- 2
- ,
- 3
- 0
- 9
To Quiz Yourself: Select OFF by clicking the button to hide the diagnosis & additional resources under the case.
Quick Browser: Select ON by clicking the button to hide the additional resources for faster case review.
CASE NUMBER
323
Diagnosis
Susac Disease
Note
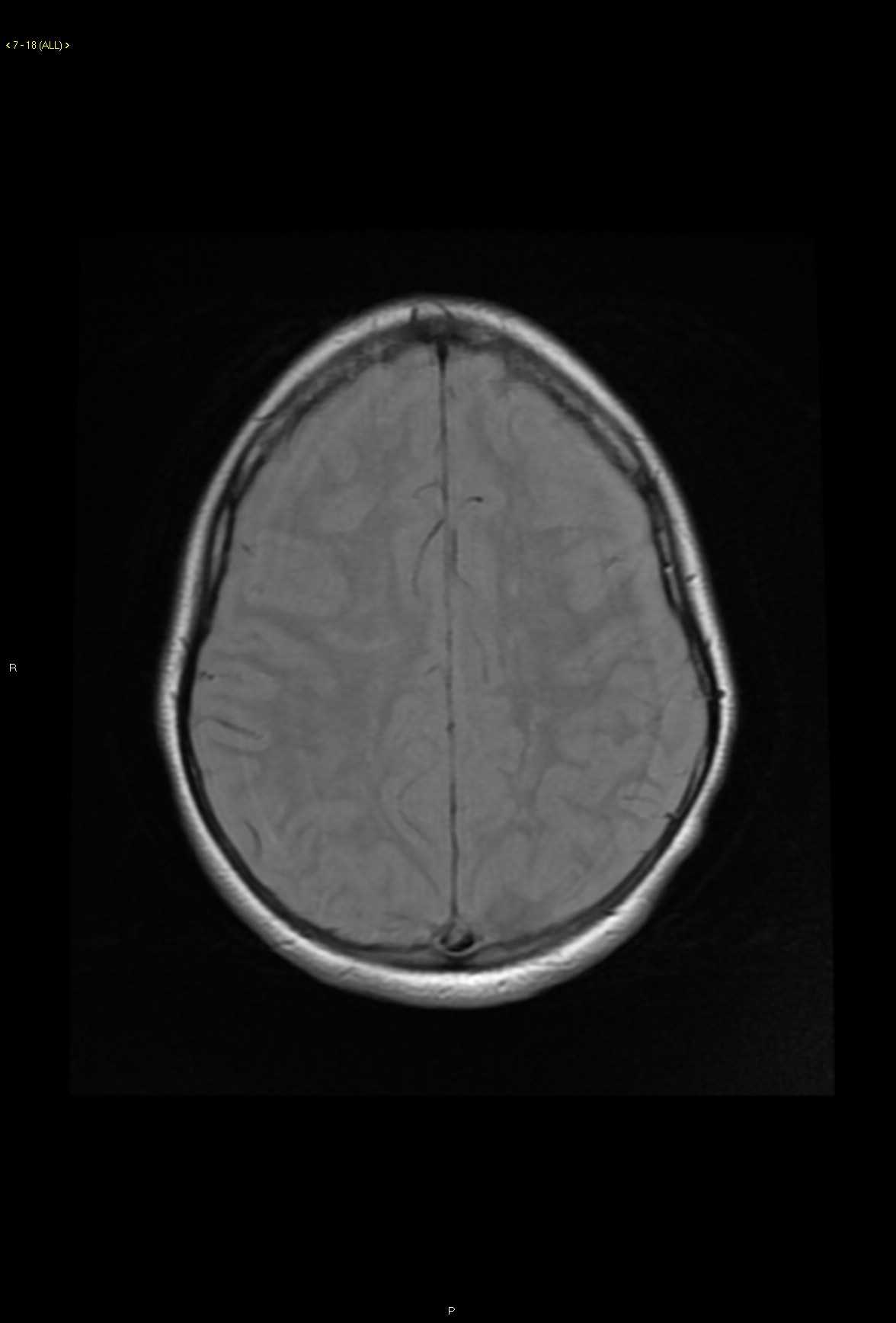
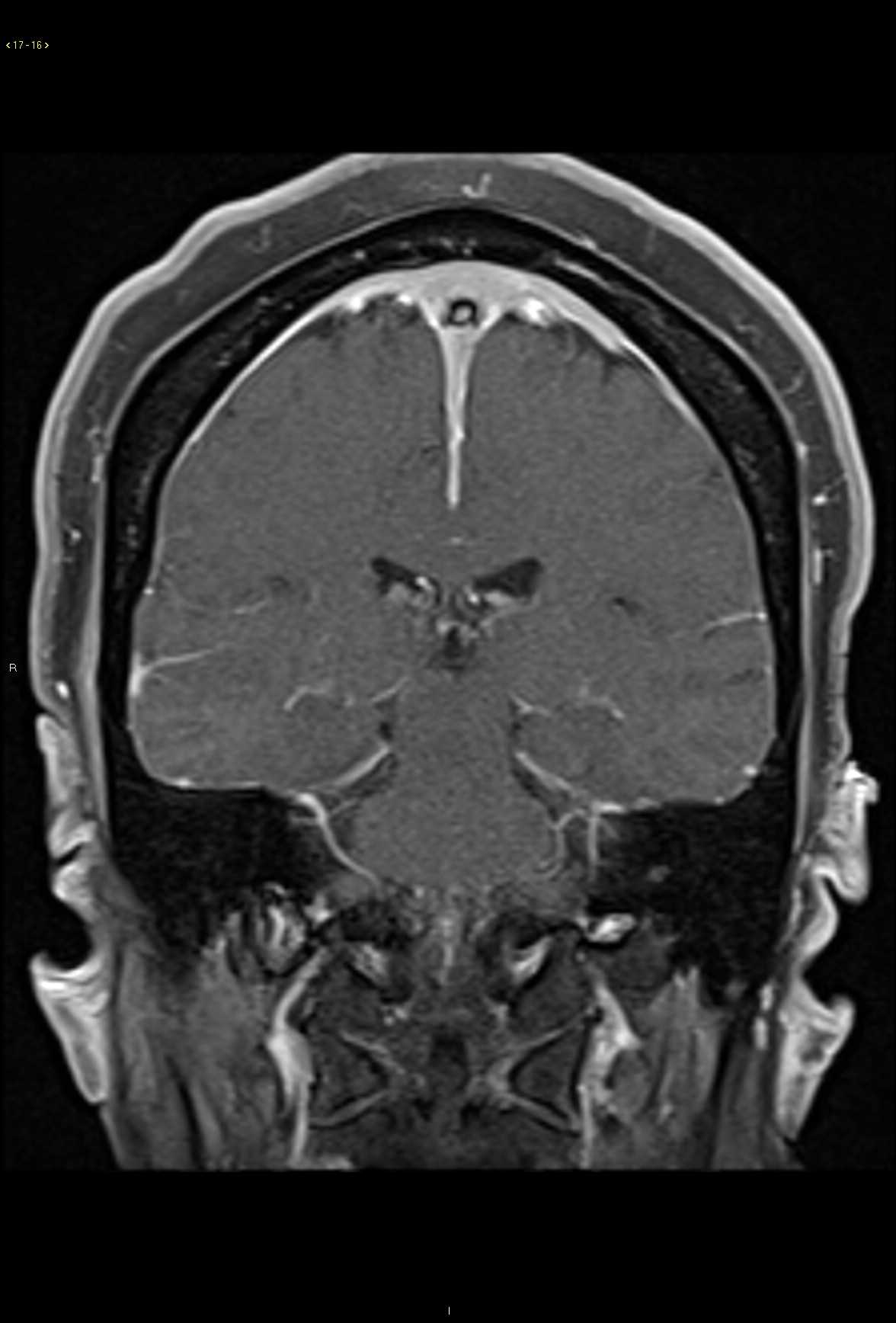
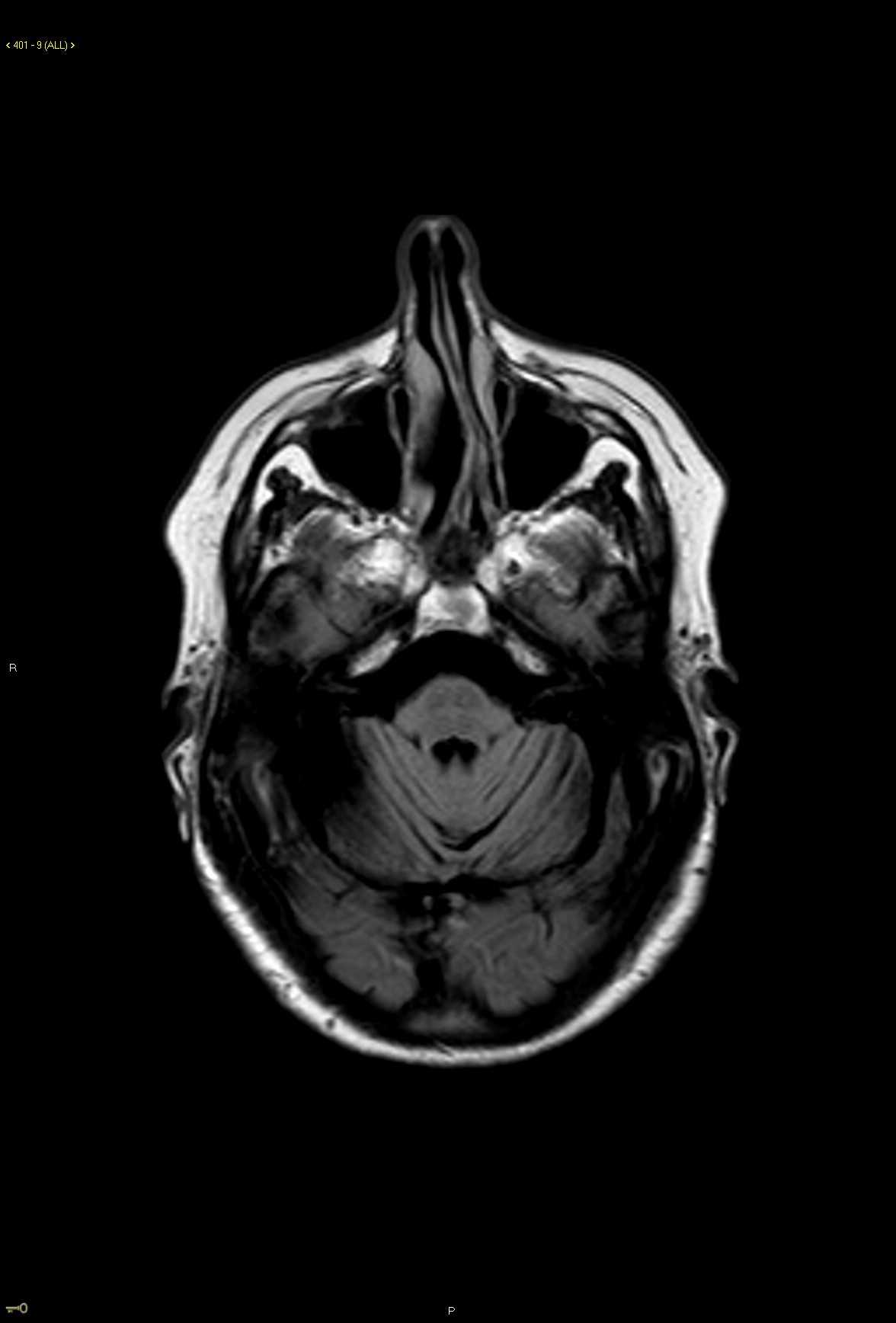
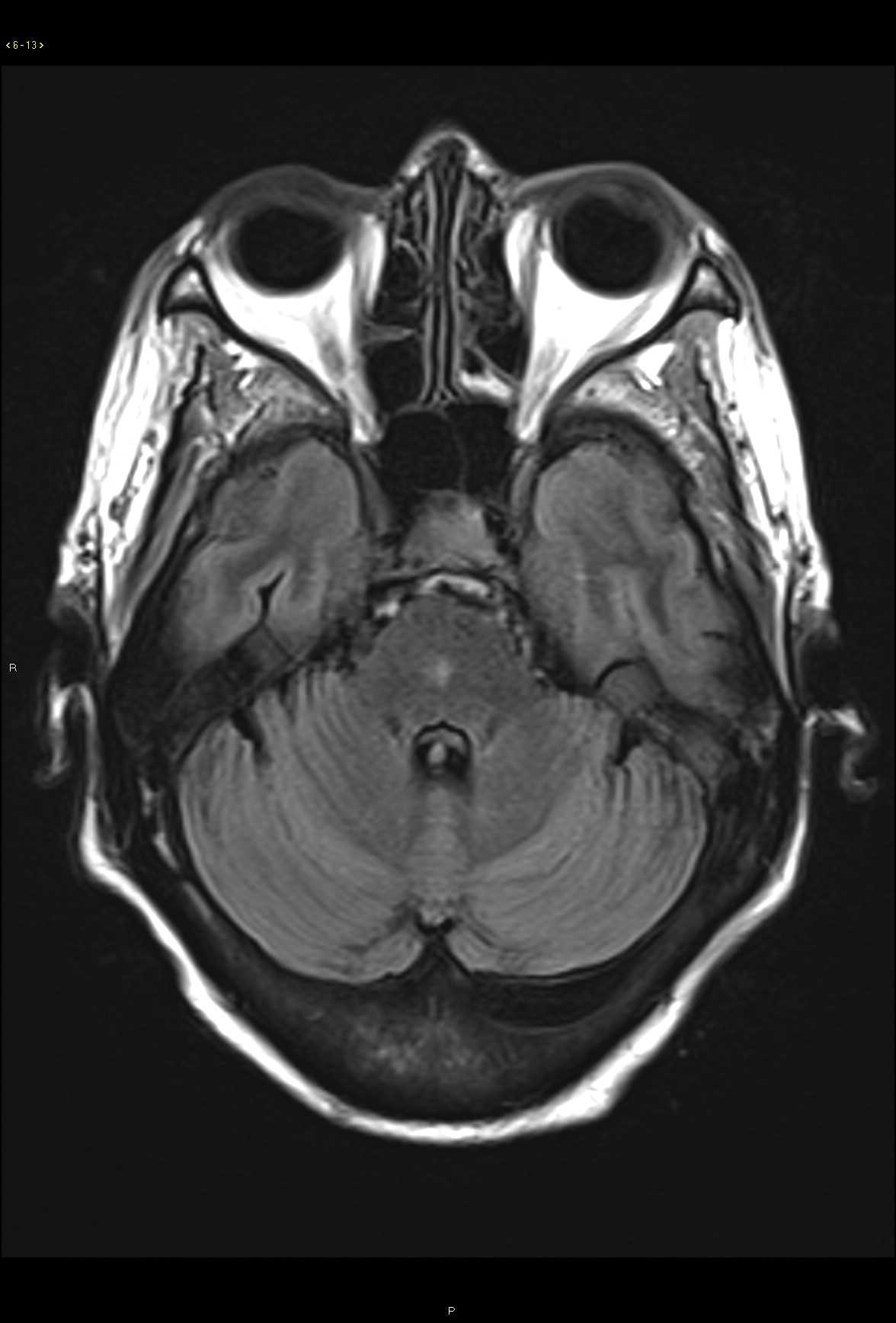
28-year-old male who presents for gradual onset altered mental status, hearing loss, and slowly progressive visual changes. On the axial proton density weighted images, there are subtle ovoid and linear hyperintense lesions centered within the white matter in the subcortical and deep white matter regions. Lesions extend to involve the corpus callosal body and are redemonstrated on the fluid sensitive T2 weighted images with corresponding diffusion restriction and FLAIR hyperintense signal. Post contrast axial and coronal T1-weighted images demonstrate faint enhancement at the numerous sites of involvement in the supratentorial compartment. A differential diagnosis of demyelinating disorder was given as well as vasculitis, CADASIL, and thromboembolic disease. Given the clinical history, Susac syndrome was also listed. This case went to open biopsy at which time a diagnosis of Susac syndrome was made. Susac syndrome consists of a clinical triad of acute or subacute encephalopathy including features such as memory impairment, confusion, behavioral disturbances, ataxia, dysarthria, paranoid psychosis and headaches. There is also sensorineural hearing loss and visual changes secondary to retinal artery occlusion. Typical imaging features include multiple small lesions in the supratentorial compartment with typical involvement of the corpus callosum. Sussac syndrome is typically self-limited but may fluctuate over time.
THIS IS CASE
323
OF
367