Cardiothoracic Manifestations of HIV/AIDS: An Anatomic Approach
Cardiothoracic Manifestations of HIV/AIDS: An Anatomic Approach Hannah Recht, MD The Russel H. Morgan Department of Radiology and Radiological Science The Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions Baltimore, MD, USA |
Disclosures
|
Teaching Points
|
Teaching Points
|
An anatomic approach to the broad spectrum of HIV/AIDS related cardiothoracic pathology: Cardiac
|
Cardiac Involvement in HIV 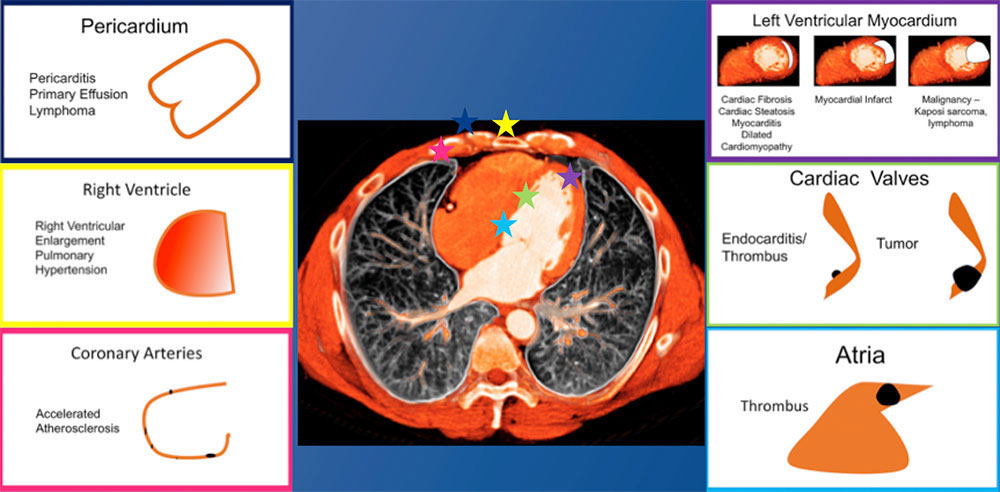 |
Cardiac: Myocardium/Cardiac Valves
|
57 year old male with HIV and complex cardiac history including CAD s/p CABG The short axis T1 post contrast late delayed gadolinium enhanced image from a cardiac MRI demonstrates cardiac fibrosis of the mid lateral left ventricular wall, as well as late delayed enhancement of the right ventricular attachment sites. The other two images are derived from pre-contrast T1 mapping for assessment of fibrosis. The lighter orange of the lateral ventricular wall is reflective of myocardial fibrosis. The T1 map demonstrates that the extent of cardiac fibrosis in the lateral wall is greater than would be predicted based on the delayed enhancement images alone. 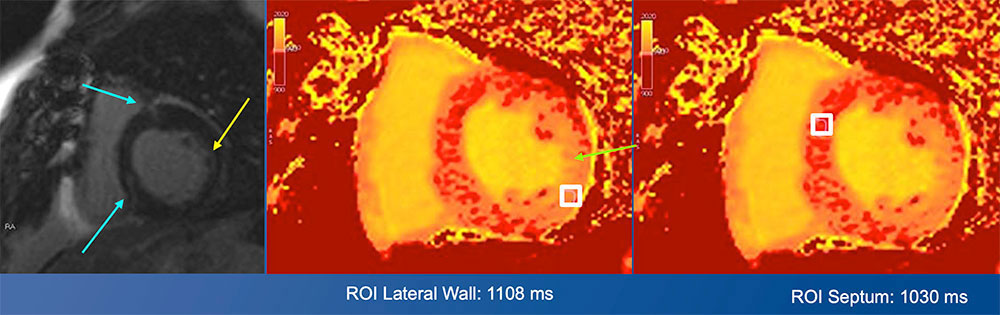 |
Coronary artery disease and ischemic cardiomyopathy
