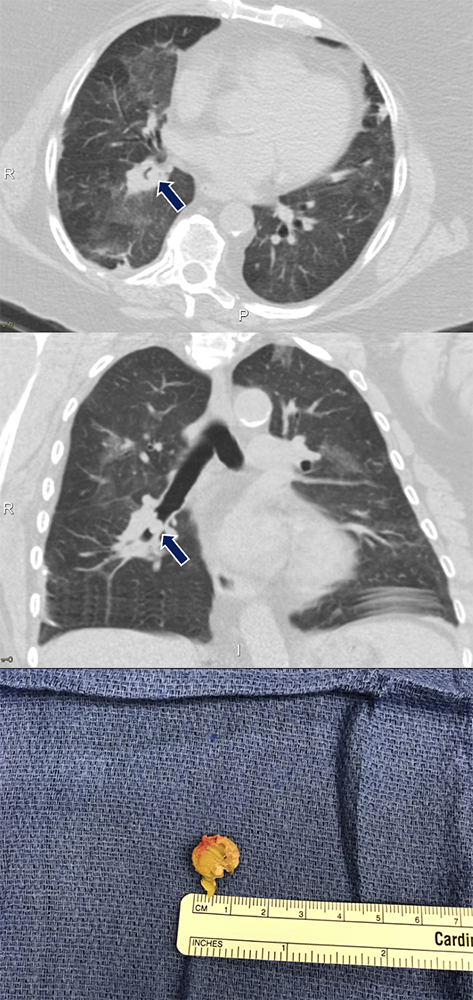 |
Foreign Body Top:76 yo M with aspirated food particle in the right lower lobe bronchus (arrows), retrieved by bronchoscopy Bottom:9 yo M with cough and chest pain after aspirating a coil spring from a pen. A metallic foreign body (arrows) is lodged within the left mainstem bronchus with partial collapse of the left lung. 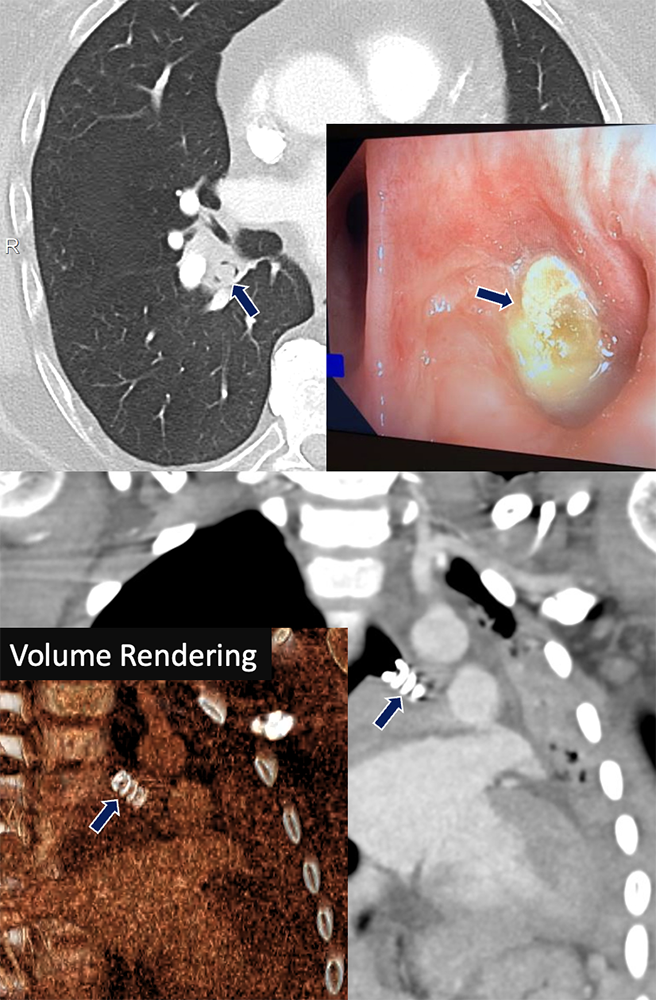 |
Mucous Plug Left:72 yo F with large mucous plugging of the entire left-sided airways (arrows) with associated complete left lung collapse. Right:64 yo M with metastatic urothelial cell carcinoma. A small mucous plug was found within a subsegmental bronchus
 |
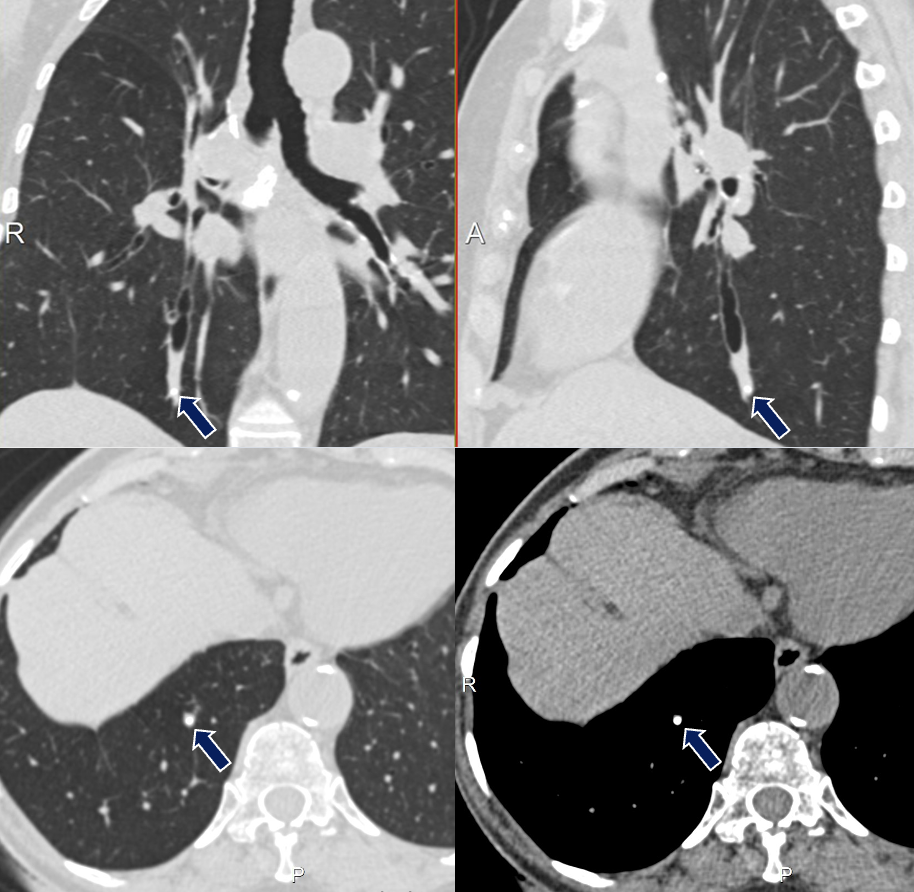
Broncholith 78 yo F with history of lung cancer presenting with left-sided chest pain. A calcified density compatible with broncholith (arrows) is demonstrated in a distal bronchus with proximal mucous plugging and bronchiectasis. Note the ipsilateral calcified nodes.
