- 2
- ,
- 3
- 8
- 1
To Quiz Yourself: Select OFF by clicking the button to hide the diagnosis & additional resources under the case.
Quick Browser: Select ON by clicking the button to hide the additional resources for faster case review.
CASE NUMBER
298
Diagnosis
Cryptococcal Meningitis
Note
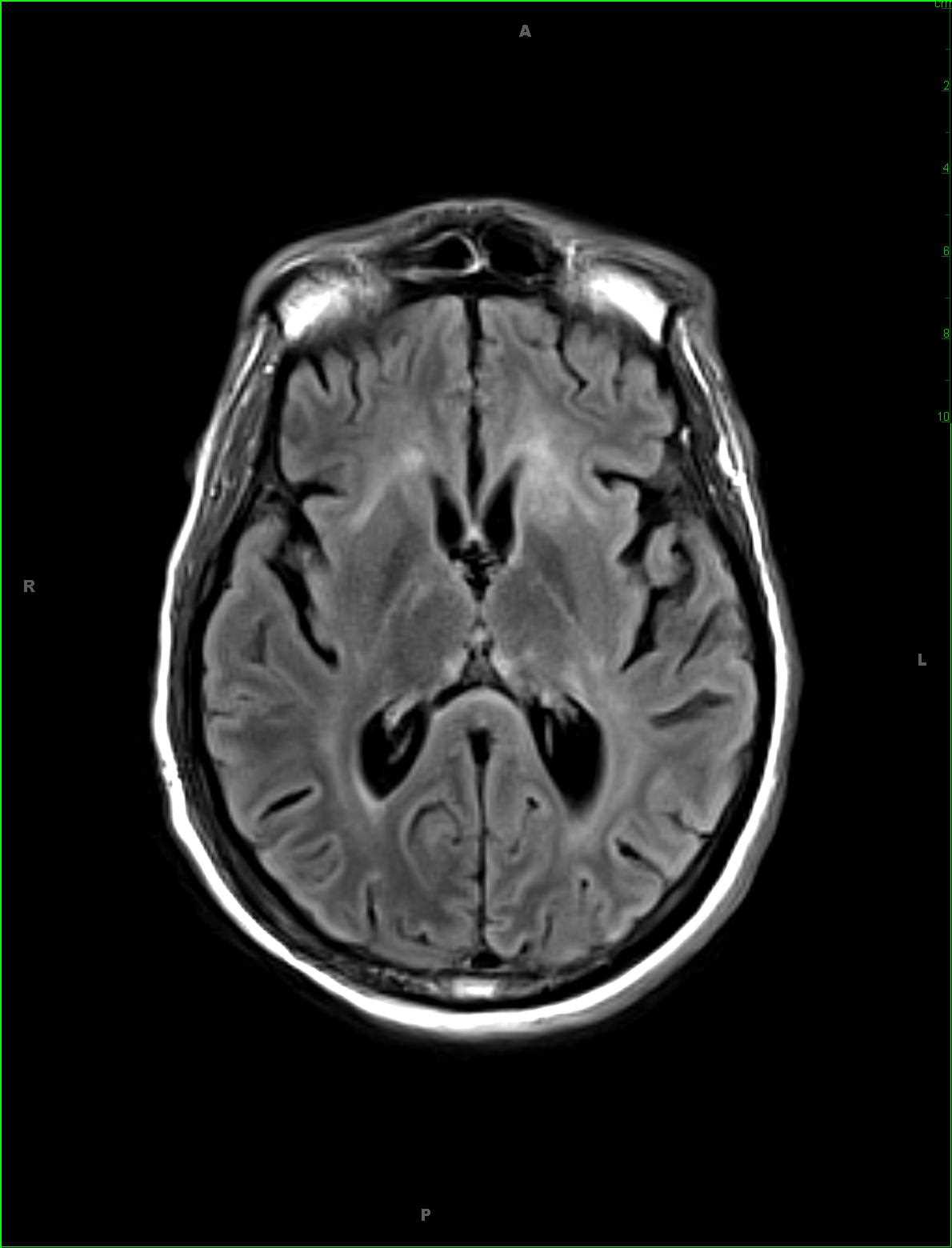
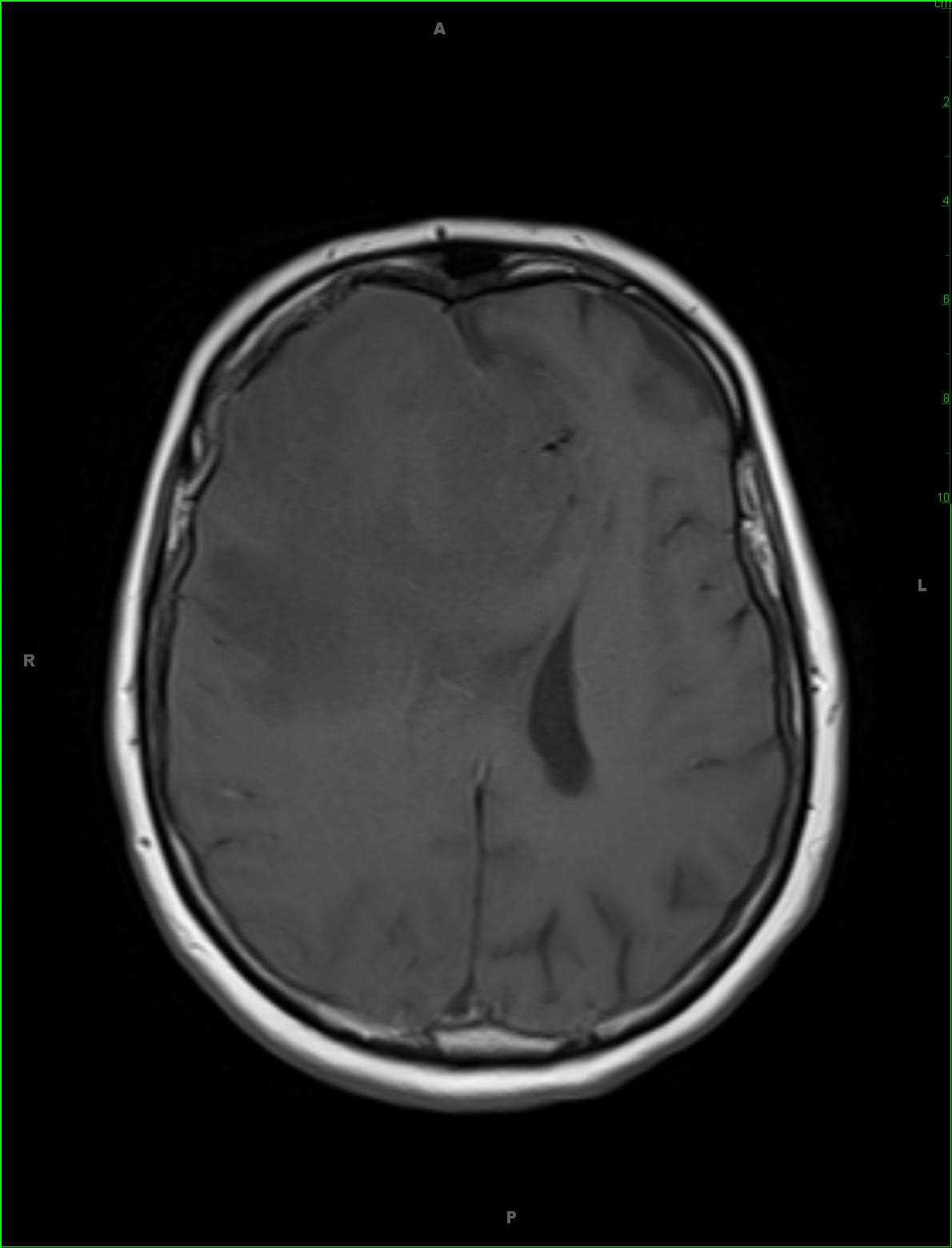
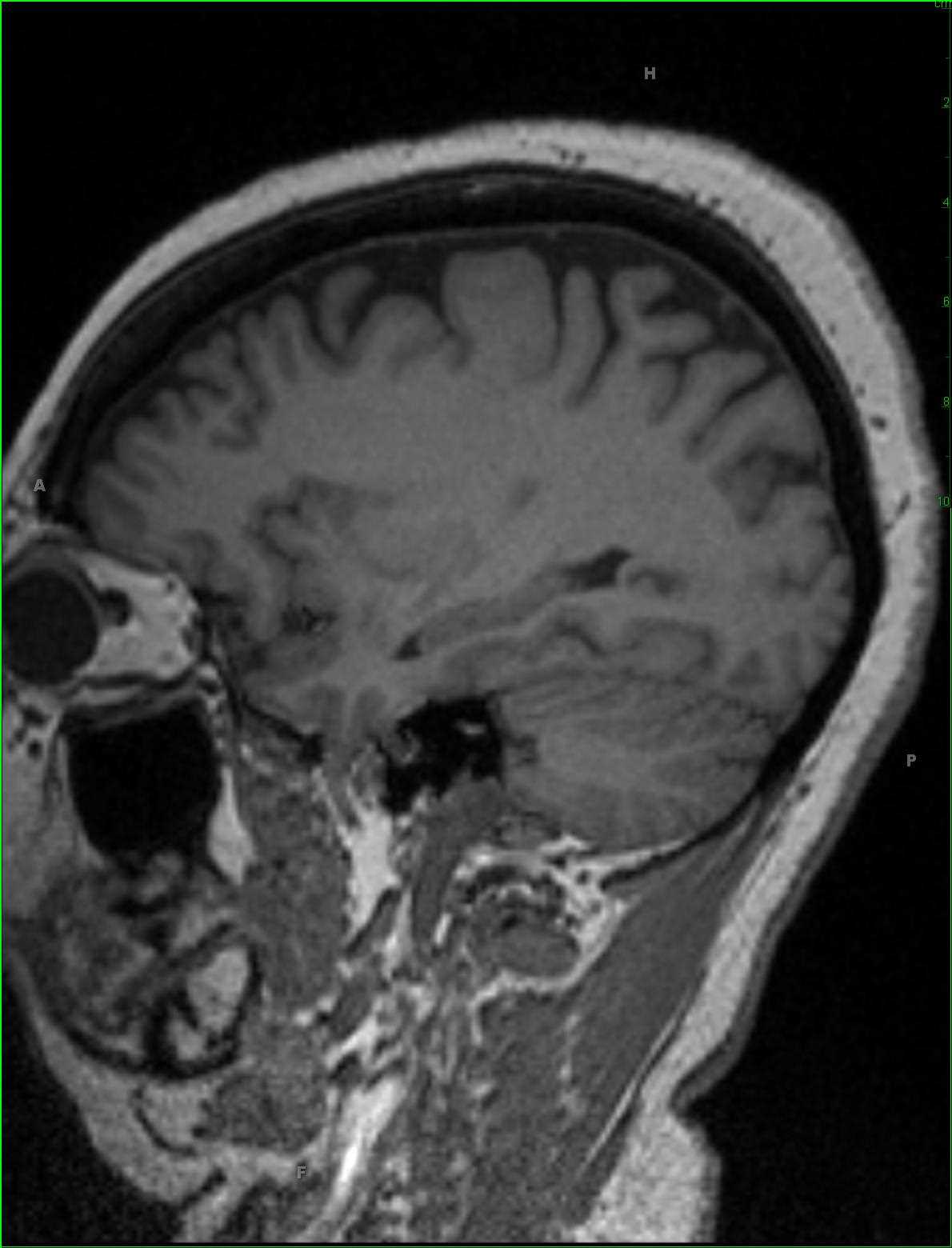
52-year-old female that presented with acute onset delirium and seizures. There is patchy ill-defined T2 FLAIR hyperintense signal involving the subcortical, deep, and periventricular white matter of the supratentorial compartment, worse in the frontal horn and periatrial regions. There is a more nodular region of T2 FLAIR hyperintense signal within the subcortical white matter of the posterolateral left temporal lobe and patchy T2 FLAIR hyperintense signal abnormality in the substance of the midbrain tegmentum extending into the tectal plate. There are no suspicious abnormalities on the diffusion-weighted images, and post contrast sequences demonstrate ill-defined enhancement along the perivascular spaces worse in the bilateral frontal regions. A differential of meningoencephalitis, demyelinating disease, and vasculitis was given. Lumbar puncture and CSF fluid analysis was performed demonstrating a cryptococcal meningitis. CNS cryptococcosis results from infection of the central nervous system the with the fungus cryptococcus neoformans. Disease is more commonly seen in immunocompromised individuals. Clinical presentation typically begins with meningitis or meningoencephalitis, headache, seizure or altered vision due to raised intracranial pressure. Common MR imaging features include enlarged perivascular spaces within the basal ganglia with a pseudocyst appearance.
THIS IS CASE
298
OF
396