|
49 year old female with poorly controlled HIV/AIDS with chest and epigastric pain The axial CT images at the level of the heart demonstrate masses infiltrating both the right and the left atria. The axial and coronal CT images at the level of the abdomen demonstrate a large, part cystic and part solid mass within the pancreas. Biopsy of this pancreatic mass was positive for Burkitt lymphoma. 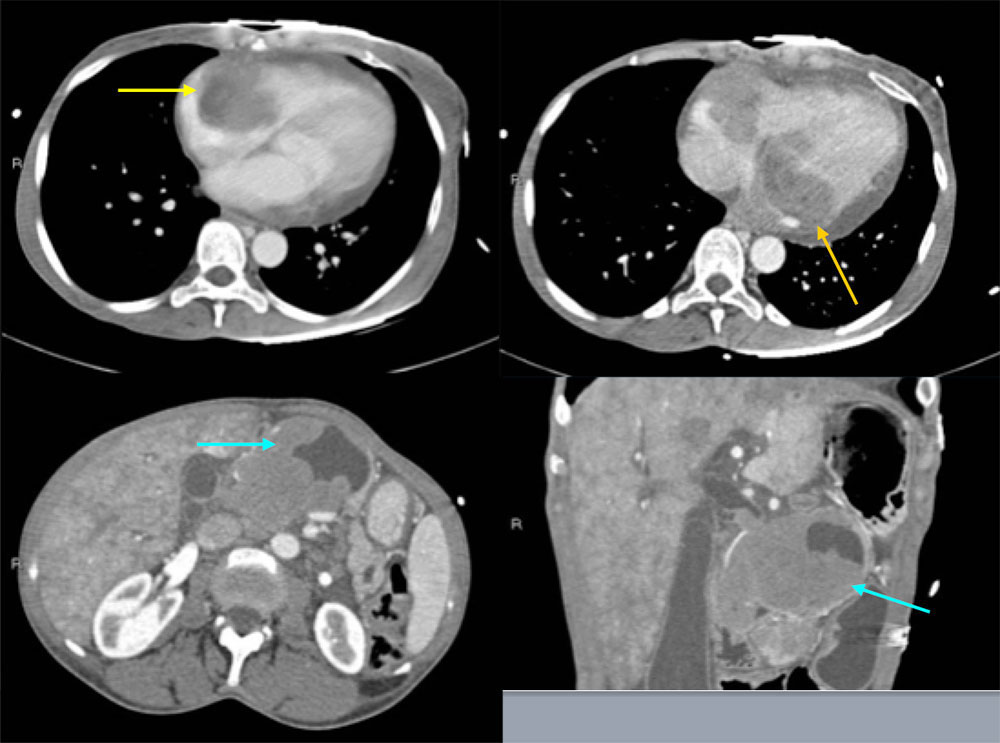 |
Burkitt Lymphoma Cardiac MRI demonstrates a large soft tissue mass in the right atrium extending into the free wall and apex of the right ventricle and into the pericardial space. There is also a moderate pericardial effusion. The post contrast axial image demonstrates enhancement of the infiltrative mass. The patient passed away eight days after this MRI from arrhythmia (complete heart block and ventricular tachycardia) and hypotension. 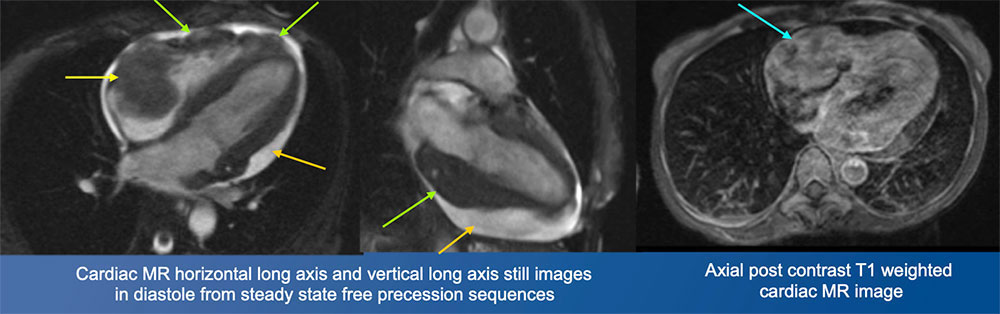 |
Cardiac Lymphoma
|
Cardiac: Vasculature
|
39 year old woman with HIV with cough Axial and sagittal CT images at the level of the pulmonary artery demonstrate prominent enlargement of the main pulmonary artery, measuring up to 4.4 cm. The patient had a long history of pulmonary arterial hypertension, for which she was taking ambrisentan (an endothelin receptor antagonist). Other CT findings in pulmonary arterial hypertension include pruning of the peripheral pulmonary arteries, and cardiomegaly with enlargement of the right heart. 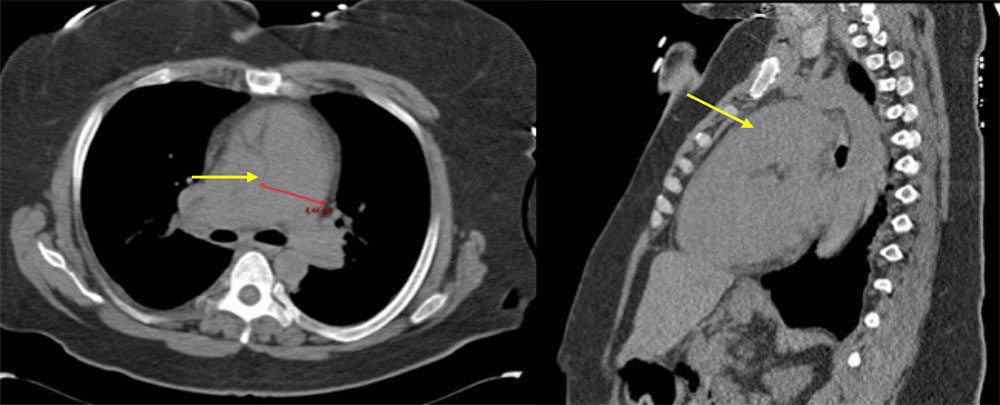 |
Pulmonary Hypertension
Jarrett H, Barnett C. HIV-associated pulmonary hypertension. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2017 Nov;12(6):566-571. |
An anatomic approach to the broad spectrum of HIV/AIDS related cardiothoracic pathology: Cardiac
|
Thoracic: Mediastinum
|
27 year old male with perinatally acquired HIV 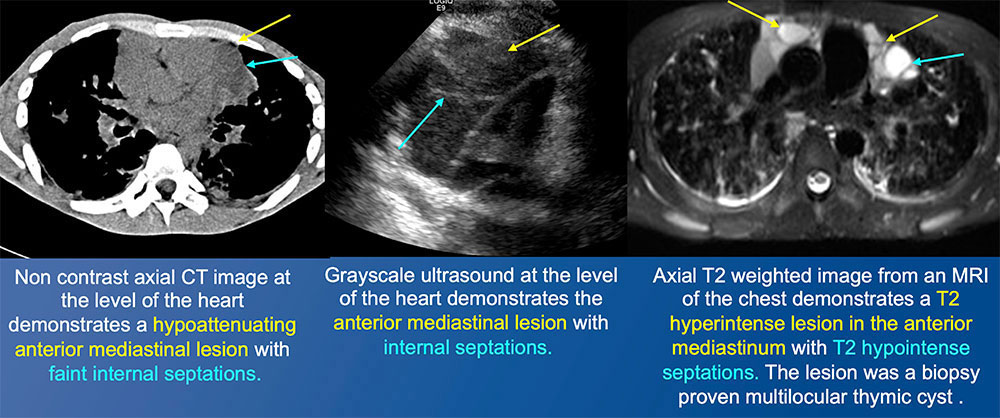 |
Multilocular thymic cyst
|
Thoracic: Lungs/Airways
|
41 year old female with history of HIV, HCV, tricuspid endocarditis, pulmonary hypertension, MAI lung infection on treatment Axial CT at the level of the aortic arch and coronal CT images demonstrate a large left upper lobe cavitary lesion, with internal soft tissue density. The axial CT through the lower lungs demonstrates cystic changes in the right middle lobe, which was sequela of the patient’s prior MAI lung infection. There is also left lower lobe nodularity. Sputum culture grew Aspergillus niger. 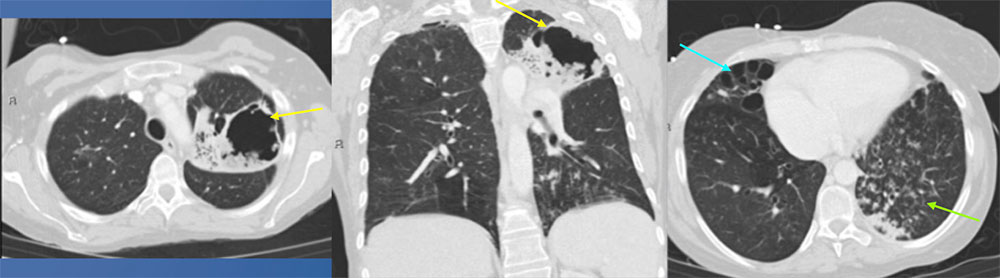 |
Pulmonary Aspergillosis