 |
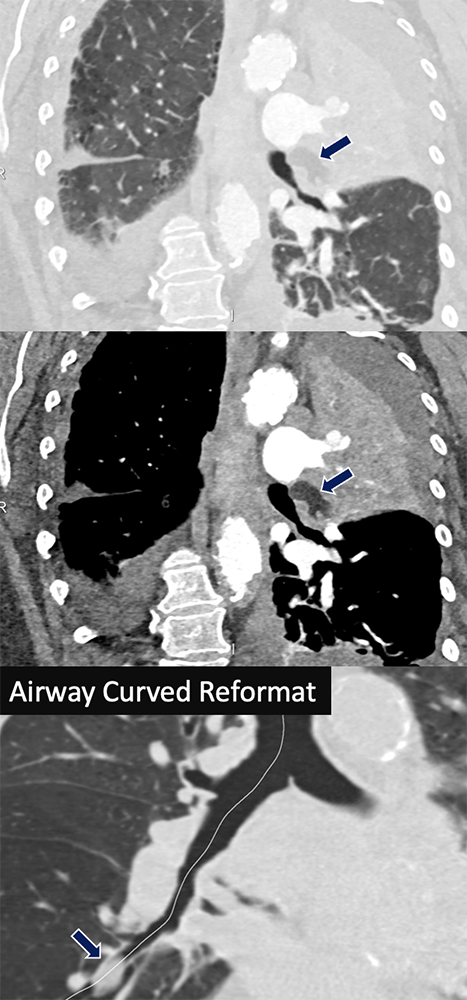
Pulmonary Hamartoma Top 2: 74 yo F with acute shortness of breath and weakness. A fat-containing lesion (arrows) occludes the left upper lobe bronchus causing complete lobar collapse. Bottom: Companion case of endobronchial hamartoma in the right lower lobe.
 |
Pulmonary Hamartoma 65 yo F with history of pneumonia causing pain and dyspnea, improved with antibiotics. A small nodular soft tissue lesion (arrows)is seen within the lobar bronchi (left and center). An endobronchial polypoid lesion was found on bronchoscopy (right) at the anterior wall entrance of the right lower lobe bronchus and subsequently resected at its stalk. 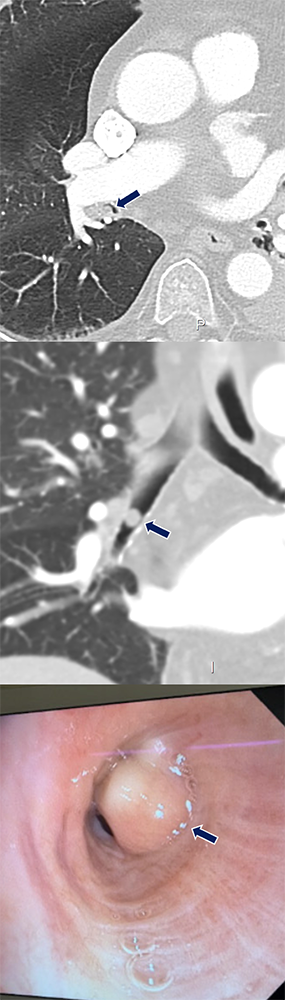 |
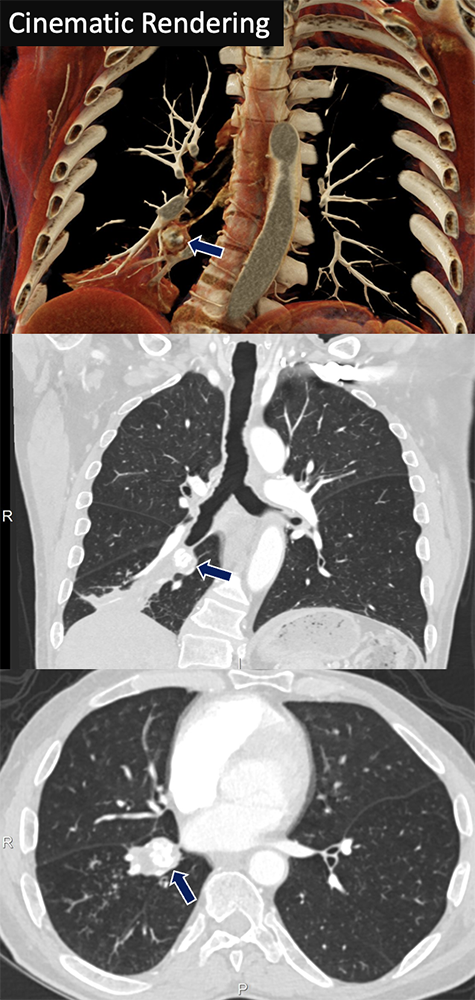
Carcinoid 67 yo M with history of COPD presenting with right lower lobe pneumonia. A coarsely calcified mass (arrows) expands and occludes the right lower lobe bronchus with post-obstructive atelectasis.
 |
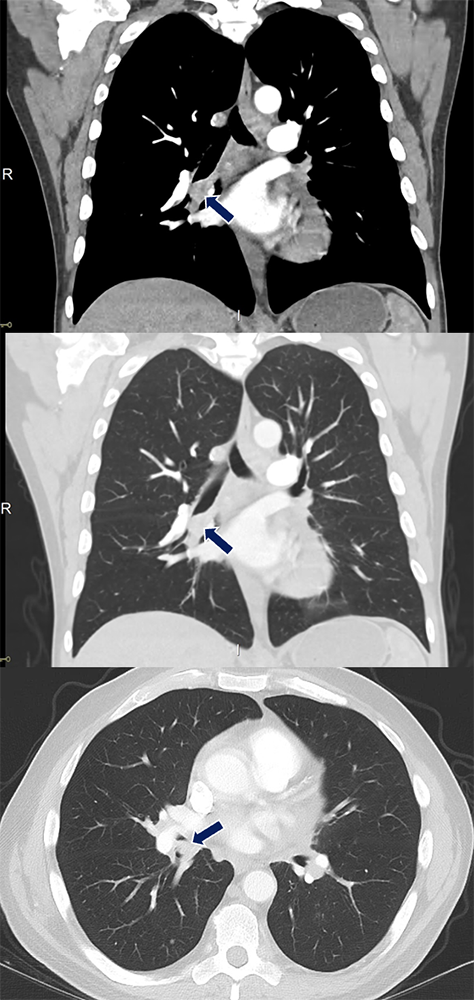
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma 59 yo F with history of COPD who presented with chest pain and dyspnea. An endobronchial lesion with small calcifications (arrows) is seen in the bronchus intermedius along with collapse of the right lower and middle lobes.
 |
Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma 52 yo F with no PMH who presented with cough, fevers, chills, generalized aches. An endobronchial pedunculated tumor (arrows) occupies the right mainstem bronchus and partially obstructs the lumens of the right upper lobe and bronchus intermedius.
 |
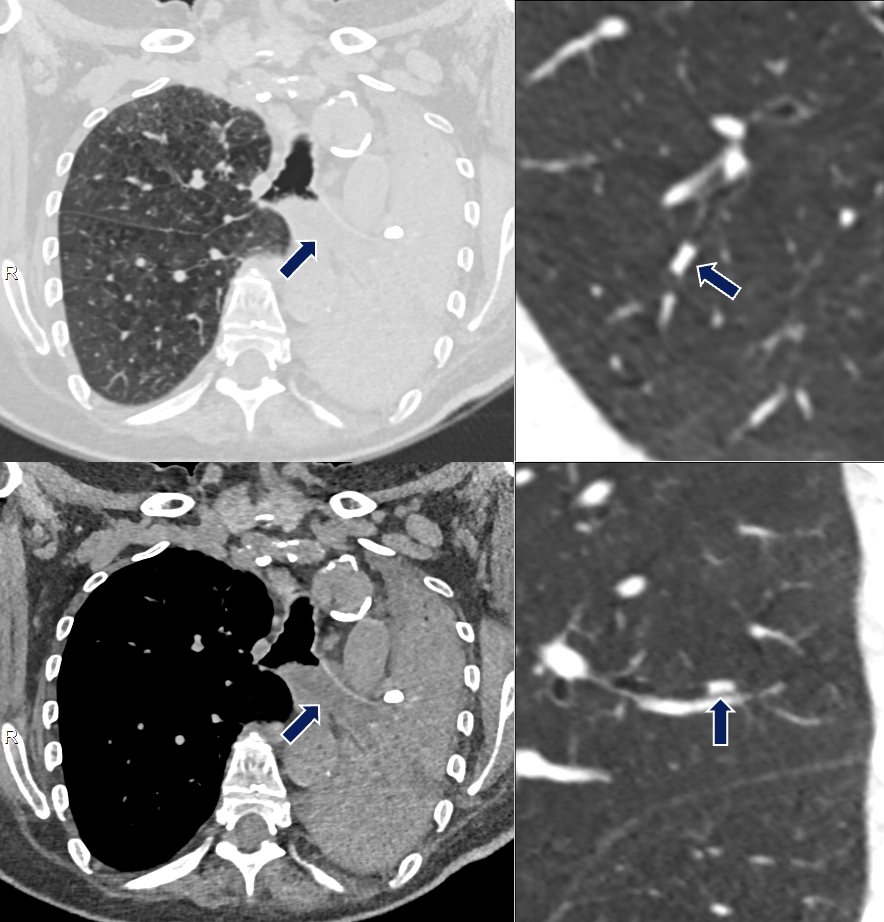
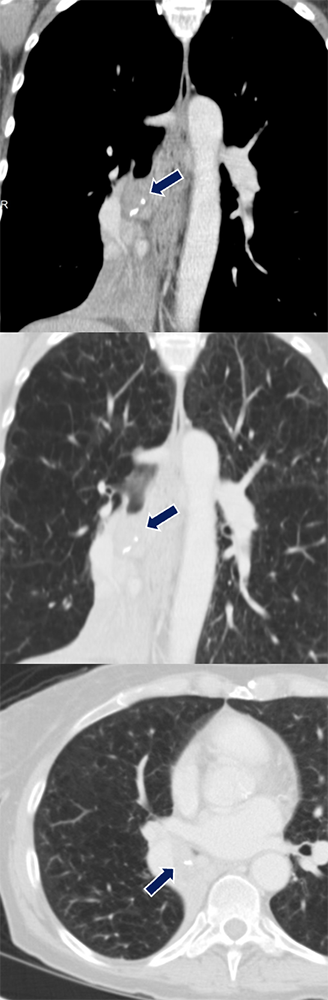
Metastasis from Renal Cell Carcinoma 64 yo M with history of metastatic clear cell carcinoma status post nephrectomy on immunotherapy and chemotherapy. A soft tissue nodule (arrows) developed in the right lower lobe airway later confirmed to be a metastasis.
 |
Differential Dx: Bronchial Stenosis/Wall Thickening
|
Bronchial Stenosis 74 yo F status post left lung transplant with decline in PFTs. CT and pre-treatment bronchoscopy images (left) showed anastomotic narrowing at the left mainstem bronchus, worse on expiration. A cryoprobe was used to debride exophytic granulation tissue in the airway followed by balloon dilation of the bronchus. The left mainstem bronchus regained patency on post-treatment images (right).