Miller WT Jr, et al. Pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with AIDS. Clinical and radiographic correlations. Chest. 1994 Jan;105(1):37-44 |
49 year old male with HIV Initial AP chest radiograph demonstrates subtle right upper lobe cavitary lesions. Multiple right upper lobe cavitary lesions are better identified on coronal and axial images from a noncontrast CT of the chest. Bilateral nodularity was also seen. Initially, findings raised suspicion for Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection with endobronchial spread. Culture from bronchoscopy revealed Mycobacterium avium intracellulare complex. 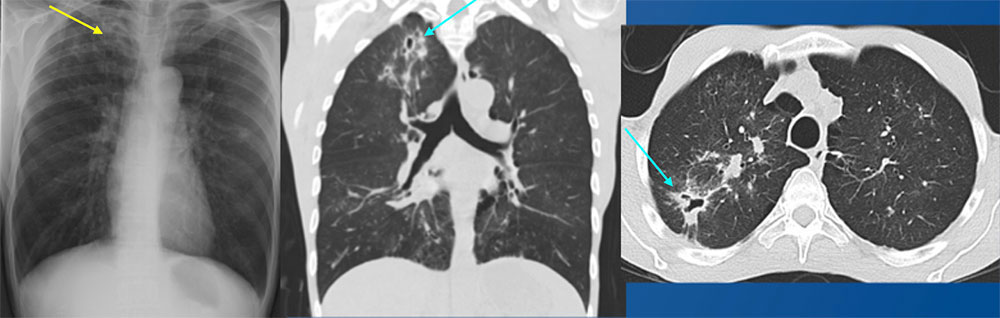 |
Nontuberculous mycobacterial infection
|
38 year old male with recently diagnosed and untreated HIV with fever and cough The axial CT images of the upper lung fields, and the coronal CT image demonstrate diffuse, upper lobe predominant, bilateral, bronchovascular ground glass consolidations, with subpleural sparing. The second axial CT image demonstrates a consolidation with cavitation/cystic changes in the superior segment of the right lower lobe. Culture from bronchoscopy grew Pneumocystis jirovecii. 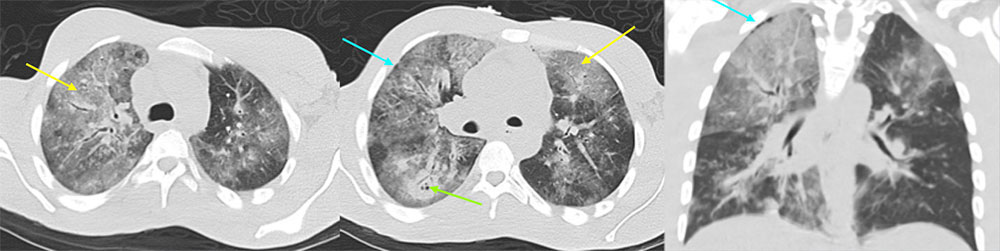 |
Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia
|