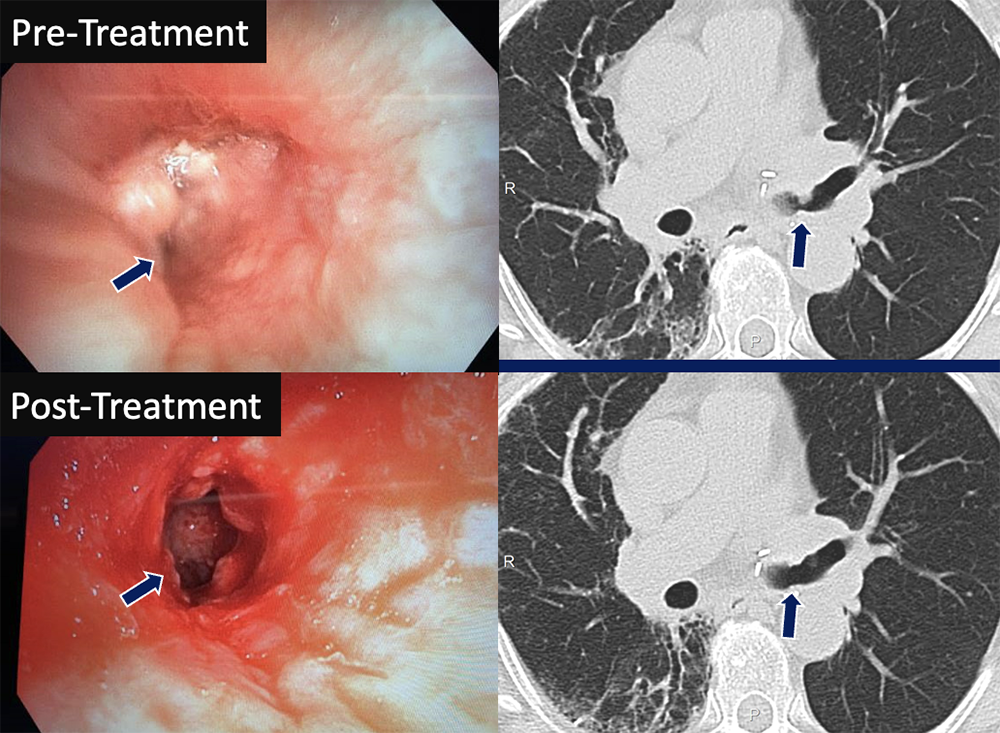 |
Bronchial Asthma 54 yo M presenting with acute cough, wheezing, and fatigue. Segmental and subsegmental bronchi (arrows), particularly in the lower lobes, are diffusely thickened and narrowed.
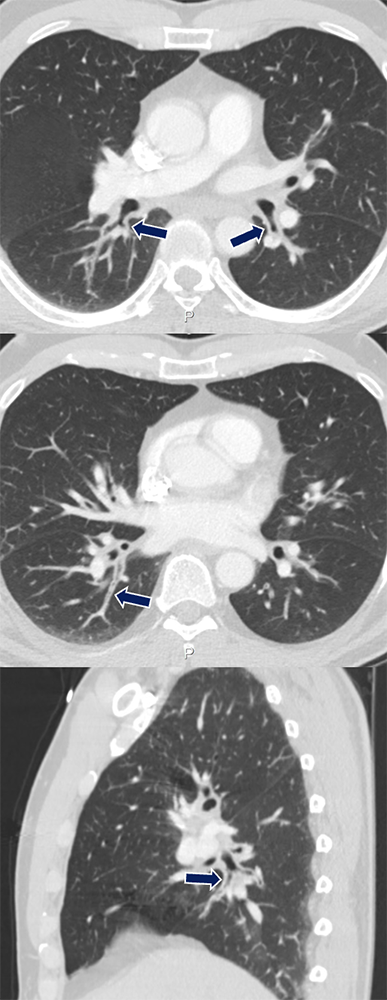 |
Relapsing Polychondritis 35 yo F presenting with hemoptysis and chest pain. The trachea and bilateral mainstem bronchi show diffuse and smooth wall thickening (arrows) with sparing of the posterior membrane and associated luminal narrowing.
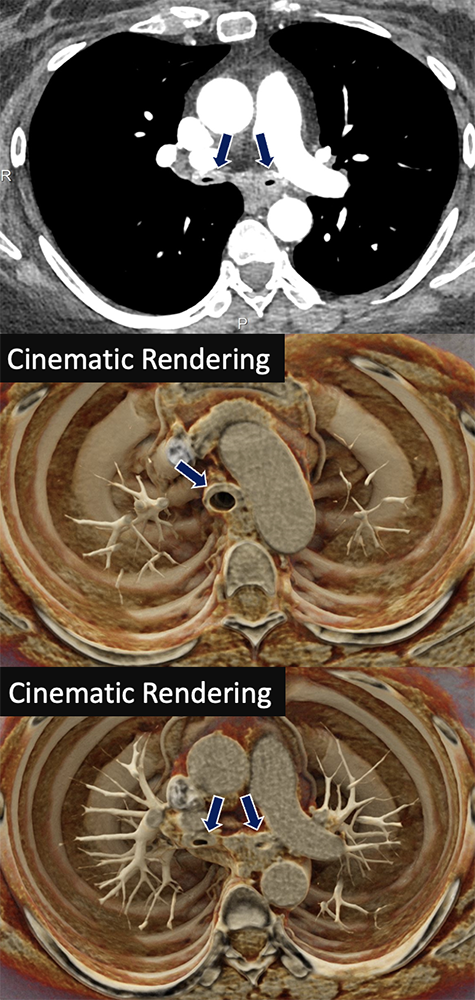 |
Tracheobronchial Amyloidosis 62 yo F with history of amyloidosis presenting with dyspnea. Images show marked circumferential soft tissue thickening (arrows) of the walls of the distal trachea extending into the right mainstem bronchus with associated narrowing and partially collapsed left lung.
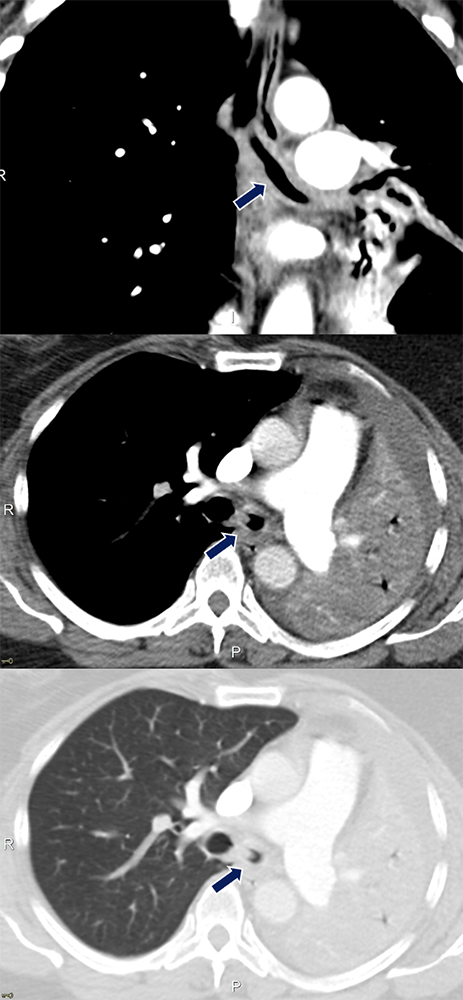 |
Sarcoidosis 60 yo M with history of multisystem sarcoidosis presents with chronic cough and baseline dyspnea. Multifocal bronchial wall thickening and stenosis (arrows)was noted in the left lower lobe, lingula, and right middle lobe bronchus with right middle lobe collapse.