36 year old man with well controlled HIV with right sided chest pain, left leg pain, weight loss and night sweats The PA chest radiograph demonstrates a left upper lobe cavitary lesion. An axial image from a noncontrast CT better demonstrates the dominant left upper lobe cavitary lesion. There were additional smaller satellite cavitary lesions in the left upper lobe, as well as a mass-like consolidation in the left perihilar region, not seen on these images. An axial CT image in bone window from the same CT demonstrates a lytic lesion of the right lateral seventh rib, with an associated soft tissue component. 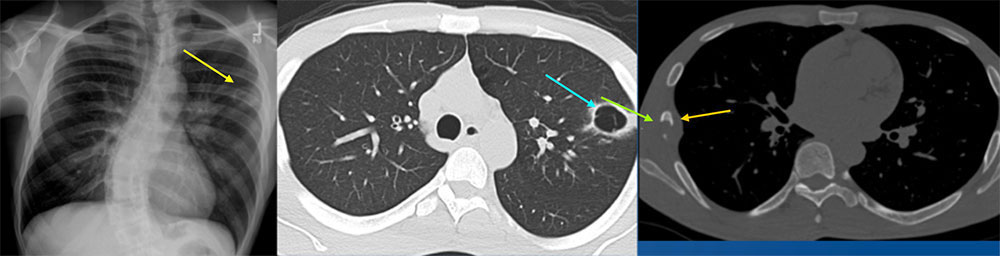 |
Follow up PET/CT six days later The axial fused PET/CT image of the lung demonstrates hypermetabolic cavitary masses in the left upper lobe with a hypermetabolic left hilar mass. The axial image of the upper abdomen shows bilateral hypermetabolic adrenal lesions. The coronal image demonstrates hypermetabolic lytic osseous metastases involving the lateral right seventh rib and left iliac bone. The coronal fused PET/CT image also demonstrates central necrosis of the right adrenal lesion. Pathology from left upper lobe resection revealed poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma with focal sarcomatoid features. The leading differential prior to biopsy was mycobacterial infection. 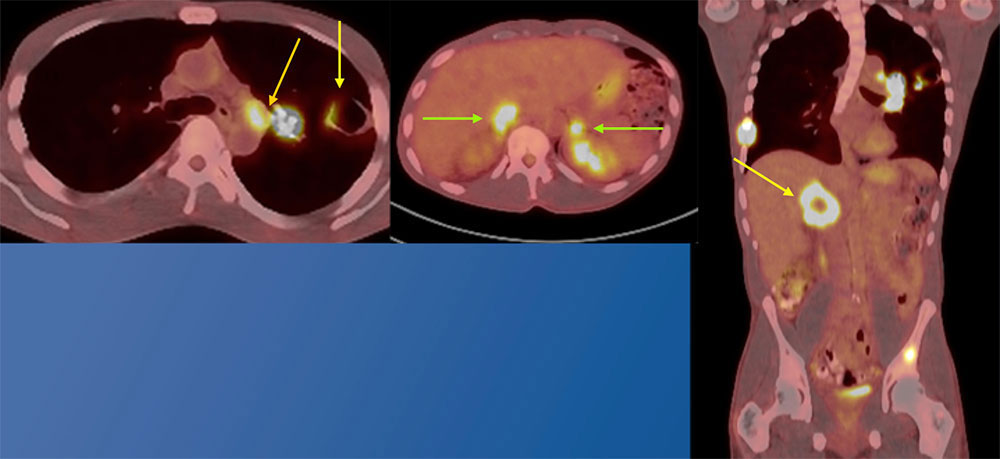 |