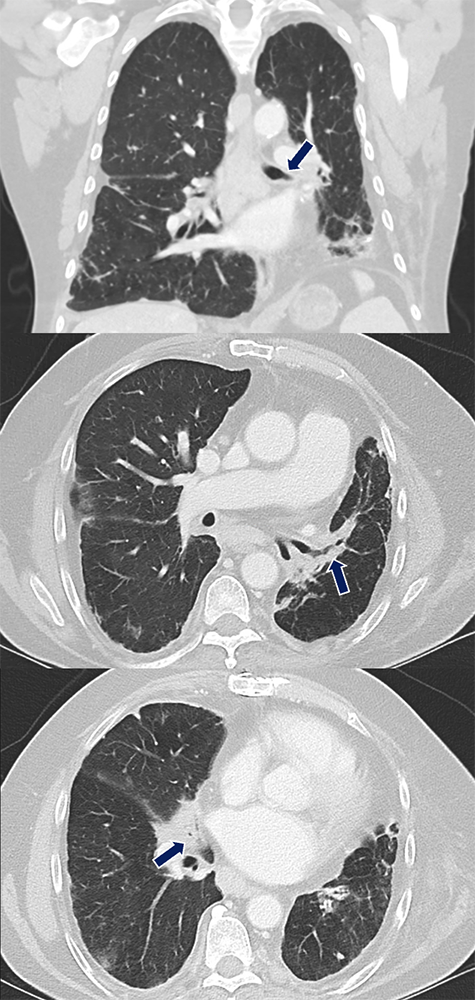 |
Tuberculosis 43 yo F with history of treated tuberculosis. The left lung was completely collapsed with fibrotic/atretic appearance of the left mainstem bronchus (arrows). Note the associated volume loss and mediastinal shift.
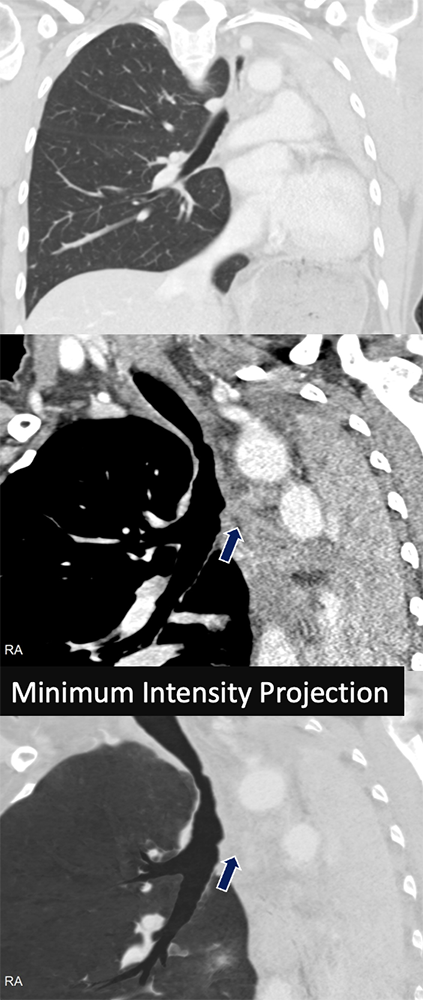 |
Differential Dx: Bronchiectasis Focal
|
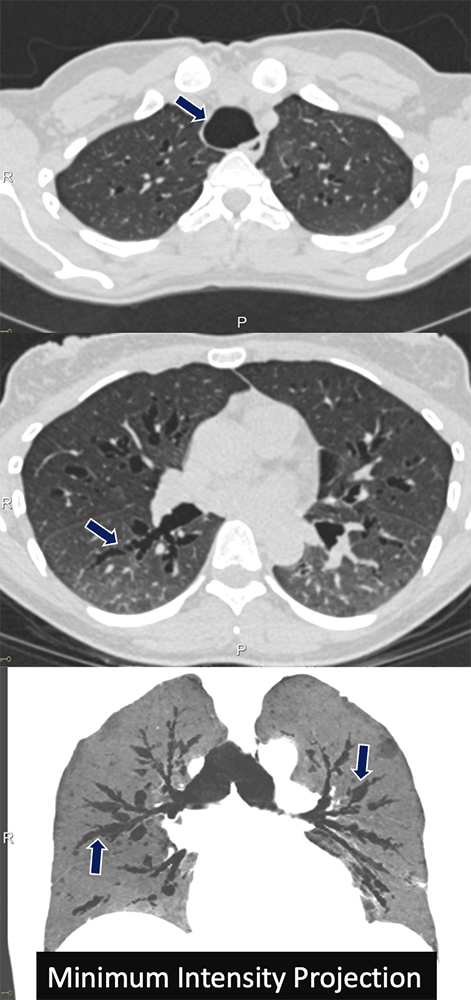
Bronchial Atresia 20 yo F presents with acute chest pain. A low density tubular lesion occludes the right upper lobe segmental bronchus with marked distal air-trapping (arrows).
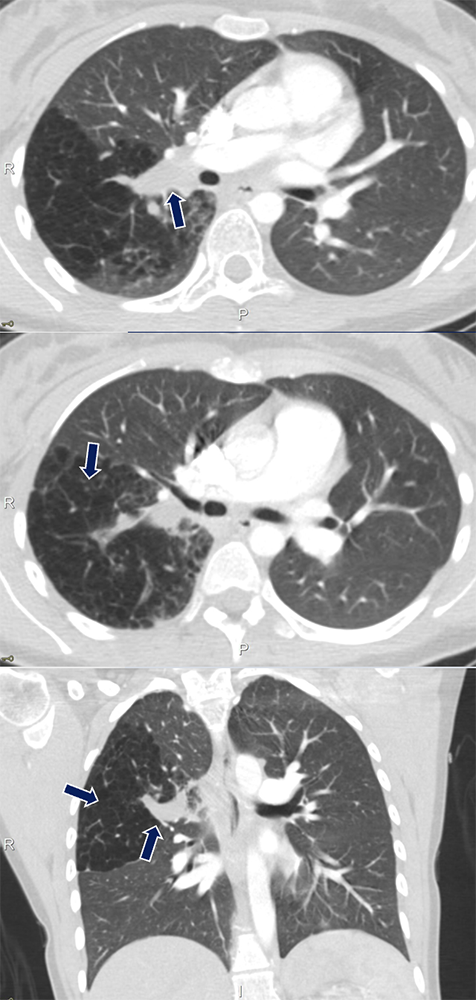 |
Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Infection 67 yo F with idiopathic bronchiectasis presenting with worsening productive cough, fevers, and chills. Mucoceles seen as dilated tubular structures that fills the airway spaces with mucus (arrows), worse at the lower lobes. Abnormal bronchial wall thickening and centrilobular tree-in-bud nodularity representing involvement of the bronchioles and alveolar spaces.
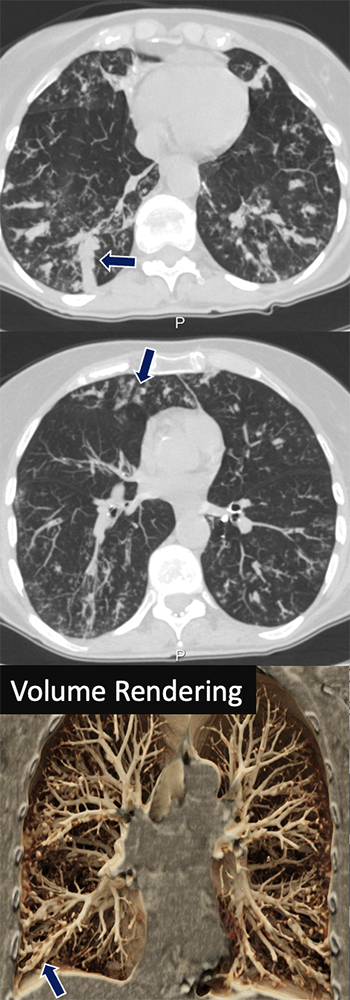 |
Pseudomonas Infection 63 yo F with recurrent pseudomonas infections who presents with worsening productive cough. Extensive bronchiectasis, bronchial wall thickening, tubular mucous plugging, and centrilobular tree-in-bud nodularity was found (arrows), better seen on MIP.
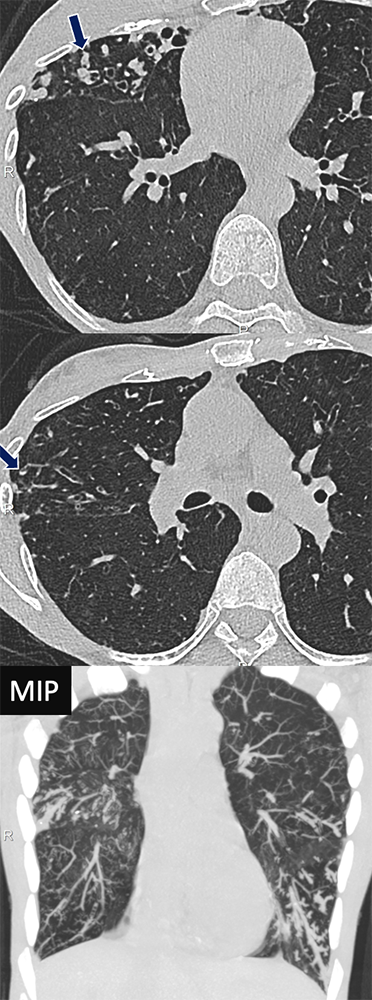 |
Cystic Fibrosis 25 yo F with cystic fibrosis presenting with chest pain. CT showing cystic and varicose atelectasis and areas of bronchial wall thickening and mucous plugging (arrows).
Lopes-Pacheco M. CFTR Modulators: The Changing Face of Cystic Fibrosis in the Era of Precision Medicine. Front Pharmacol. 2020 Feb 21;10:1662. 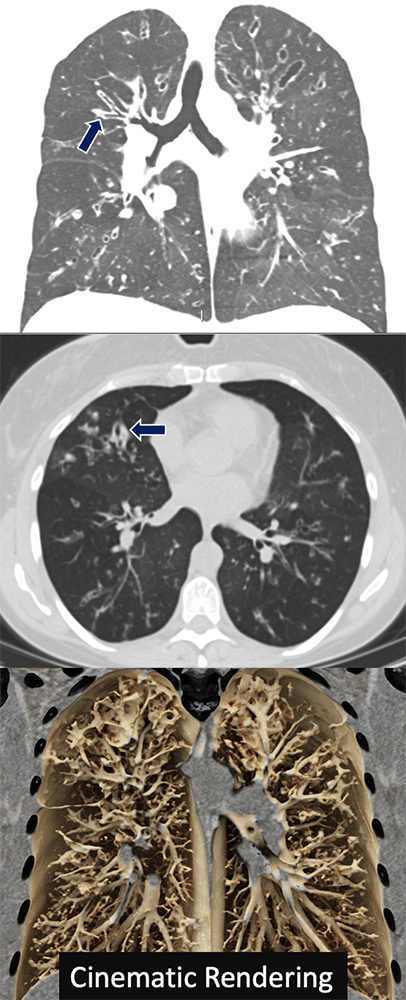 |
Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis 54 yo F with presenting with productive cough, prior history of dyspnea and intermittent chest tightness. CT demonstrated multiple tubular mucous plugging seen as Y-shaped finger-in-glove opacities involving the central bronchi (arrows).