Squamous cell lung carcinoma
|
36 year old male with recently diagnosed HIV not on HAART The AP chest radiograph demonstrates multiple bilateral pulmonary opacities, one of which has a spiculated appearance in the right lower lobe. The contrast enhanced CT of the chest demonstrates multiple bilateral nodular opacities, with “flame shaped” appearance, classically seen in Kaposi sarcoma. The patient was diagnosed with Kaposi’s sarcoma of the lung and skin. At the time of diagnosis, the patient’s CD4 count was 6. 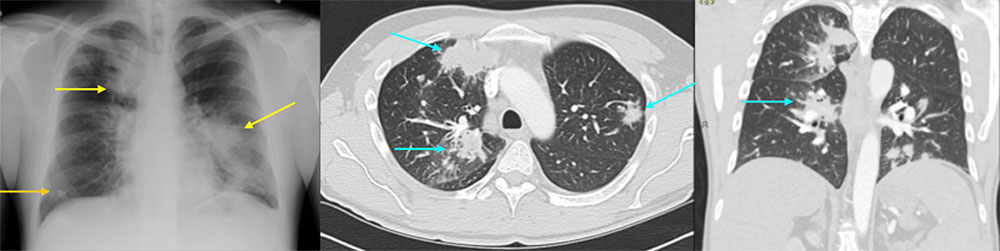 |
Same patient, five years later In addition to starting HAART therapy, the patient underwent 8 cycles of Doxil ® (doxorubicin Hcl liposome injection) chemotherapy. The patient had an excellent response to treatment. This surveillance CT five years after diagnosis demonstrates an irregular right upper lobe nodular opacity, which had been stable over multiple studies, without evidence of disease recurrence. 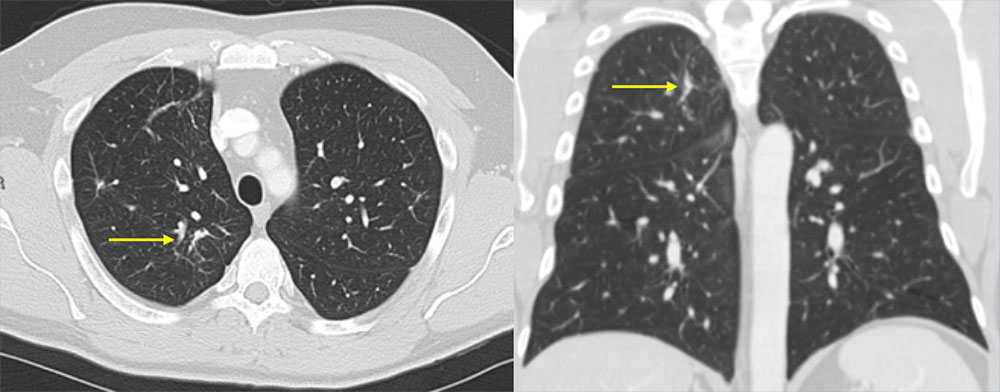 |
Kaposi Sarcoma
|
28 year old male with congenital HIV, dyspnea, and chest pain Axial and coronal CT images demonstrate bilateral ground glass opacities, as well as multiple thin walled cysts. The patient had a known history of lymphocytic interstitial pneumonitits. 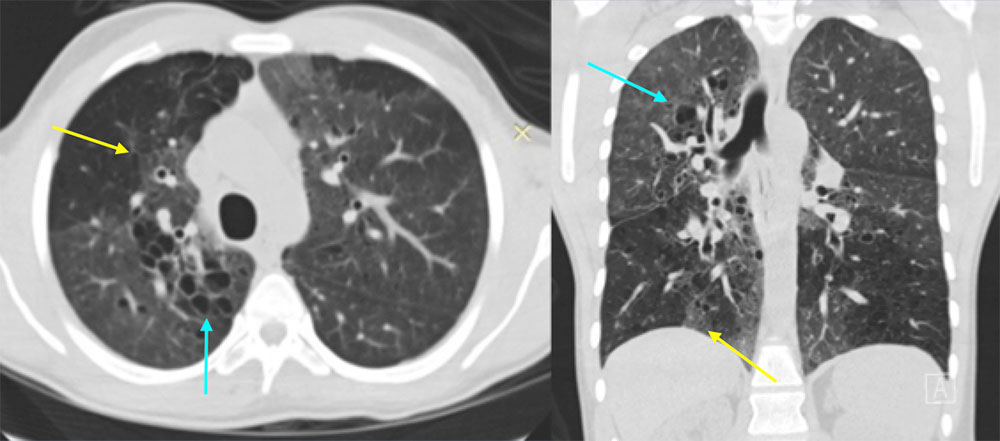 |
Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonitis (LIP)
|
27 year old female with history of HIV not on treatment, admitted for retinal necrosis from VZV infection The initial AP chest radiograph demonstrates lower lobe predominant bilateral reticulonodular interstitial opacities. Axial CT image of the lungs demonstrates bilateral, lower predominant nodular interstitial opacities, with lower lobe consolidations. The contrast enhanced axial CT image of the mediastinum demonstrates enlarged mediastinal and axillary lymph nodes. There were also enlarged hilar lymph nodes. Wedge resections of the left lower and upper lobes found EBV positive immunodeficiency-associated lymphoproliferative disorder. CD4 count was 93 at the time of diagnosis. Differential considerations included atypical infection as well as LIP. 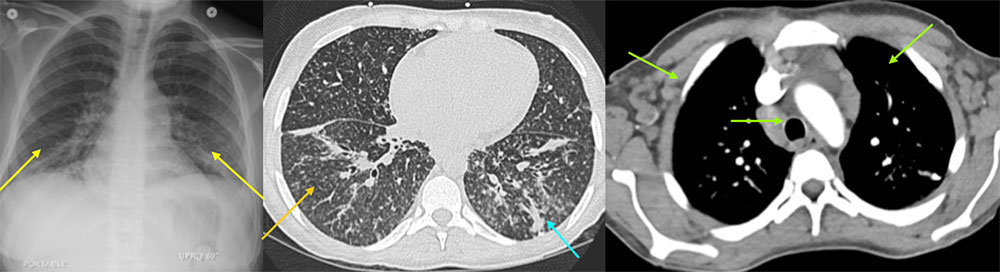 |
EBV positive immunodeficiency-associated lymphoproliferative disorder
|
34 year old female recently started on HAART for new diagnosis of HIV 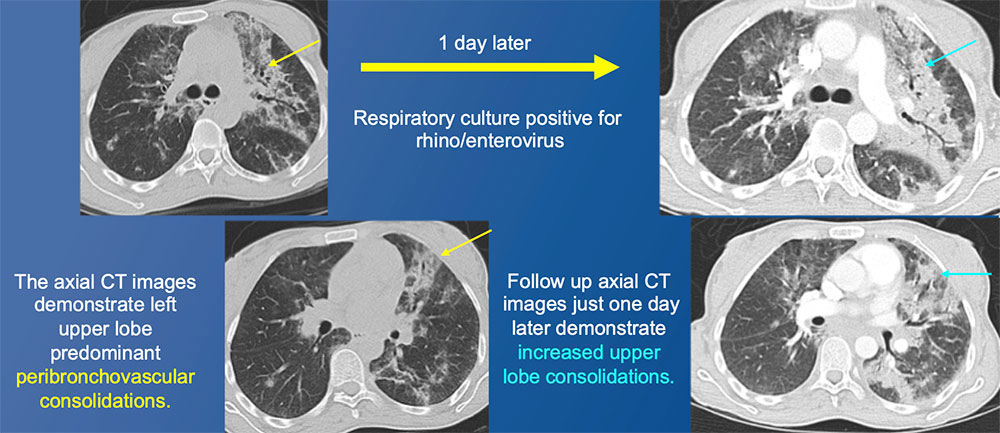 |
Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome (IRIS)
|
Takeaway Points
|
References
Acknowledgements:
|