Franquet T, Müller NL, Giménez A, Guembe P, de La Torre J, Bagué S. Spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis: histologic, clinical, and radiologic findings. Radiographics. 2001 Jul-Aug;21(4):825-37. 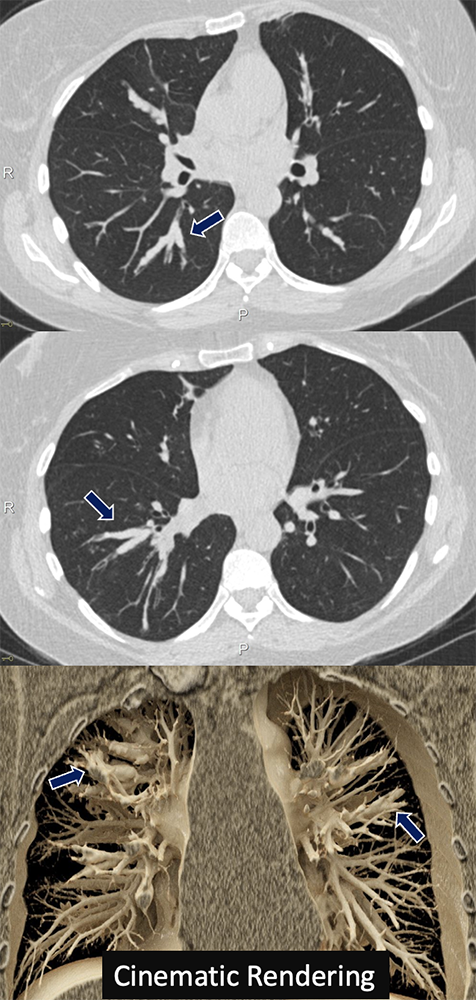 |
Graft Versus Host Disease 66 yo F with history of AML s/p bone marrow transplant who presented with hypoxia and cough. CT scan showed significant bronchiectasis and bronchial wall thickening most severe in the left lower lobe (arrows).
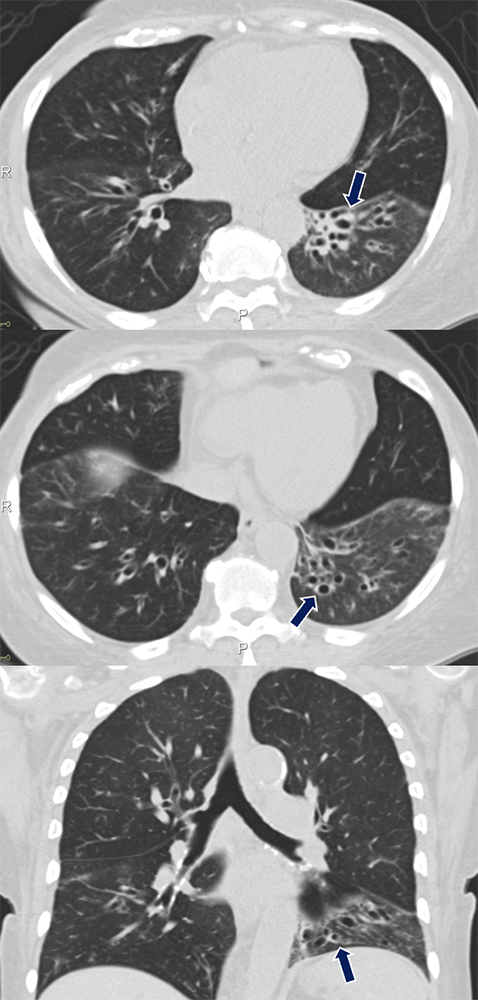 |
Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia 34 yo M with history of primary ciliary dyskinesia (Kartagener's syndrome) who presents with productive cough and fever. Marked bronchial wall thickening and bronchiectasis are seen in the lower lungs (arrows). Note the associated cardiac situs inversus.
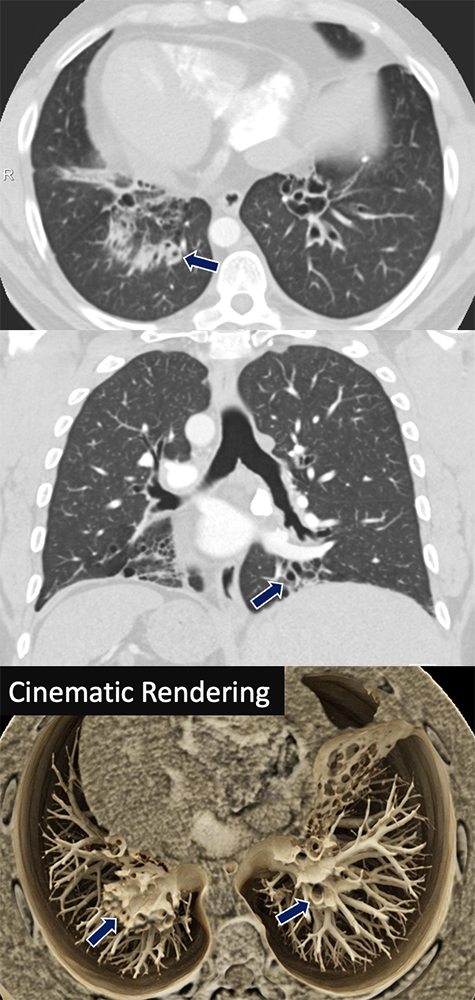 |
Tracheobronchomegaly 36 yo F with history of recurrent pneumonia who presented with confusion and shortness of breath. Imaging shows diffuse dilatation of the trachea and proximal bronchi with segments of varicose bronchiectasis (arrows).
 |
Williams-Campbell Syndrome 40 yo M previously diagnosed with asthma presenting with cough, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Branching dilated airways with thickened walls characteristic of bronchiectasis (arrows), involving the mid-order bronchi.
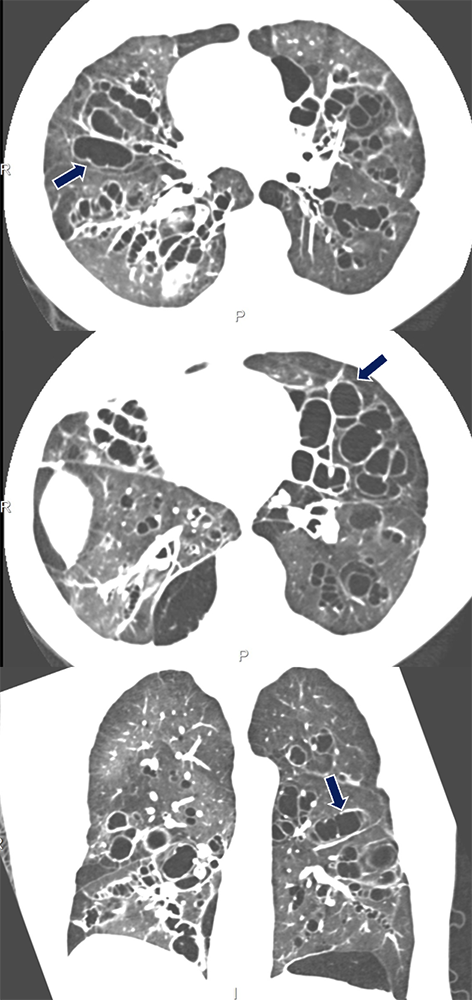 |
Bronchomalacia 82 yo F presenting with persistent cough. Inspiratory CT show patent and normal-sized bilateral mainstem bronchi. Dynamic CT during expiration show dynamic collapse of the bilateral mainstem bronchi (arrows) with associated air trapping.
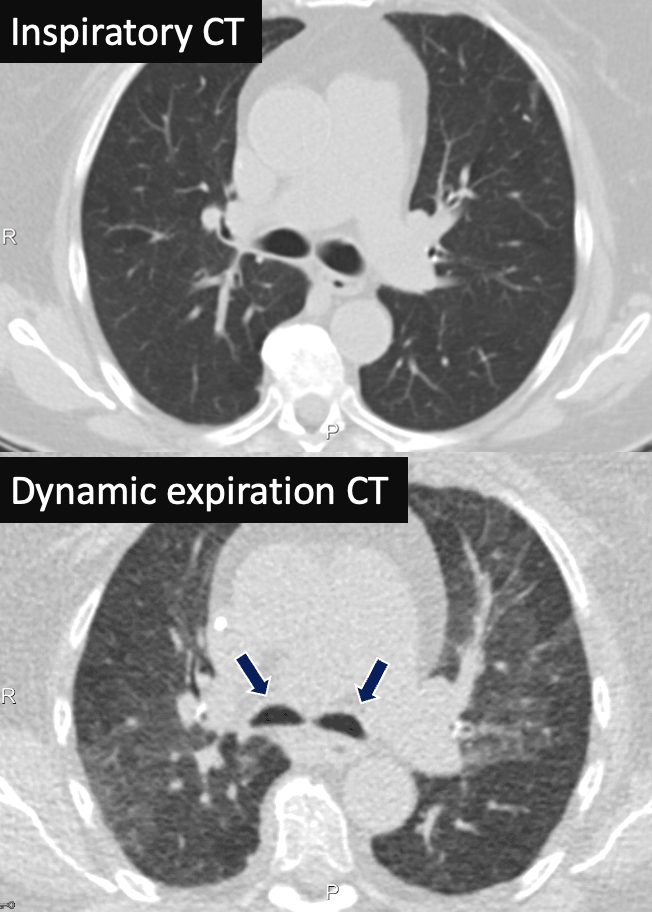 |
Bronchomalacia 76 yo M with cough and shortness of breath, intermittent for several years. Inspiratory chest CT demonstrated patent bilateral mainstem bronchi. On bronchoscopy, the airways were inspected and notable for dynamic airway collapse. Expiratory images show 80% dynamic airway obstruction. 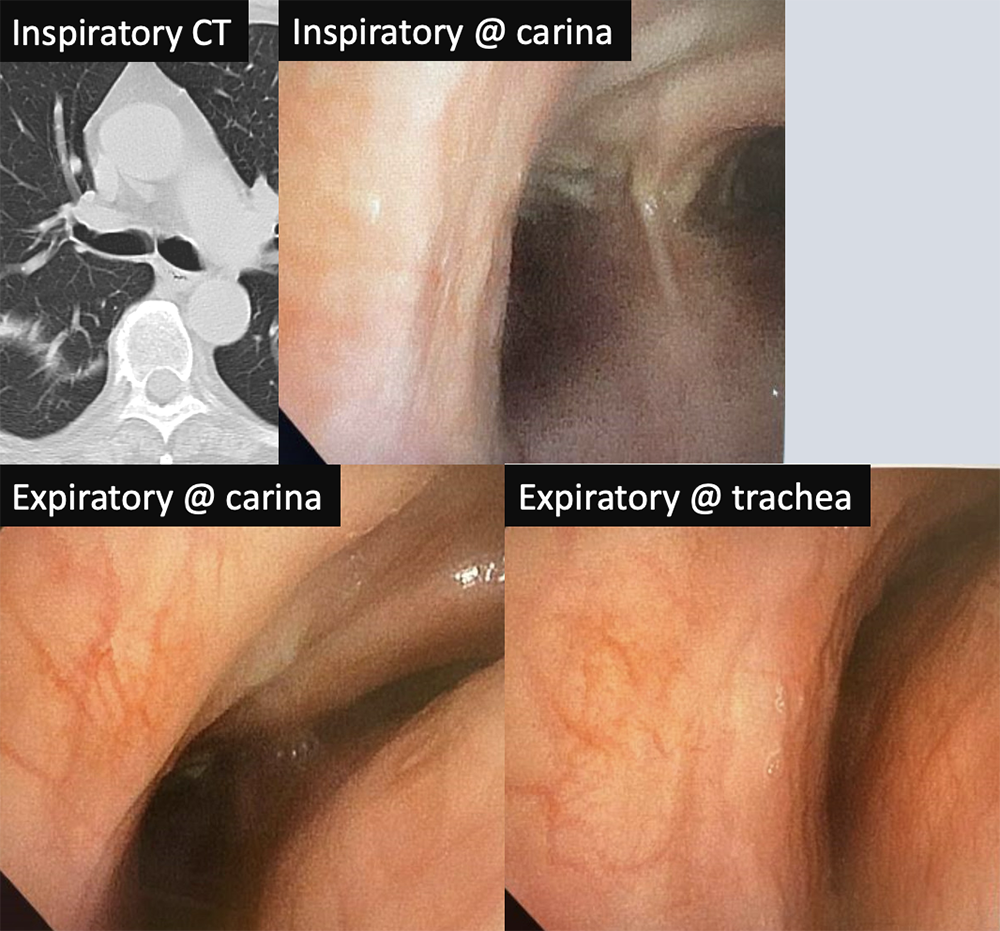 |
Conclusion
|
